ABSTRACT
Literature showed that soluble fiber has beneficial effects on cardiometabolic risk factors and leptin and adiponectin serum levels. Our aim in this meta-analysis was to determine the effect of soluble fiber supplementation on leptin and adiponectin serum levels. A systematic search was conducted using PubMed, Scopus, and ISI Web of Science for eligible trials up to December 2021. A random-effects model was used to pool calculated effect sizes. Our analysis showed that soluble fiber supplementation did not significantly affect adiponectin (standardized mean difference [SMD], −0.49 Hedges’s, 95% confidence interval [CI], −1.20, 0.21, p value = 0.167; I2 = 95.4, p value < 0.001) and leptin (SMD, −0.8 Hedges’s, 95% CI, −1.70, 0.08, p value = 0.076; I2 = 94.6, p value < 0.001) concentrations in comparison with placebo. However, in the subgroup, soluble fiber supplementation had a significant improvement in leptin concentration in overweight and obese patients (SMD, −0.22 Hedges’s, 95% CI, −0.43, −0.01, p value = 0.048) and a non-significant beneficial effect in adiponectin level in female (SMD, 0.29 Hedges’s, 95% CI, −0.13, 0.71, p value = 0.183) and diabetic patients (SMD, 0.32 Hedges’s, 95% CI, −0.67, 1.32, p value = 0.526). A non-linear association between soluble fiber dosage and adiponectin (pnon-linearity < 0.001) was observed. Soluble fiber supplementation could not change the circulatory leptin and adiponectin levels. However, beneficial effects were seen in overweight and obese leptin, and increases in adiponectin may also be observed in female and diabetic patients. Further studies are needed to confirm this results.
-
Keywords: Adiponectin; Leptin; Cardiometabolic risk; Meta-analysis
INTRODUCTION
Adiponectin is a protein secreted by adipose tissue that makes up about 0.01% of total plasma proteins [
1,
2]. According to previous studies, adiponectin’s beneficial effects can be attributed to multiple mechanisms, such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-atherogenic, and antithrombotic. It also reduces insulin resistance and improves blood glucose control [
3,
4,
5]. Literature also suggests that adiponectin may be a marker for lower cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome (MetS), and diabetes risk [
6].
Researchers have studied dietary changes that can improve adipokines concentration in recent years. In this regard, dietary content has attracted a lot of attention. Dietary changes, especially soluble fiber intake and lifestyle modifications, seem to influence adiponectin concentration [
7,
8].
Leptin regulates various physiological mechanisms linked to obesity and cardiovascular disease, including energy balance, neuroendocrine function, and metabolic pathways [
9,
10]. Leptin concentrations are mainly related to fat tissue and energy balance [
11]. Hypothalamic receptors are responsible for the leptin effect, activating several signal transduction pathways, such as Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (JAK-STAT3), which is involved in the regulation of energy homeostasis, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, involved in the regulation of food intake and glucose homeostasis [
12,
13,
14]. Leptin induces beneficial effects in the body.
Literature reported a variety of soluble fiber-containing foods, including fruits and vegetables, legumes, and especially whole-grain cereals, have been suggested to promote cardiometabolic risk factors and leptin and adiponectin levels [
15,
16,
17]. In recent decades, numerous studies have examined the efficacy of soluble fiber supplementation on leptin and adiponectin concentration; however, results have often been contradictory and inconsistent despite similar methodology.
Previous studies report that soluble fiber could decrease leptin secretion via a decrease in fat mass [
18]. Also, soluble fiber may improve adipokine levels by decreasing lipogenesis in the liver and adipose tissue. Besides, the soluble fiber may also decrease leptin levels by improvement of leptin resistance [
19].
The effect of soluble fiber supplementation on leptin and adiponectin concentration is also considered in some trials [
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37]; however, the results are inconclusive. Studies reported controversial results in adiponectin [
20,
21,
23,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
35,
36] and leptin [
20,
21,
22,
25,
26,
32,
33,
34,
35] following soluble fiber supplementation. These inconsistencies in clinical findings might be explained by the differences in study and/or subjects characteristics (dose and duration of supplementation, sex, mean body mass index [BMI], and health status).
Therefore, attempting to resolve the inconsistencies focusing on soluble fiber’s beneficial effects, this study aimed to systematically review and meta-analyse to derive a more precise estimate of the findings of randomised controlled trials (RCTs) reporting the changes in serum leptin and adiponectin concentration following soluble fiber supplementation in adults.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The standard guidelines of Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses were followed to improve the quality of the systematic review and meta-analysis. Our study protocol was not registered on any website; however, it is available from the authors upon request.
Search strategy
An internet literature search was performed in scientific databases: PubMed (
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov), Scopus (
http://www.scopus.com), ISI Web of Science (
http://www.webofscience.com), with no language or time frame restriction up to December 2021. The search strategy was drawn up using the following keywords and Medical Subject Heading terms: “Dietary Fiber,” “soluble dietary fiber,” “soluble fiber,” “viscous fiber,” “plant mucilage,” “glucan,” “beta glucan,” “alginate,” “plant gum,” “gum,” “gellan gum,” “gum arabic,” “acacia gum,” “guar gum,” “resistant starch,” “psyllium,” “inulin,” “resistant maltodextrin,” “wheat dextrin,” “polydextrose.” “prebiotic,” “prebiotic fiber,” “fermentable fiber,” “galactomannan,” “konjac,” “soluble corn fiber,” “fructooligosaccharide,” “oligofructose,” “galactooligosaccharide,” “pectin,” “oat,” “barley,” “randomized controlled trial,” “controlled clinical trial,” “clinical trial,” “controlled trial,” “randomized,” “placebo,” “intervention studies,” “intervention,” “random,” “randomly,” “blind,” “trial,“ Boolean operators (“AND” and “OR”) were used to connect the terms listed above. Finally, electronic searches were supplemented by a hand search of the reference sections and citations of pertinent review articles and studies that met the inclusion criteria.
First, irrelevant articles were excluded by scanning the titles and/or abstracts. Second, full-text versions of the remaining studies were obtained and carefully assessed for the following items: study design, participants; interventions; and reported outcome. Then, RCTs that investigated the efficacy of soluble fiber (as a supplement) on adults were included. At the end of the selection process, studies involving soluble fiber as part of a combination intervention, treatment duration of fewer than 2 weeks, were conducted on children/adolescents (< 18 years old) and pregnant female. A lack of a control group, means, and standard deviations (SDs) for targeted variables went unreported, and grey literature such as conference papers, dissertations, and patents were excluded from the systematic review and meta-analysis. To ensure accuracy, all steps of the study selection process were performed separately by at least 2 authors (A.Z. and H.G.). Any discrepancies were resolved by consensus. The participants, intervention/exposure, comparison, outcomes, and study design (PICOS) criteria used to describe the research question are presented in
Table 1.
Table 1Participants, intervention/exposure, comparison, outcomes, and study design criteria for inclusion and exclusion of studies
Table 1
|
Parameters |
Descriptions |
|
Participants |
Adults |
|
Intervention |
Soluble fiber (as supplement) |
|
Comparison |
Any comparator/control that incorporated a non-intervention group |
|
Outcomes |
Serum leptin and adiponectin concentration |
|
Setting |
Randomized controlled trials |
Data extraction
Each RCT was validated independently by 2 reviewers who were blinded to the authors or results, or all reviewers independently performed the screening of studies, selection, validation, data extraction and the assessment of methodological quality. Disagreements in the assessment of data were resolved by discussion and consensus was reached in all cases.
For each article included, pertinent information was extracted by 2 scholars independently and in duplicate, using a data abstraction form. Disagreements were settled through consultation. Data regarding the study characteristics (first author’s name, publication year, location, population), subject characteristics (mean age, gender, mean BMI), intervention details (type and dosage of soluble fiber, type of placebo or control groups, treatment duration, and background diet), trial design (cross-over or parallel, blinding, funding).
Risk of bias assessment
Cochrane Collaboration tool was used to evaluate the risk of bias assessment among the studies included [
38]. This validated tool explores the risk of bias in the following categories: random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding (participants and investigators), incomplete outcome data, selective outcome reporting, and other sources of bias. Each category was judged as high risk of bias (H), unclear risk of bias (U), or low risk of bias (L), based on the available information presented in the studies included. Studies were considered poor studies when they received (H) in ≥ 2 or (U) in ≥ 3 criteria. The risk of bias assessment was also undertaken by 2 authors separately. The difference in the overall quality score of the studies was resolved by discussion.
The whole process of statistical analysis was carried out using the STATA software version 17.0 (Stata Corporation, College Station, TX, USA). All data were collected as means ± SD for each variable to estimate the pooled effects. In those studies, mean changes were not directly reported in the intervention and control groups, this was calculated by subtracting post-intervention data from the baseline values. SD was estimated by:
where n = number of subjects, SEM was reported.
SD of mean change was calculated according to the following formula [
39]:
assuming a correlation coefficient (R) = 0.75
Due to leptin and adiponectin reported in different units of measure, standardized mean difference (SMD) with 95% confidence interval (CI) was used for analysis. A random-effects model was applied to the meta-analysis to compensate for potential heterogeneity among included studies [
40]. Heterogeneity among RCTs was assessed by the p value and I
2 statistic. In all analyses, a p value of 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Random-effects meta-regression was used to detect the potential associations between changes in leptin and adiponectin outcomes and putative moderators, including dose (≤ 10 g/day, > 10 g/day), duration (≥ 8 weeks, < 8 weeks) of supplementation, gender (female, both [male and female]), mean BMI (≥ 30 kg/m
2 and < 30 kg/m
2) and study population (overweight-obese, MetS, type 2 diabetes [T2DM], healthy).
Sensitivity analysis was conducted to explore the contribution of each study to the reliability of the pooled effect sizes. Publication bias was assessed by Egger’s regression and Begg’s test [
41]. Fractional polynomials modelling was executed to examine potential non-linear effects of soluble fiber dose (g/d) on targeted outcomes. A p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
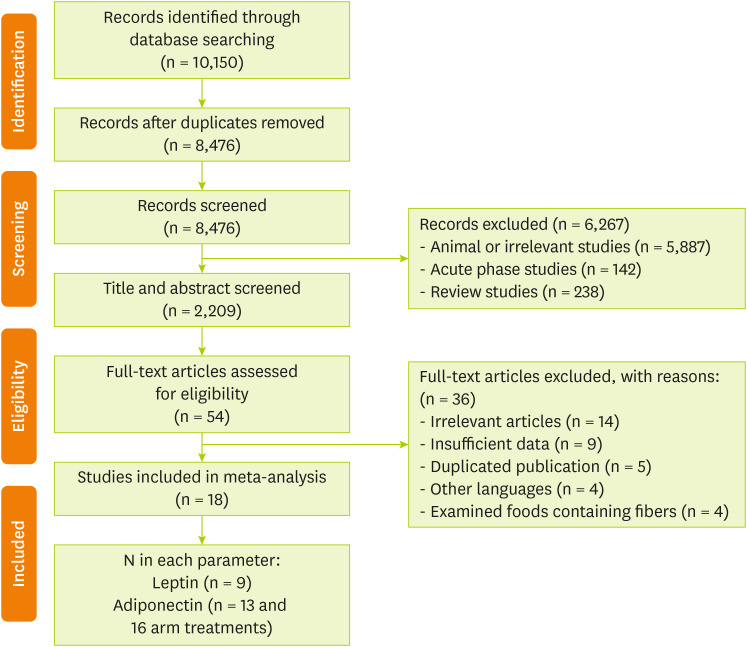
RESULTS
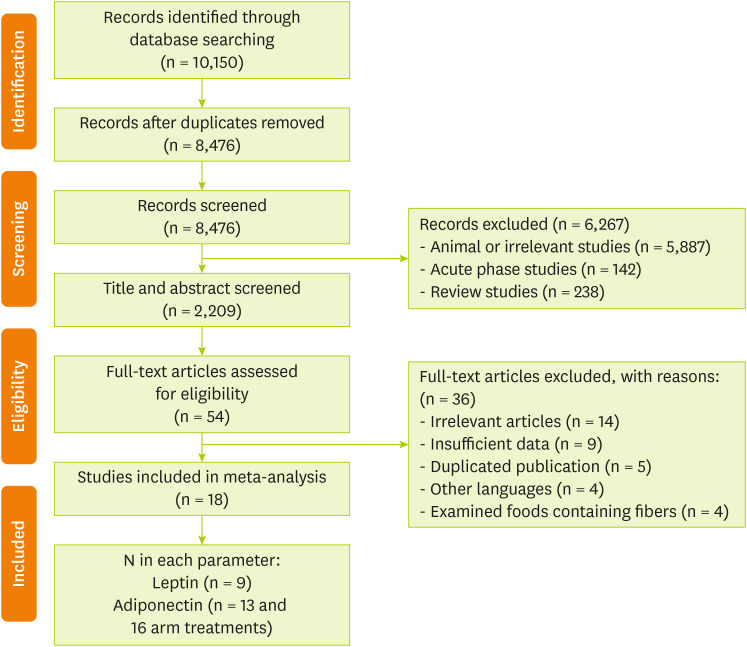
A total of 10,150 potentially relevant studies were identified through electronic search. After removing duplicate records (n = 8,476), 2,209 articles remained after the title and abstract screening; and 54 studies of them were selected for the full-text evaluation. Among the remained articles, 36 were excluded for the following reasons: irrelevant articles (n = 14), insufficient data (n = 9), duplicated publication (n = 5), other languages (n = 4), and examined foods containing fibers (n = 4). Therefore, 18 studies [
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37] met the eligibility criteria and were included in a systematic review and meta-analysis. A flow chart of the systematic search and study selection process is presented in
Figure 1.
Figure 1 Flow chart of the process of the study selection.
Study characteristics
The characteristics of the eligible studies are presented in
Table 2. Three studies were conducted in the USA [
25,
29,
36], 6 in Japan [
21,
26,
27,
30,
33,
34], 2 in Canada [
31,
32], one in Germany [
24], one in Hungary [
20], one in Australia [
22], one in China [
28], one in Belgium [
23], one in the Netherlands [
37] and one in Poland [
35]. All studies were published between the years 2006–2020. All studies were controlled clinical trials. Most studies were performed on both sexes, while 3 were conducted only on females [
20,
22,
23], and 2 were conducted only on males [
27,
28]. Three studies were cross-over designs [
24,
36,
37]. The results of the quality assessment of the eligible studies are presented in
Table 3. Seven studies have good quality [
24,
25,
26,
28,
31,
32,
34], 5 studies have fair quality [
21,
22,
23,
29,
35], and 6 studies have poor quality [
20,
27,
30,
33,
36,
37].
Table 2Demographic characteristics of the included studies
Table 2
|
Study |
Participants characteristic |
Study characteristic |
Intervention/Control characteristic |
|
Population |
Sex (M/F) |
Mean BMI (kg/m2) |
Mean age (yr) |
Location |
Design |
Duration (wk) |
Blinding |
Funding |
Type of fiber |
Dose (g/d) |
Form of administration |
Comparator |
Background diet |
|
Garcia et al. (2006) [24] |
IGT |
11 (4/7) |
30.1 ± 5.7 |
55.5 ± 6.2 |
Germany |
C |
6 |
S |
A |
AX |
15 |
Two bread rolls, each containing 5 g AX concentrate |
Isocaloric bread rolls |
Usual |
|
Antal et al. (2010) [20] |
Obese |
23 (0/23) |
28.7 ± 4.29 |
46.65 ± 8.25 |
Hungary |
P |
12 |
NR |
A |
Oligofructose |
14 |
Jerusalem artichoke-concentrate products |
Jerusalem artichoke-free products |
LCD |
|
Beck et al. (2010) [22] |
Overweight |
66 (0/66) |
29.2 ± 2.2 |
37.19 ± 5.60 |
Australia |
P |
12 |
NR |
A |
Oat β-glucan |
5–9 |
Products with oat β-glucan |
High fiber products with no oat β-glucan |
ERD |
|
Li et al. (2010) [28] |
Overweight |
120 (120/0) |
24.5 ± 0.2 |
30.0 ± 4.2 |
China |
P |
12 |
D |
I |
Glucose polysaccharide |
34 |
250 mL of fruit juice that contained NUTRIOSE |
Maltodextrin |
Usual |
|
Dewulf et al. (2012) [23] |
Obese |
30 (0/30) |
35.85 ± 3.7 |
47.5 ± 8.5 |
Belgium |
P |
12 |
D |
A |
Inulin/oligofructose |
16 |
Powder added to warm drinks |
Maltodextrin |
Usual |
|
Hashizume et al. (2012) [26] |
MetS |
30 (20/10) |
27.45 ± 2.6 |
60.65 ± 10.25 |
Japan |
P |
12 |
D |
A |
Resistant maltodextrin |
9 |
Tea containing resistant maltodextrin |
Tea without resistant maltodextrin |
Usual |
|
Maki et al. (2012) [29] |
Obese |
33 (11/22) |
30.6 ± 0.5 |
49.5 ± 1.6 |
USA |
P |
4 |
D |
A |
High-amylose maize RS2 |
15 or 30 |
Mixed into cold or room-temperature beverages or foods |
Starch |
Usual |
|
Reimer et al. (2013) [33] |
Obesity |
64 (28/36) |
26.95 ± 2.6 |
20–65 |
Japan |
P |
14 |
D |
A |
PGX |
15 |
Powder |
Rice flour |
Usual |
|
Wanders et al. (2013) [37] |
Healthy |
32 (8/24) |
21.8 ± 1.9 |
21 ± 2 |
Netherlands |
C |
15 days |
D |
A |
Pectin |
5 |
Pectin containing foods |
Isocaloric |
Usual |
|
Kobayakawa et al. (2013) [27] |
Obesity |
30 (30/0) |
27.7 ± 0.8 |
53.5 ± 5.4 |
Japan |
P |
12 |
D |
I |
Galactomannan, inulin, β-glucan, alginic acid, cellulose, hemicelluloses |
7.5 |
The adding the test food to the daily average diet |
Blend of starch, colorant, and flavor |
Usual |
|
Geliebter et al. (2014) [25] |
Overweight |
36 (18/18) |
32.2 ± 3.4 |
35.6 ± 6.1 |
USA |
P |
4 |
NR |
A |
Oat fibre |
NR |
Oat porridge breakfast |
No-breakfast control |
Usual |
|
Nishimura et al. (2015) [30] |
Healthy |
47 (8/39) |
21.9 ± 3.12 |
53.6 ± 10.6 |
Japan |
P |
4 |
D |
A |
Inulin-type fructans |
0.9 |
Chicory root extract |
Non-chicory root extract |
Usual |
|
Upadhyaya et al. (2015) [36] |
Met |
20 (8/39) |
32.8 ± 1.1 |
NR |
USA |
C |
26 |
D |
A |
RS4 |
NR |
Flour containing 30% resistant starch type 4 |
Control flour |
Usual |
|
Aoe et al. (2017) [21] |
Healthy |
100 (NR) |
27.5 ± 2.7 |
30–70 |
Japan |
P |
12 |
D |
A |
β-glucan |
4.4 |
High-β-glucan barley |
β-glucan-free barley |
Usual |
|
Parnell et al. (2017) [31] |
Obesity |
20 (8/39) |
29.9 |
≤ 18 |
Canada |
P |
12 |
D |
A |
Oligofructose |
21 |
Powder |
Maltodextrin |
Usual |
|
Strączkowski et al. (2018) [35] |
Obesity |
52 (27/25) |
27.4 ± 2.6 |
27.7 ± 4.8 |
Poland |
P |
12 |
NR |
A |
β-glucan |
500 mg |
NR |
NR |
LCD |
|
Sakai et al. (2019) [34] |
T2DM |
30 (22/8) |
25.1 ± 3.8 |
59.1 ± 13.2 |
Japan |
P |
12 |
D |
A |
Fucoidan |
1,620 mg |
Beverage containing fucoidan |
Fucoidan–free beverage |
Usual |
|
Reimer et al. (2020) [32] |
T2DM |
290 (83/207) |
40.0 ± 6.8 |
54.8 ± 9.2 |
Canada |
P |
52 |
D |
I |
PGX |
15–20 |
Supplement packets |
Rice flour |
Usual |
Table 3The summary of review authors’ judgments about each risk of bias item for included studies
Table 3
|
Study |
Random sequence generation |
Allocation concealment |
Blinding |
Incomplete outcome data |
Selective reporting |
Other bias |
Overall |
|
Garcia et al. (2006) [24] |
L |
L |
L |
L |
L |
U |
Good |
|
Antal et al. (2010) [20] |
H |
L |
U |
L |
L |
U |
Poor |
|
Beck et al. (2010) [22] |
L |
U |
L |
U |
L |
U |
Fair |
|
Li et al. (2010) [28] |
L |
L |
L |
L |
L |
U |
Good |
|
Dewulf et al. (2012) [23] |
U |
L |
L |
H |
L |
U |
Fair |
|
Hashizume et al. (2012) [26] |
L |
L |
L |
L |
L |
U |
Good |
|
Maki et al. (2012) [29] |
L |
U |
L |
H |
L |
U |
Fair |
|
Reimer et al. (2013) [33] |
U |
U |
L |
U |
L |
U |
Poor |
|
Wanders et al. (2013) [37] |
L |
U |
L |
U |
L |
U |
Poor |
|
Kobayakawa et al. (2013) [27] |
U |
U |
L |
U |
L |
U |
Poor |
|
Geliebter et al. (2014) [25] |
L |
L |
L |
L |
L |
U |
Good |
|
Nishimura et al. (2015) [30] |
L |
U |
U |
U |
L |
U |
Poor |
|
Upadhyaya et al. (2015) [36] |
L |
U |
U |
H |
L |
U |
Poor |
|
Aoe et al. (2017) [21] |
L |
L |
U |
U |
L |
U |
Fair |
|
Parnell et al. (2017) [31] |
U |
L |
L |
L |
L |
U |
Good |
|
Strączkowski et al. (2018) [35] |
L |
L |
U |
U |
L |
U |
Fair |
|
Sakai et al. (2019) [34] |
U |
L |
U |
L |
L |
U |
Good |
|
Reimer et al. (2020) [32] |
L |
U |
L |
L |
L |
U |
Good |
Meta-analysis results
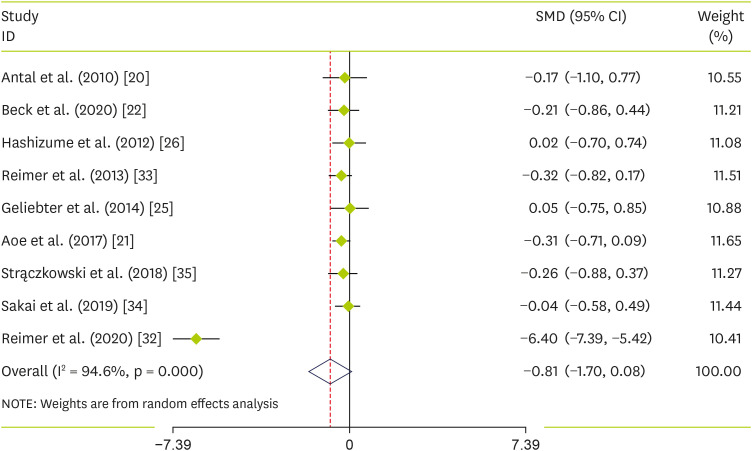
The influence of soluble fiber on leptin levels
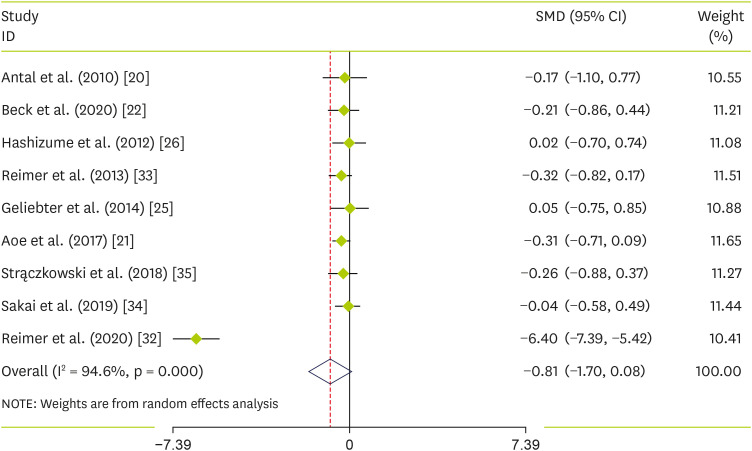
Nine studies [
20,
21,
22,
25,
26,
32,
33,
34,
35] containing a total of 470 individuals (intervention = 241, control = 229) reported changes in serum leptin concentrations as an outcome measure. Pooled results using the random-effects model demonstrated an overall non-significant decline in leptin levels following soluble fiber interventions (SMD, −0.8 Hedges’s, 95% CI, −1.70, 0.08, p value = 0.076;
Figure 2). However, a significant degree of heterogeneity was observed among the studies (p < 0.001, I
2 = 94.6%).
Figure 2
Forest plot of the effect of soluble fiber supplementation on leptin levels.
SMD, standardized mean difference; CI, confidence interval.
To identify the source of this heterogeneity, we further sub-grouped based on duration (≥ 8 weeks and < 8 weeks), dose (≤ 10 g/day and >10 g/day), gender (female and both), baseline BMI (≥ 30 kg/m
2 and < 30 kg/m
2) and study population (overweight-obese, MetS, T2DM and healthy). The results showed that subgroup analysis based on dose and baseline BMI could explain this heterogeneity. Sub-group analysis showed that soluble fiber could more decrease in leptin levels in participant with BMI ≥ 30 kg/m
2 (SMD, −3.17 Hedges’s, 95% CI, −9.49, 3.15, p value = 0.326; I
2 = 99.0%, p < 0.001) and overweight and obese patients (SMD, −0.22 Hedges’s, 95% CI, −0.43, −0.01, p value = 0.048; I
2 = 0.0%, p = 0.975) (
Table 4).
Table 4Result of subgroup analysis of included studies in meta-analysis
Table 4
|
Sub-grouped by |
No. of trials |
Effect size*
|
95% CI, p value |
I2 (%) |
p for heterogeneity |
p for between subgroup heterogeneity |
|
Leptin |
9 |
−0.80 |
(−1.70, 0.08), 0.076 |
94.6 |
< 0.001 |
|
|
Duration (wk) |
|
|
|
|
|
0.199 |
|
|
< 8 |
1 |
0.05 |
(−0.75, 0.85), 0.903 |
- |
- |
|
|
≥ 8 |
8 |
−0.92 |
(−1.90, 0.07), 0.068 |
95.2 |
< 0.001 |
|
Dose (g/d) |
|
|
|
|
|
< 0.001 |
|
|
≤ 10 |
4 |
−0.19 |
(−0.45, 0.08), 0.162 |
0.0 |
0.803 |
|
|
> 10 |
3 |
−2.28 |
(−5.86, 1.29), 0.211 |
98.4 |
< 0.001 |
|
Sex |
|
|
|
|
|
0.302 |
|
|
Female |
2 |
−0.20 |
(−0.73, 0.34), 0.470 |
0.0 |
0.937 |
|
|
Both |
7 |
−0.99 |
(−2.10, 0.12), 0.081 |
95.9 |
< 0.001 |
|
Baseline BMI (kg/m2) |
|
|
|
|
|
< 0.001 |
|
|
< 30 |
7 |
−0.22 |
(−0.43, −0.01), 0.048 |
0.0 |
0.975 |
|
|
≥ 30 |
2 |
−3.17 |
(−9.49, 3.15), 0.326 |
99.0 |
< 0.001 |
|
Study population |
|
|
|
|
|
< 0.001 |
|
|
Overweight–Obese |
5 |
−0.22 |
(−0.51, 0.07), 0.137 |
0.0 |
0.959 |
|
|
MetS |
1 |
0.02 |
(−0.70, 0.74), 0.958 |
- |
- |
|
|
T2DM |
2 |
−3.21 |
(−9.44, 3.02), 0.313 |
99.2 |
< 0.001 |
|
|
Healthy |
1 |
−0.31 |
(−0.71, 0.09), 0.131 |
- |
- |
|
Adiponectin |
16 |
−0.49 |
(−1.20, 0.21), 0.167 |
95.4 |
< 0.001 |
|
|
Duration (wk) |
|
|
|
|
|
0.079 |
|
|
< 8 |
5 |
−0.16 |
(−0.65, 0.33), 0.534 |
61.3 |
0.035 |
|
|
≥ 8 |
11 |
−0.83 |
(−1.82, 0.16), 0.102 |
96.8 |
< 0.001 |
|
Dose (g/d) |
|
|
|
|
|
0.001 |
|
|
≤ 10 |
5 |
−0.38 |
(−0.87, 0.10), 0.123 |
69.1 |
0.012 |
|
|
> 10 |
10 |
−0.94 |
(−2.10, 0.22), 0.114 |
97.0 |
< 0.001 |
|
Sex |
|
|
|
|
|
0.127 |
|
|
Male |
4 |
−9.69 |
(−14.28, −5.11), < 0.001 |
98.7 |
< 0.001 |
|
|
Female |
4 |
0.29 |
(−0.13, 0.71), 0.183 |
30.9 |
0.229 |
|
|
Both |
8 |
−0.35 |
(−0.97, 0.26), 0.264 |
91.9 |
< 0.001 |
|
Baseline BMI (kg/m2) |
|
|
|
|
|
< 0.001 |
|
|
< 30 |
9 |
−1.59 |
(−2.93, −0.25), 0.020 |
97.0 |
< 0.001 |
|
|
≥ 30 |
7 |
0.18 |
(−0.19, 0.55), 0.344 |
65.4 |
0.008 |
|
Study population |
|
|
|
|
|
< 0.001 |
|
|
Overweight–Obese |
10 |
−1.16 |
(−2.38, 0.06), 0.062 |
96.7 |
< 0.001 |
|
|
MetS |
2 |
−0.05 |
(−0.52, 0.42), 0.833 |
0.0 |
0.647 |
|
|
T2DM |
2 |
0.32 |
(−0.67, 1.32), 0.526 |
85.8 |
0.008 |
|
|
Healthy |
2 |
−0.68 |
(−1.32, −0.05), 0.034 |
50.0 |
0.155 |
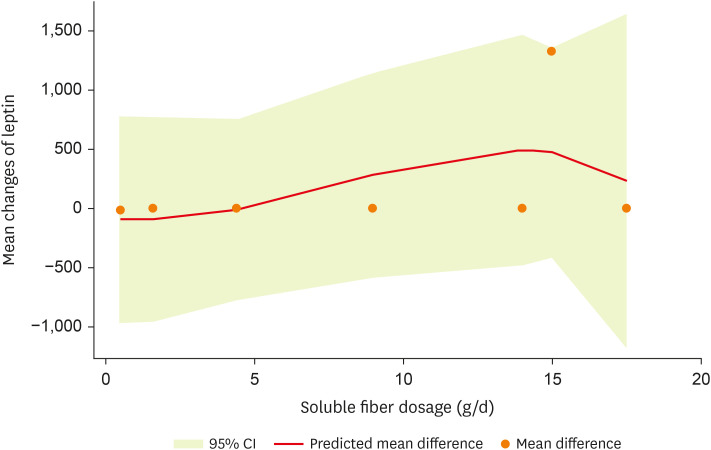
No evidence of publication bias was found for leptin (p value = 0.229, Begg’s test and p value = 0.466, Egger’s test). Also, the sensitivity analysis showed that the overall estimate was not affected by the elimination of any study.
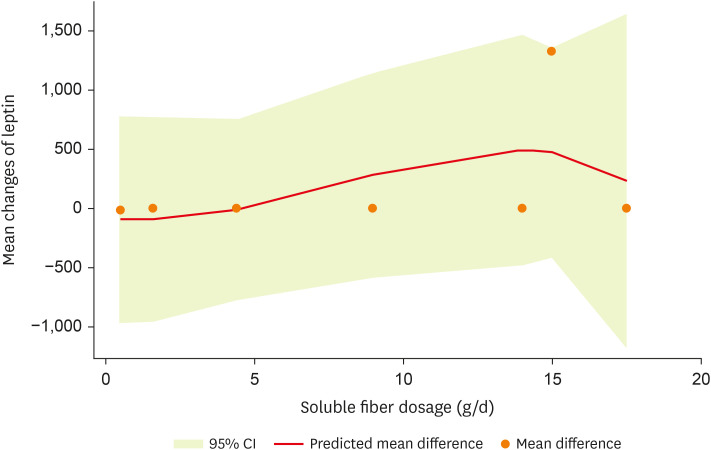
A non-significant non-linear association between soluble fiber dosage and leptin (p
non-linearity = 0.364;
Figure 3) was noted in the non-linear dose-response analysis.
Figure 3
Non-linear dose-response effects of soluble fiber supplementation on leptin levels.
CI, confidence interval.
The influence of soluble fiber on adiponectin levels
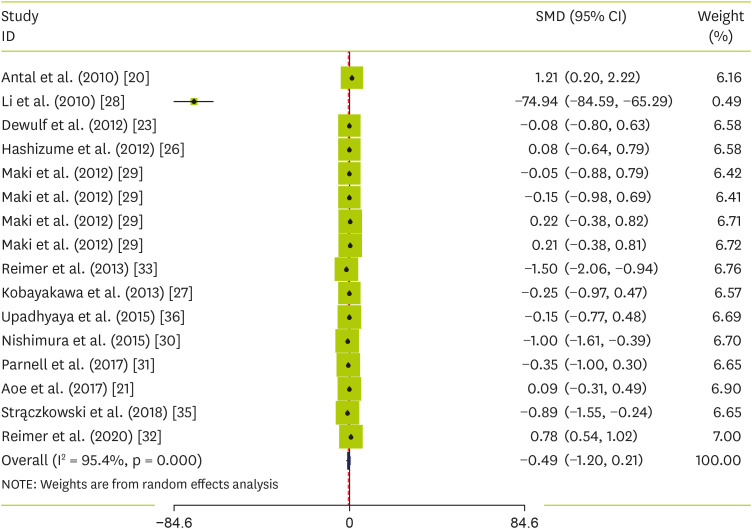
Thirteen studies [
20,
21,
23,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
35,
36] containing 16 treatment arms with a total of 980 individuals (intervention = 498, control = 482) reported changes in serum adiponectin concentrations as an outcome measure. Pooled results using the random-effects model demonstrated an overall non-significant effect in serum adiponectin following soluble fiber supplementation (SMD, −0.49 Hedges’s, 95% CI, −1.20, 0.21, p value = 0.167;
Figure 4). However, a significant degree of heterogeneity was observed among the studies (p value < 0.001, I
2 = 95.4%).
Figure 4
Forest plot of the effect of soluble fiber supplementation on adiponectin levels.
SMD, standardized mean difference; CI, confidence interval.
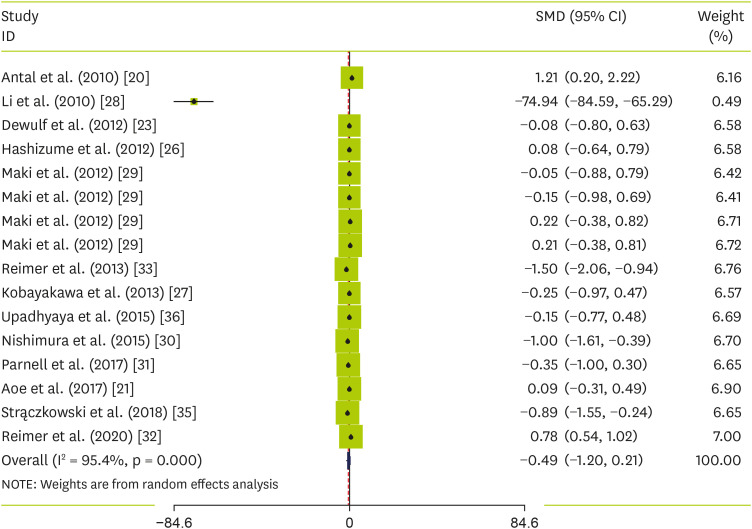
Subgroup analysis based on the study population could explain the source of heterogeneity. Also, soluble fiber supplementation had a non-significant increase in adiponectin level in female (SMD, 0.29 Hedges’s, 95% CI, −0.13, 0.71, p = 0.183) and T2DM (SMD, 0.32 Hedges’s, 95% CI, −0.67, 1.32, p value = 0.526) (
Table 4).
To discover the impact of every single study on the combined effect size, we removed each trial, one at a time, from the analysis and accounted for their individuality. We observed no significant effects of any individual study on the combined effect sizes.
The Egger’s tests did not find a significant publication bias among the studies (p value = 0.499, Begg’s test and p value = 0.003, Egger’s test). The trim-and-fill method to detect sources of bias resulted in different results (SMD, −2.035 Hedges’s, 95% CI, −3.056, −1.013).
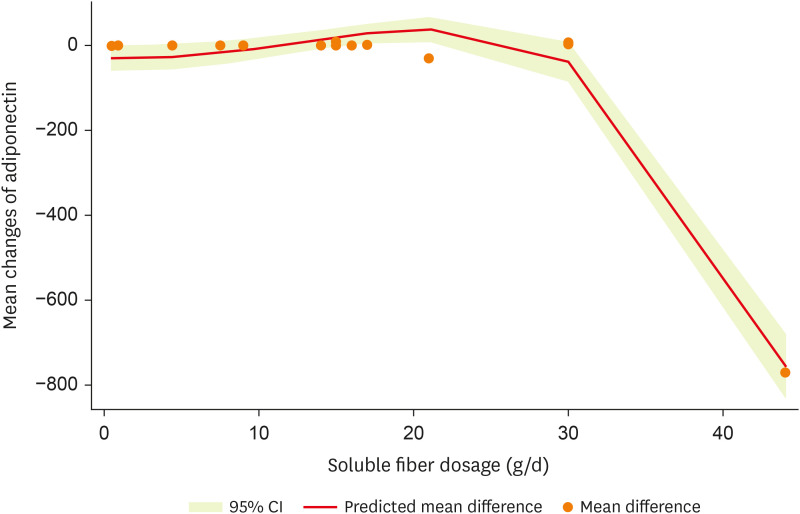
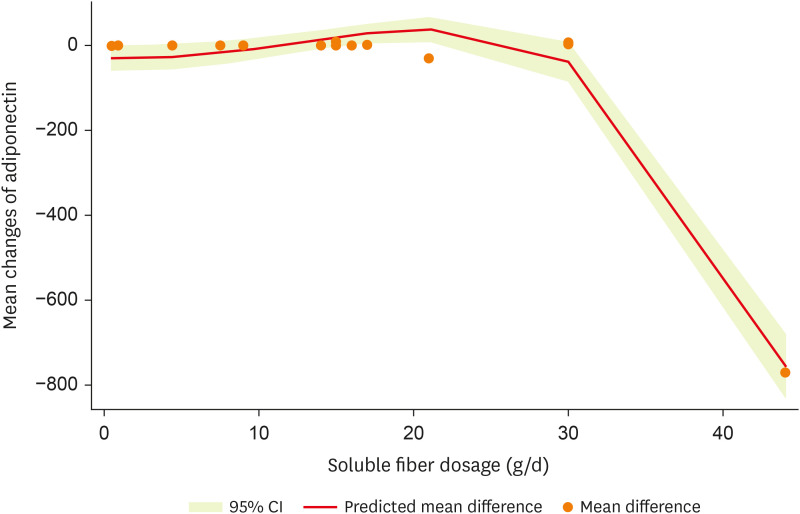
After non-linear dose-response analysis, a significant non-linear association between dosage and adiponectin (p
non-linearity < 0.001;
Figure 5) was observed.
Figure 5
Non-linear dose-response effects of soluble fiber supplementation on adiponectin levels.
CI, confidence interval.
DISCUSSION
This systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the effects of soluble fiber supplementation on serum leptin and adiponectin concentrations. Our findings indicate that soluble fiber supplementation did not lead to significant changes in serum leptin or adiponectin levels overall. However, subgroup analyses provided valuable insights, revealing that soluble fiber supplementation was associated with a significant reduction in leptin concentrations among overweight and obese individuals. Additionally, a non-linear dose-response relationship was observed between soluble fiber dosage and adiponectin levels.
The observed reduction in leptin concentrations among overweight and obese participants is of particular interest. Leptin, a hormone mainly produced by adipose tissue, has important acts in regulating weight management, food intake, energy homeostasis, glucose homeostasis, angiogenesis, immune responses, lipolysis, and fertility [
42,
43]. Serum leptin concentrations positively correlate with adiposity [
44,
45]. Therefore, overweight or obese individuals with hyperleptinemia development of leptin resistance usually cannot exert anorexigenic effects [
44,
45]. Recently, novel approaches have been introduced to attenuate the leptin levels in adiposity [
45]. Applying soluble fiber supplementation as one of the dietary strategies has been suggested to improve adipokine levels [
46]. Our findings suggest that soluble fiber supplementation might contribute to alleviating hyperleptinemia in these individuals. Mechanistically, soluble fiber could potentially impact leptin levels through various pathways. By reducing fat mass and influencing gut hormone release, soluble fiber might indirectly decrease leptin secretion [
18]. Furthermore, soluble fiber’s potential to improve adipokine levels by affecting lipogenesis, adenosine monophosphate-activated protein (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity, and leptin resistance warrants further investigation.
Previous studies have documented that soluble fiber administration may help to decrease fat mass and may consequently improve adipokines levels through slowing gastric emptying, declining glycemic index, and a load of meals, influencing gut hormone release, taking further time to be chewed, and decreasing calorie absorption of foods [
47,
48]. In addition, some studies indicated that soluble fiber might improve adipokine levels by decreasing lipogenesis in liver and adipose tissue, activating the AMPK, decreasing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase expression in the liver, and increased expression of carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1β in skeletal muscle [
49,
50]. The soluble fiber also may decrease leptin levels by improvement of leptin resistance. Zhang et al. [
19], in an animal study, revealed that soluble fiber supplementation enhanced leptin activity by augmenting the expression of leptin receptors in white fat mass, increasing the leptin signaling pathway by improving JAK2/STAT3 and decreasing suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 expression [
19]. Also, garlic administration as an important source of dietary soluble fiber may affect adiponectin and leptin levels.
The previous documents have revealed that garlic may affect adipokines through antioxidant properties. For example, garlic increases the nitric oxide bioavailability via advancing the cellular antioxidant capacity by providing cellular thiol antioxidants like cysteine and diminished glutathione, maintaining the functionally appropriate concentration of tetrahydrobiopterin and controlling oxidative inactivation of tetrahydrobiopterin [
51,
52]. Thus, according to the mentioned mechanisms, the consumption of soluble fiber can be suggested to manage leptin levels and resistance among overweight or obese subjects. Another important finding showed a non-linear association between soluble fiber dosage and adiponectin levels. Adiponectin has several physiological benefits, including anti-inflammation, anticancer, cardioprotective, decreasing hepatic steatosis, sensitizing tissues to insulin, hypolipidemic, and increasing high-density lipoprotein in the serum [
53]. Given adiponectin's positive metabolic and physiological function, interventions that increase adiponectin levels can help improve health status. It seems that soluble fiber, as one of the contents of functional foods through their properties, improves anthropometric and metabolic outcomes [
54], consequently positively affecting adiponectin concentrations [
55]. A further potential mechanism that can be considered in this context is the role of soluble fiber in adiponectin-mediated insulin resistance. Adiponectin is associated well with whole-body insulin sensitivity and is reduced in T2DM patients [
56,
57]. Brockman et al. [
54], in an animal study on the Zucker Diabetic Fatty rats model, the high viscous soluble fiber group had the highest levels of adiponectin and the most significant insulin sensitivity. They suggested that adiponectin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis and enhances fatty acid oxidation in the muscle via advanced AMP kinase and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha activity, as a result, led to improved insulin sensitivity [
58]. Future prospective randomized clinical trials with more extended supplementation period are required to obtain a more exact conclusion.
Our investigation has strengths, including completing a comprehensive search of published literature without limitations and adherence to the PRISMA criteria for writing our study. Additionally, most of the studies included in our investigation had high quality. We also used conservative statistical methods and sub-group analyses to detect any effect of study duration, dose, gender, baseline BMI, and study population on the overall effect examinations.
This study also has some limitations that need to be noted. Firstly, there was significant statistical heterogeneity in the selected studies. However, sub-groups analysis and sensitivity analyses were conducted. Secondly, the influence of the confounding variables, namely the genetic variants, lifestyle factors, race, and ethnicity, on evaluating the efficacy of soluble fiber administration on leptin and adiponectin serum concentrations was disregarded. Thus, our outcomes should be interpreted with caution.
The results of the present study also showed a beneficial effect of soluble fiber supplementation on decreasing serum leptin concentration among overweight and obese individuals.
In future studies, confounding factors such as genetic background, differences in lifestyle, race, and ethnicity on this efficacy should be assessed. A further controlled clinical trial with a good study design, long follow-up duration, and adequate power is warranted to verify the potential effect of soluble fiber supplementation on serum adipokines levels, notably among overweight and obese patients.
In conclusion, our findings contribute to the growing body of knowledge on the potential metabolic effects of soluble fiber supplementation. While the overall impact on serum leptin and adiponectin concentrations may be subtle, the specific reduction in leptin levels among overweight and obese individuals suggests a targeted benefit in this population. As we continue to uncover the intricate connections between dietary interventions and metabolic health, further research is warranted to fully harness the potential of soluble fiber as a component of effective strategies for weight management and metabolic improvement.
Department of Sports Physiology Lamerd Branch, Islamic Azad University
162434145
NOTES
-
Funding: This study was supported by the Department of Sports Physiology Lamerd Branch, Islamic Azad University, Lamerd, Iran (grant No. 162434145).
-
Data Availability Statement: The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors without undue reservation.
-
Author Contributions:
Conceptualization: Ghaedi H.
Data curation: Zeinabi A, Ghaedi H.
Formal analysis: Zeinabi A, Hosseini SA.
Investigation: Zeinabi A, Hosseini SA.
Methodology: Ghaedi H.
Writing - original draft: Zeinabi A, Ghaedi H, Hosseini SA.
Writing - review & editing: Zeinabi A, Ghaedi H, Hosseini SA.
REFERENCES
- 1. Guerre-Millo M. Adiponectin: an update. Diabetes Metab 2008;34:12-18.
- 2. Fang H, Judd RL. Adiponectin regulation and function. Compr Physiol 2018;8:1031-1063.
- 3. Villarreal-Molina MT, Antuna-Puente B. Adiponectin: anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective effects. Biochimie 2012;94:2143-2149.
- 4. Lee S, Kwak HB. Role of adiponectin in metabolic and cardiovascular disease. J Exerc Rehabil 2014;10:54-59.
- 5. Cui J, Panse S, Falkner B. The role of adiponectin in metabolic and vascular disease: a review. Clin Nephrol 2011;75:26-33.
- 6. Frühbeck G, Catalán V, Rodríguez A, Gómez-Ambrosi J. Adiponectin-leptin ratio: a promising index to estimate adipose tissue dysfunction. Relation with obesity-associated cardiometabolic risk. Adipocyte 2018;7:57-62.
- 7. Silva FM, de Almeida JC, Feoli AM. Effect of diet on adiponectin levels in blood. Nutr Rev 2011;69:599-612.
- 8. Qi L, Meigs JB, Liu S, Manson JE, Mantzoros C, Hu FB. Dietary fibers and glycemic load, obesity, and plasma adiponectin levels in women with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006;29:1501-1505.
- 9. Kelesidis T, Kelesidis I, Chou S, Mantzoros CS. Narrative review: the role of leptin in human physiology: emerging clinical applications. Ann Intern Med 2010;152:93-100.
- 10. Friedman JM. Leptin and the endocrine control of energy balance. Nat Metab 2019;1:754-764.
- 11. Jéquier E. Leptin signaling, adiposity, and energy balance. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2002;967:379-388.
- 12. Martin RL, Perez E, He YJ, Dawson R Jr, Millard WJ. Leptin resistance is associated with hypothalamic leptin receptor mRNA and protein downregulation. Metabolism 2000;49:1479-1484.
- 13. Guo Z, Jiang H, Xu X, Duan W, Mattson MP. Leptin-mediated cell survival signaling in hippocampal neurons mediated by JAK STAT3 and mitochondrial stabilization. J Biol Chem 2008;283:1754-1763.
- 14. Xu Y, Hill JW, Fukuda M, Gautron L, Sohn JW, Kim KW, Lee CE, Choi MJ, Lauzon DA, Dhillon H, Lowell BB, Zigman JM, Zhao JJ, Elmquist JK. PI3K signaling in the ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus is required for normal energy homeostasis. Cell Metab 2010;12:88-95.
- 15. Reynolds AN, Akerman AP, Mann J. Dietary fibre and whole grains in diabetes management: systematic review and meta-analyses. PLoS Med 2020;17:e1003053.
- 16. Pourghassem Gargari B, Houjeghani S, Farzadi L, Houjeghani S, Safaeiyan A. Relationship between serum leptin, ghrelin and dietary macronutrients in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Int J Fertil Steril 2015;9:313-321.
- 17. Mirmiran P, Hosseini S, Hosseinpour-Niazi S, Azizi F. Legume consumption increase adiponectin concentrations among type 2 diabetic patients: a randomized crossover clinical trial. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr (Engl Ed) 2019;66:49-55.
- 18. Sánchez D, Miguel M, Aleixandre A. Dietary fiber, gut peptides, and adipocytokines. J Med Food 2012;15:223-230.
- 19. Zhang R, Jiao J, Zhang W, Zhang Z, Zhang W, Qin LQ, Han SF. Effects of cereal fiber on leptin resistance and sensitivity in C57BL/6J mice fed a high-fat/cholesterol diet. Food Nutr Res 2016;60:31690.
- 20. Antal M, Péter S, Regöly-Mérei A, Biró L, Arató G, Schmidt J, et al. Effects of oligofructose containing diet in obese persons. Orv Hetil 2010;4:141-152.
- 21. Aoe S, Ichinose Y, Kohyama N, Komae K, Takahashi A, Abe D, Yoshioka T, Yanagisawa T. Effects of high β-glucan barley on visceral fat obesity in Japanese individuals: a randomized, double-blind study. Nutrition 2017;42:1-6.
- 22. Beck EJ, Tapsell LC, Batterham MJ, Tosh SM, Huang XF. Oat β-glucan supplementation does not enhance the effectiveness of an energy-restricted diet in overweight women. Br J Nutr 2010;103:1212-1222.
- 23. Dewulf EM, Cani PD, Claus SP, Fuentes S, Puylaert PG, Neyrinck AM, Bindels LB, de Vos WM, Gibson GR, Thissen JP, Delzenne NM. Insight into the prebiotic concept: lessons from an exploratory, double blind intervention study with inulin-type fructans in obese women. Gut 2013;62:1112-1121.
- 24. Garcia AL, Steiniger J, Reich SC, Weickert MO, Harsch I, Machowetz A, Mohlig M, Spranger J, Rudovich NN, Meuser F, Doerfer J, Katz N, Speth M, Zunft HJ, Pfeiffer AH, Koebnick C. Arabinoxylan fibre consumption improved glucose metabolism, but did not affect serum adipokines in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. Horm Metab Res 2006;38:761-766.
- 25. Geliebter A, Astbury NM, Aviram-Friedman R, Yahav E, Hashim S. Skipping breakfast leads to weight loss but also elevated cholesterol compared with consuming daily breakfasts of oat porridge or frosted cornflakes in overweight individuals: a randomised controlled trial. J Nutr Sci 2014;3:e56.
- 26. Hashizume C, Kishimoto Y, Kanahori S, Yamamoto T, Okuma K, Yamamoto K. Improvement effect of resistant maltodextrin in humans with metabolic syndrome by continuous administration. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 2012;58:423-430.
- 27. Kobayakawa A, Suzuki T, Ikami T, Saito M, Yabe D, Seino Y. Improvement of fasting plasma glucose level after ingesting moderate amount of dietary fiber in Japanese men with mild hyperglycemia and visceral fat obesity. J Diet Suppl 2013;10:129-141.
- 28. Li S, Guerin-Deremaux L, Pochat M, Wils D, Reifer C, Miller LE. NUTRIOSE dietary fiber supplementation improves insulin resistance and determinants of metabolic syndrome in overweight men: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 2010;35:773-782.
- 29. Maki KC, Pelkman CL, Finocchiaro ET, Kelley KM, Lawless AL, Schild AL, Rains TM. Resistant starch from high-amylose maize increases insulin sensitivity in overweight and obese men. J Nutr 2012;142:717-723.
- 30. Nishimura M, Ohkawara T, Kanayama T, Kitagawa K, Nishimura H, Nishihira J. Effects of the extract from roasted chicory (Cichorium intybus L.) root containing inulin-type fructans on blood glucose, lipid metabolism, and fecal properties. J Tradit Complement Med 2015;5:161-167.
- 31. Parnell JA, Klancic T, Reimer RA. Oligofructose decreases serum lipopolysaccharide and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in adults with overweight/obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2017;25:510-513.
- 32. Reimer RA, Wharton S, Green TJ, Manjoo P, Ramay HR, Lyon MR, Gahler RJ, Wood S. Effect of a functional fibre supplement on glycemic control when added to a year-long medically supervised weight management program in adults with type 2 diabetes. Eur J Nutr 2021;60:1237-1251.
- 33. Reimer RA, Yamaguchi H, Eller LK, Lyon MR, Gahler RJ, Kacinik V, Juneja P, Wood S. Changes in visceral adiposity and serum cholesterol with a novel viscous polysaccharide in Japanese adults with abdominal obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2013;21:E379-E387.
- 34. Sakai C, Abe S, Kouzuki M, Shimohiro H, Ota Y, Sakinada H, et al. A randomized placebo-controlled trial of an oral preparation of high molecular weight fucoidan in patients with type 2 diabetes with evaluation of taste sensitivity. Yonago Acta Med 2019;62:14-23.
- 35. Strączkowski M, Nikołajuk A, Majewski R, Filarski R, Stefanowicz M, Matulewicz N, Karczewska-Kupczewska M. The effect of moderate weight loss, with or without (1, 3)(1, 6)-β-glucan addition, on subcutaneous adipose tissue inflammatory gene expression in young subjects with uncomplicated obesity. Endocrine 2018;61:275-284.
- 36. Upadhyaya B, McCormack L, Fardin-Kia AR, Juenemann R, Nichenametla S, Clapper J, Specker B, Dey M. Impact of dietary resistant starch type 4 on human gut microbiota and immunometabolic functions. Sci Rep 2016;6:28797.
- 37. Wanders AJ, Mars M, Borgonjen-van den Berg KJ, de Graaf C, Feskens EJ. Satiety and energy intake after single and repeated exposure to gel-forming dietary fiber: post-ingestive effects. Int J Obes 2014;38:794-800.
- 38. Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, Savovic J, Schulz KF, Weeks L, Sterne JA. Cochrane Bias Methods Group. Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011;343:d5928.
- 39. Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons; 2019.
- 40. DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 1986;7:177-188.
- 41. Sterne JA, Gavaghan D, Egger M. Publication and related bias in meta-analysis: power of statistical tests and prevalence in the literature. J Clin Epidemiol 2000;53:1119-1129.
- 42. Obradovic M, Sudar-Milovanovic E, Soskic S, Essack M, Arya S, Stewart AJ, Gojobori T, Isenovic ER. Leptin and obesity: role and clinical implication. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2021;12:585887.
- 43. Khodamoradi K, Parmar M, Khosravizadeh Z, Kuchakulla M, Manoharan M, Arora H. The role of leptin and obesity on male infertility. Curr Opin Urol 2020;30:334-339.
- 44. Bhat H, Bhat JA, Bhat MH, Rashid M, Jan R, Afroze D. Leptin in obesity and hypertension. Arter Hypertens 2022;26:26-31.
- 45. Izquierdo AG, Crujeiras AB, Casanueva FF, Carreira MC. Leptin, obesity, and leptin resistance: where are we 25 years later? Nutrients 2019;11:2704.
- 46. Basu A, Crew J, Ebersole JL, Kinney JW, Salazar AM, Planinic P, Alexander JM. Dietary blueberry and soluble fiber improve serum antioxidant and adipokine biomarkers and lipid peroxidation in pregnant women with obesity and at risk for gestational diabetes. Antioxidants 2021;10:1318.
- 47. Jane M, McKay J, Pal S. Effects of daily consumption of psyllium, oat bran and polyGlycopleX on obesity-related disease risk factors: a critical review. Nutrition 2019;57:84-91.
- 48. Emilien CH, Hsu WH, Hollis JH. The effect of soluble fiber dextrin on subjective and physiological markers of appetite: a randomized trial. Nutrients 2020;12:3341.
- 49. Palou M, Sánchez J, García-Carrizo F, Palou A, Picó C. Pectin supplementation in rats mitigates age-related impairment in insulin and leptin sensitivity independently of reducing food intake. Mol Nutr Food Res 2015;59:2022-2033.
- 50. Islam A, Civitarese AE, Hesslink RL, Gallaher DD. Viscous dietary fiber reduces adiposity and plasma leptin and increases muscle expression of fat oxidation genes in rats. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2012;20:349-355.
- 51. Shekarchizadeh-Esfahani P, Hassani B, Roshanravan N, Sorraya N. Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised, controlled trials on the effects of garlic supplementation on serum adiponectin and leptin levels. Int J Clin Pract 2021;75:e14200.
- 52. Jahantigh A, Delavar R, Mogharnasi M. The effect of eight weeks of combined training and garlic supplementation on adiponectin and lipid changes among inactive boys. Armaghane Danesh 2017;22:18-31.
- 53. Janiszewska J, Ostrowska J, Szostak-Węgierek D. The influence of nutrition on adiponectin—a narrative review. Nutrients 2021;13:1394.
- 54. Brockman DA, Chen X, Gallaher DD. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, a viscous soluble fiber, reduces insulin resistance and decreases fatty liver in Zucker Diabetic Fatty rats. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2012;9:100.
- 55. Hung SC, Bartley G, Young SA, Albers DR, Dielman DR, Anderson WH, Yokoyama W. Dietary fiber improves lipid homeostasis and modulates adipocytokines in hamsters. J Diabetes 2009;1:194-206.
- 56. Hara K, Horikoshi M, Yamauchi T, Yago H, Miyazaki O, Ebinuma H, Imai Y, Nagai R, Kadowaki T. Measurement of the high-molecular weight form of adiponectin in plasma is useful for the prediction of insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care 2006;29:1357-1362.
- 57. Hotta K, Funahashi T, Arita Y, Takahashi M, Matsuda M, Okamoto Y, Iwahashi H, Kuriyama H, Ouchi N, Maeda K, Nishida M, Kihara S, Sakai N, Nakajima T, Hasegawa K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Hanafusa T, Matsuzawa Y. Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2000;20:1595-1599.
- 58. Tishinsky JM, Robinson LE, Dyck DJ. Insulin-sensitizing properties of adiponectin. Biochimie 2012;94:2131-2136.