ABSTRACT
Migraine is a common neurological disease correlated with oxidative stress and lipid profile disorders. The present study was designed to determine the effects of Coenzyme Q10 (Co-Q10) supplementation on oxidative status and lipid profile in migraine individuals. This clinical trial was conducted on 84 females aged 18–50 years, diagnosed for episodic migraine according to the International Headache Society. Subjects were randomized to receive either Co-Q10 supplement (400 mg/day) or placebo for 12 weeks. Lipid profile and oxidative stress indices including malondialdehyde (MDA) and total antioxidant capacity (TAC) were measured before and after intervention in both groups. Also, anthropometric indices, dietary intakes, and clinical features were collected. Data analysis was conducted using SPSS version 16. Seventy-seven of the participants, with mean age of 33.70 ± 7.75 years, completed the study. After 12-week intervention, Co-Q10 led to a significant decrease in MDA levels compared to placebo (p = 0.009), with no effect on TAC levels (p = 0.106). A significant increase in serum Co-Q10 concentration and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) level in Co-Q10 group was observed, but no significant differences were found in other lipid profile variables (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides and total cholesterol). Among anthropometric variables, Co-Q10 only caused a significant reduction in body fat percentage (BFP), but we did not find any significant changes in others. A 12-week Co-Q10 supplementation led to significant improvement in clinical features, BFP, and HDL-C level among migraine individuals.
-
Trial Registration
-
Keywords: Coenzyme Q10; Clinical trial; Migraine; Oxidative stress
INTRODUCTION
Migraine is a common neurovascular disorder that interferes with daily activity and impact on the quality of life and characterized by moderate or severe pulsing recurring type of headache that usually on one side of the head [
1,
2]. This frequent and debilitating headache is accompanied by photo-, phono- or osmophobia and nausea or vomiting [
3]. Global migraine prevalence is 14.7% and 3 times common in females and usually begins in early ages [
4]. The pathophysiology of migraine attacks is complex and not clearly understood, although these attacks caused by behavioral, environmental, dietary, and pharmacological reasons [
5]. Results from previous studies suggest that high levels of serum lipids, free fatty acids, and oxidative stress may be the common denominator underlying migraine triggers [
6].
Previous studies have shown an association between lipid profile impairment and severity and frequency of migraine [
7,
8], however, a one study have not shown this association [
9]. It has also been shown that increased levels of oxidative stress are associated with migraines and cause migraine-related metabolic complications [
10], and in general, almost all triggers of migraine symptoms can increase the level of oxidative stress [
5]. Patients with migraine appear to have increased oxidative stress indices, and migraine attacks may also be a neuroprotective reply to increased levels of oxidative stress [
11]. Therefore, it seems that finding a way that can reduce the level of oxidative stress and also regulate the lipid profile may reduce the severity and frequency of attacks and ultimately leading to control of migraine.
Pharmacological migraine treatment may be acute or prevention therapy. The choice of a prevention medication depends on effectiveness, side effects, contraindications, cost, and adoption of prophylaxis agent [
12]. In recent years, the use of nutritional supplements as well as natural compounds to control migraine attacks such as the use of vitamins and minerals has been increased [
2,
13]. Coenzyme Q10 (Co-Q10) is a naturally vitamin-like compound that acts as an electron carrier from involved 1 and 2 to cytochrome C in the mitochondrial electron transport chain [
12,
14,
15]. Co-Q10 possess antioxidant activity and has been extensively used for the treatment of mitochondrial disorders and migraine attacks with no identifiable side-effects in humans [
16,
17].
However, the effect of Co-Q10 on lipid profile and oxidative stress factors in migraine patients is not investigated. Therefore, this study was designed to investigate the prophylactic effect of oral Co-Q10 supplementation on nutritional status, migraine attacks and oxidative stress biomarkers in women with migraine.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study design and participants
The study was done as a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled, trial with the registration number: IRCT201508265670N10 in the Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials (
www.irct.ir).
Eighty-four individuals aged between 18 and 50 years, who were suffering from a headache and referred to the clinic of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences at Razi Hospital (Tabriz, Iran) from December 2015 to October 2016, were recruited for the present study. The diagnosis of migraine headache was performed based on International Headache Society criteria for episodic migraine (< 15 headache days/month) by a neurologist during the first visit. Patients with at least 2 attacks per month for more than one year were included in the trial. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences (reference number TBZMED.REC.1394.835), prior to the commencement. Patients who accepted to participate in the study gave informed written consent before trial beginning based on declaration of Helsinki [
18].
Exclusion criteria include having other types of headache disorder or tension-type, experiencing the menopause, having stroke or heart problem such as myocardial infarction, suffering from a serious organic or inflammatory disease or psychiatric problem, using prophylactic drugs during the proceeding 6 month, taking of Co-Q10 or other supplementations containing antioxidants for at least 3 month prior to enrollment, use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, smoking, pregnancy or intention of pregnancy, and lactation.
Trial protocol and intervention
Eighty-four eligible women were enrolled in the study based on the inclusion criteria. The trial duration was 4 months, including one-month run-in period before starting the 3-month treatment phase. All patients received an anticonvulsant and a tricyclic antidepressant as a prophylactic medication in their first visit by a neurologist in consideration of ethical issues.
After the first month, patients were randomly assigned to 2 groups. Intervention group received 400 mg of Co-Q10 supplements per day divided into 2 doses for 12 weeks after meal, while the other received placebo capsules containing wheat starch for the same duration.
The dose of Co-Q10 was calculated based on the previous study and in consideration of observed safe level [
6]. Patients’ compliance was monitored for at least 4 weeks by counting the number of returned capsules at the follow-up visits.
The allocation was carried out based on block randomization procedure in equal blocks of size 4 with a random number generator (
http://www.randomizer.org) stratified by age (less or more than 35), history of prophylactic drug usage and years of migraine diagnosis (less or more than 5 years). All patients and researchers were blinded to the randomized group throughout the study. Patients were informed not to change their usual diet and physical activity during the study.
Anthropometric data, including height, weight, waist and hip circumference (WC and HC), and body fat percentage (BFP), were obtained at baseline, at the middle of the study (6th weeks) and at the end of the study (12th weeks). Height was measured with a precision of 0.1 cm. Weight was measured by a Seca scale to the nearest 0.1 kg, with light clothes and no shoes. WC was measured at the most lateral contour at the abdomen by a measuring tape, and HC was measured at the widest portion of the hips by a measuring tape. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as follows: Weight (kg)/Height (m
2). Physical activity levels were evaluated using the international physical activity questionnaire, and participants were categorized into 3 satges (high, moderate, and low) based on their physical activity level [
19].
Blood samples (10 mL) were collected from patients after an overnight fast of 12 hours at the baseline and at the end of the study. Then whole blood samples were centrifugated at 3,500 rpm for 10 minutes to separate serum. Serum samples were stored at −70ºC until the analyses were performed. Serum level of malondialdehyde (MDA) was determined by thiobarbituric acid reactive substances method described by Bilici et al. [
20]. Measurement of total antioxidant capacity (TAC) was performed using spectrophotometry method with Randox kit (Randox Laboratories, Ltd., Crumlin, UK).
Serum levels of total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and triglycerides (TGs) were measured enzymatically in serum samples at baseline and after the study. The amount of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) was calculated using the Friedewald formula: LDL (mg/dL) = TC − HDL − TG/5. In our previous work, the potential effects of Co-Q10 on migraine characteristics (frequency, severity, and duration of attacks and headache) were reported [
6].
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS for Windows version 16.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). In all the analyses, results with p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was used to check the normal distribution of the variables. Results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation or frequency and percentage. Independent samples t-test and χ2 tests were performed to assess the differences between groups at baseline in quantitative and categorical variables, respectively. Paired t-test and repeated measures analysis of variance with post hoc Sidak tests were used to explore within-group differences before and after the intervention. Analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was used to evaluate the effects of Co-Q10 on the serum levels of variables, considering the influence of potential confounders.
RESULTS
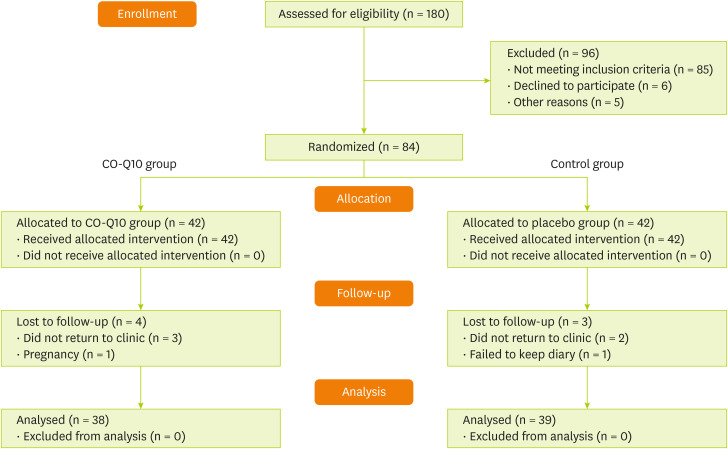
Thirty-nine patients in the Co-Q10 group and thirty-eight in the placebo group (total 77 participants) completed the study (
Figure 1). As presented in
Table 1, no significant differences in baseline characteristics between the 2 groups were observed (p > 0.05). The results revealed no significant differences between the 2 groups for any of the measured serum TAC and MDA level at baseline (p > 0.05) (
Table 2).
Figure 1
Flow diagram of study recruitment.
Co-Q10, Coenzyme Q10.
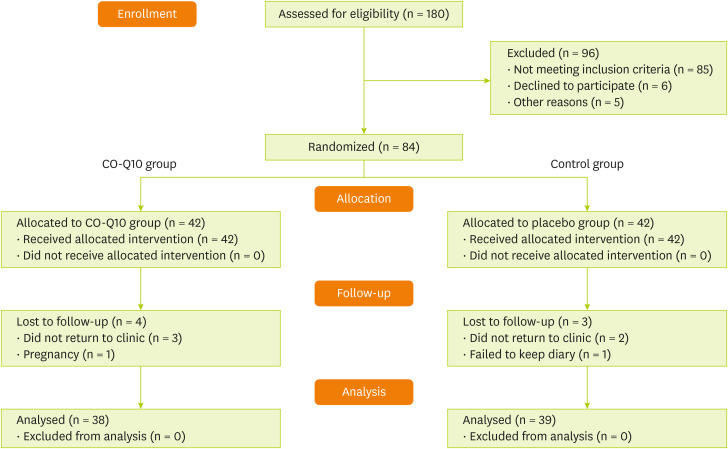
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of participants
Table 1
|
Variables |
Co-Q10 (n = 39) |
Placebo (n = 38) |
p value |
|
Age (yr) |
33.44 ± 7.30 |
33.97 ± 8.28 |
0.763 |
|
Marital status |
|
|
0.391 |
|
Single |
8 (20.5) |
11 (28.9) |
|
Married |
31 (79.5) |
27 (71.1) |
|
Positive migraine family history*
|
24 (61.5) |
26 (68.4) |
0.527 |
|
Years with migraine |
11.51 ± 7.47 |
9.07 ± 6.46 |
0.129 |
|
Migraine with aura*
|
11 (28.2) |
11 (28.9) |
0.943 |
|
Body mass index |
25.78 ± 4.03 |
25.08 ± 3.84 |
0.436 |
|
Body fat percentage†
|
32.94 ± 5.84 |
31.07 ± 6.52 |
0.188 |
|
Waist circumference†
|
83.05 ± 8.86 |
81.24 ± 8.60 |
0.365 |
|
Hip circumference†
|
103.77 ± 7.61 |
101.82 ± 6.91 |
0.243 |
|
Physical activity level*
|
|
|
0.957 |
|
High |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
Moderate |
7 (17.9) |
7 (18.4) |
|
Low |
32 (82.1) |
31 (81.6) |
Table 2 Oxidative stress markers at study baseline and 12-week after the intervention in patients who received either Co-Q10 or placebo
Table 2
|
Variables |
Co-Q10 (n = 39) |
Placebo (n = 38) |
MD (95% CI), p value |
|
TAC (mmol/L) |
|
|
|
|
Before |
1.52 ± 0.24 |
1.52 ± 0.27 |
−0.004 (−0.11, 0.12), 0.950†
|
|
After |
1.57 ± 0.28 |
1.51 ± 0.28 |
−0.07 (−0.16, 0.02), 0.106‡
|
|
MD (95% CI) |
0.05 (−0.01, 0.11) |
−0.01 (−0.07, 0.05) |
|
|
p value*
|
0.087 |
0.683 |
|
|
MDA (nmol/mL) |
|
|
|
|
Before |
1.66 ± 0.57 |
1.63 ± 0.46 |
−0.03 (−0.26, 0.21), 0.818†
|
|
After |
1.53 ± 0.50 |
1.79 ± 0.55 |
0.30 (0.08, 0.52), 0.009‡
|
|
MD (95% CI) |
−0.13 (−0.30, 0.03) |
0.16 (−0.02, 0.33) |
|
|
p value*
|
0.118 |
0.077 |
|
At the end of the study, serum levels of TAC increased in the Co-Q10 group, whereas they decreased in the placebo group. Serum level of MDA increased in the placebo group but decreased in the Co-Q10 group. Results of ANCOVA adjusted for baseline values and confounder variables also showed a significant difference between the groups for MDA serum levels at the end of the study (p = 0.009) (
Table 2).
Results indicated no significant differences at baseline in TG, TC, LDL-C, and HDL-C between groups (p > 0.05). In the same pattern, between-group comparison based on ANCOVA adjusted for baseline values and confounder variables didn’t show a significant reduction in the serum levels of TG, TC, LDL-C, and HDL-C in Co-Q10 group compared to placebo group (p > 0.05). A significant increase in HDL-C was found in the Co-Q10 group after intervention (p = 0.012) (
Table 3).
Table 3 Lipid profile parameters at study baseline and 12-week after the intervention in patients who received either Co-Q10 or placebo
Table 3
|
Variables (mg/dL) |
Co-Q10 (n = 39) |
Placebo (n = 38) |
MD (95% CI), p value |
|
TC |
|
|
|
|
Before |
171.97 ± 37.04 |
181.29 ± 34.42 |
9.32 (−6.93, 25.56), 0.257†
|
|
After |
169.67 ± 32.25 |
184.26 ± 41.62 |
6.95 (−5.03, 18.93), 0.251‡
|
|
MD (95% CI) |
−2.31 (−9.40, 4.78) |
2.97 (−6.00, 11.94) |
|
|
p value*
|
0.514 |
0.506 |
|
|
LDL-c |
|
|
|
|
Before |
100.33 ± 29.74 |
104.00 ± 29.32 |
3.67 (−9.74, 17.08), 0.588†
|
|
After |
93.62 ± 28.54 |
104.92 ± 33.53 |
9.38 (−1.35, 20.11), 0.086‡
|
|
MD (95% CI) |
−6.72 (−14.36, 0.92) |
0.92 (−5.92, 7.77) |
|
|
p value*
|
0.083 |
0.787 |
|
|
HDL-c |
|
|
|
|
Before |
50.77 ± 10.31 |
53.84 ± 11.27 |
3.07 (−1.83, 7.98), 0.216†
|
|
After |
55.67 ± 10.10 |
55.39 ± 11.35 |
−3.67 (−8.15, 0.82), 0.108‡
|
|
MD (95% CI) |
4.90 (1.16, 8.63) |
1.55 (−1.50, 4.61) |
|
|
p value*
|
0.012 |
0.31 |
|
|
TG |
|
|
|
|
Before |
104.15 ± 46.13 |
119.63 ± 51.17 |
15.48 (−6.63, 37.58), 0.167†
|
|
After |
101.36 ± 42.36 |
119.11 ± 52.13 |
11.17 (−7.12, 29.45), 0.227‡
|
|
MD (95% CI) |
−2.80 (−16.35, 10.76) |
−0.53 (−13.18, 12.13) |
|
|
p value*
|
0.679 |
0.933 |
|
As illustrated in
Table 4, differences in anthropometric parameters (BMI, BFP, WC, and HC) were not significant in baseline characteristics between the 2 groups (p > 0.05).
Table 4 Comparisons of anthropometric indices of migraine patients at baseline, after 6 and 12 weeks of intervention between 2 groups
Table 4
|
Variables |
Co-Q10 (n = 39) |
Placebo (n = 38) |
MD (95% CI), p value |
|
BMI (kg/m2) |
|
|
|
|
Baseline |
25.78 ± 4.04 |
25.08 ± 3.84 |
−0.71 (−2.52, 1.09), 0.436†
|
|
6th wk |
25.79 ± 4.02 |
25.05 ± 3.76 |
−0.44 (−0.24, 0.15), 0.661‡
|
|
12th wk |
25.65 ± 4.00 |
25.10 ± 3.72 |
0.13 (−0.11, 0.36), 0.288‡
|
|
p value*
|
0.039 |
0.729 |
|
|
BFP (%) |
|
|
|
|
Baseline |
32.95 ± 5.84 |
31.07 ± 6.52 |
1.87 (−4.68, 0.94), 0.188†
|
|
6th wk |
32.26 ± 5.91 |
30.86 ± 6.05 |
−0.37 (−0.32, 1.05), 0.288‡
|
|
12th wk |
31.79 ± 5.51 |
31.17 ± 6.08 |
1.09 (0.38, 1.80), 0.003‡
|
|
p value*
|
< 0.001 |
0.363 |
|
|
WC (cm) |
|
|
|
|
Baseline |
83.05 ± 8.86 |
81.24 ± 8.60 |
−1.81 (−5.78, 2.15), 0.365†
|
|
6th wk |
82.97 ± 8.73 |
81.21 ± 8.43 |
0.01 (−0.54, 0.56), 0.982‡
|
|
12th wk |
82.64 ± 8.79 |
81.47 ± 8.38 |
−1.95 (−5.26, 1.35), 0.243‡
|
|
p value*
|
0.036 |
0.353 |
|
|
HC (cm) |
|
|
|
|
Baseline |
103.77 ± 7.61 |
101.82 ± 6.92 |
−1.95 (−5.26, 1.35), 0.243†
|
|
6th wk |
103.70 ± 7.50 |
101.79 ± 6.67 |
−0.11 (−0.42, 0.19), 0.467‡
|
|
12th wk |
103.26 ± 7.18 |
101.89 ± 6.62 |
−0.48 (−0.04, 0.92), 0.330‡
|
|
p value*
|
< 0.001 |
0.669 |
|
At the end of the study, 18 patients (78.3%) in the Co-Q10 group and 12 patients (54.5%) in the placebo group indicated a reduction in BFP, which resulted in a significant reduction in BFP in the Co-Q10 group (p < 0.001).
DISCUSSION
In the present study, the effect of oral Co-Q10 supplement on oxidative stress markers, anthropometric parameters and lipid profile in women with migraine were evaluated. Our findings revealed that Co-Q10 supplementation during 12-week in women with migraine was able to reduce oxidative stress levels by improving related markers (MDA and TAC). Additionally, HDL-C levels significantly increased in the intervention group compared with the control group, although it did not have a significant effect on other markers related to lipid profiles such as TG, TC, and LDL-C. Finally, our study showed that Co-Q10 supplementation reduced BFP but had no significant effect on other anthropometric indicators such as BMI, WC, and HC.
Oxidative stress describes the situation of imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body, which can damage membrane lipids, proteins, nucleic acids and extracellular matrix components, including proteoglycans and collagens [
21]. Various studies supported the hypothesis that oxidative stress and free radicals play a role in migraine pathogenesis by regulating cerebral blood flow and energy metabolism, therefore may constitute a trigger threshold for migraine attacks [
22,
23,
24].
In a study that conducted by Boćkowski et al. [
25], significant reductions in the MDA concentrations in serum and erythrocytes were observed in migraineurs compared to control group. Erol et al.’s study [
26] showed that glutathione peroxidase and catalase activity in erythrocytes of children and adolescents with migraine was higher than the control group, but no significant difference was observed in superoxide dismutase activity.
So far, several studies have examined the association between oxidative stress and the Co-Q10. Liu et al. [
27], founded that oxidative stress and inflammatory markers decreased and antioxidant enzymes activities increased in hepatocellular carcinoma patients following surgery after consumption of 300 mg/day of Co-Q10 during 12 weeks. In another study, supplemented with Co-Q10 resulted in a decrease in formation of conjugated dienes and MDA which showed the antioxidant activity of Co-Q10 in the oxidation of LDL-C [
28]. The results of these studies are in line with the findings of our study and indicate the antioxidant role of Co-Q10.
Lee et al. [
29] reported a significant increase in superoxide dismutase activity and a decrease in MDA level in multiple sclerosis patients after taking 500 mg/day of Co-Q10 for 12 weeks, although there was no effect on glutathione peroxidase levels. Supplementation of 100 mg/day of Co-Q10 during 4-week led to a decrease in TAC level in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [
30]. In our study, despite the increase in TAC level after intervention, the changes were not significant, which is probably due to differences in sample size and dose of supplement used.
In the current study, the effect of Co-Q10 on lipid profiles (TG, TC, HDL-C, and LDL-C) in migraine patients was evaluated. The results indicated a significant increase in serum HDL-C level in Co-Q10 group; however, no significant differences were found in other lipid profiles, either within or between the groups. Several studies have shown a correlation between migraine and changes in lipid profiles which are associated with the metabolic disorder. Bigal et al. [
31] reported that migraine with and without aura is associated with cardiovascular disease (CVD) and high cholesterol as a risk factor for CVD.
In the Gruber and colleagues study, evaluation of the lipid profile in migraine patients indicated a significant increase in cholesterol, LDL-C and oxidized LDL-C in normal weight migraineurs in comparison with healthy control subjects. It was also stated increased oxidized LDL-C was associated with a 7.93-fold increased risk for migraine [
32]. Saberi et al.’s study [
33] showed that higher levels of TG, TC, and LDL-C in the migraine patients compared with control group. These results suggest that hypertriglyceridemia and hypercholesterolemia leads to 3.11 and 17.14 folds more chance for migraine coincidence respectively. Different studies demonstrated a negative correlation between Co-Q10 levels and lipid profiles. Evaluation the lipid profile in subjects with type 2 diabetes indicated a significant decrease in TG and HDL-C after 12 weeks of treatment with 150 mg/day of Co-Q10, however, increased level of LDL-C was observed [
34]. Similar to our results, supplementation with 100 mg/day of Co-Q10 for 8 weeks did not affect the lipid profile in patients with metabolic syndrome [
35]. In another study, supplementation of Co-Q10 in patients with renal insufficiency only reduced the level of HDL-C in a small amount [
36]. Ritu and Manika’s study [
37] showed that treatment with 100 mg/day of Co-Q10 for 60 days didn’t influence cholesterol, TG, LDL-C and lipoprotein A levels in patients with coronary diseases. The reasons for the difference in the results of these studies with our finding are probably due to the type of disease and the dose of Co-Q10 supplement that used.
According to our results, Co-Q10 supplementation only caused a significant reduction in BFP, with no effect on other anthropometric indices. Oral administration of Co-Q10 resulted in significant weight loss in mice [
38]. The positive association between obesity and the incidence of migraine have been shown previously [
39,
40], and several studies have indicated that obesity may worsen the features of migraine attacks [
40,
41].
In the present study we asked participants not to change their physical activity and food intakes during the intervention. As a result, the weight loss and reduction in BFP, which observed at the end of the study, may be related to Co-Q10 supplementation. Carmona et al. [
42] reported that Co-Q10 supplementation could prevent an increase in body weight and adiposity through increasing of lipid oxidation in adipose tissue and reducing lipid synthesis. However, the present study had several limitations. First, the add-on design of the research made it difficult to detect either the pure effect of the Co-Q10 on the oxidative stress indices and lipid profile markers or its synergistic effectiveness with the current prophylactic therapy. Second, migraine symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and photophobia were not assessed. Finally, longer duration study with larger sample size is required to obtain long-term and clearly effects of Co-Q10 on oxidative stress, lipid profile, and anthropometric indices.
The present study was the first to show that a dose of 400 mg/day of Co-Q10 for 12-week could significantly increase serum Co-Q10 concentration and led to a reduction in BFP. But it didn’t affect other anthropometric data. Moreover, at the end of the intervention, significant differences between groups were found in MDA levels. In addition, the positive effect of Co-Q10 on serum level of HDL-C was observed without a significant effect on other lipid profile indices. These findings suggest that Co-Q10 probably has benefits for migraine patients. Nevertheless, further studies are needed to confirm our findings.
Research Vice-chancellor
Nutrition Research Center of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences
NOTES
-
Funding: This work was supported by the Research Vice-chancellor and Nutrition Research Center of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences.
-
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
-
Author Contributions:
Conceptualization: Tarighat-Esfanjani A.
Data curation: Dahri M.
Formal analysis: Asghari-Jafarabadi M.
Investigation: Nattagh-Eshtivani E.
Methodology: Asghari-Jafarabadi M, Hashemilar M.
Project administration: Dahri M.
Supervision: Tarighat-Esfanjani A.
Writing - original draft: Pahlavani N, Dahri M, Sarafan Sadeghi A, Barghchi H, Nattagh-Eshtivani E.
Writing - review & editing: Nattagh-Eshtivani E, Pahlavani N.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the participation of all individuals for their assistance in this research project.
REFERENCES
- 1. Carod-Artal FJ, Irimia P, Ezpeleta D. Chronic migraine: definition, epidemiology, risk factors and treatment. Rev Neurol 2012;54:629-637.
- 2. Nattagh-Eshtivani E, Sani MA, Dahri M, Ghalichi F, Ghavami A, Arjang P, Tarighat-Esfanjani A. The role of nutrients in the pathogenesis and treatment of migraine headaches: review. Biomed Pharmacother 2018;102:317-325.
- 3. Butt JH, Franzmann U, Kruuse C. Endothelial function in migraine with aura - a systematic review. Headache 2015;55:35-54.
- 4. Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, Shibuya K, Salomon JA, Abdalla S, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Ackerman I, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, Ali MK, Alvarado M, Anderson HR, Anderson LM, Andrews KG, Atkinson C, Baddour LM, Bahalim AN, Barker-Collo S, Barrero LH, Bartels DH, Basáñez MG, Baxter A, Bell ML, Benjamin EJ, Bennett D, Bernabé E, Bhalla K, Bhandari B, Bikbov B, Bin Abdulhak A, Birbeck G, Black JA, Blencowe H, Blore JD, Blyth F, Bolliger I, Bonaventure A, Boufous S, Bourne R, Boussinesq M, Braithwaite T, Brayne C, Bridgett L, Brooker S, Brooks P, Brugha TS, Bryan-Hancock C, Bucello C, Buchbinder R, Buckle G, Budke CM, Burch M, Burney P, Burstein R, Calabria B, Campbell B, Canter CE, Carabin H, Carapetis J, Carmona L, Cella C, Charlson F, Chen H, Cheng AT, Chou D, Chugh SS, Coffeng LE, Colan SD, Colquhoun S, Colson KE, Condon J, Connor MD, Cooper LT, Corriere M, Cortinovis M, de Vaccaro KC, Couser W, Cowie BC, Criqui MH, Cross M, Dabhadkar KC, Dahiya M, Dahodwala N, Damsere-Derry J, Danaei G, Davis A, De Leo D, Degenhardt L, Dellavalle R, Delossantos A, Denenberg J, Derrett S, Des Jarlais DC, Dharmaratne SD, Dherani M, Diaz-Torne C, Dolk H, Dorsey ER, Driscoll T, Duber H, Ebel B, Edmond K, Elbaz A, Ali SE, Erskine H, Erwin PJ, Espindola P, Ewoigbokhan SE, Farzadfar F, Feigin V, Felson DT, Ferrari A, Ferri CP, Fèvre EM, Finucane MM, Flaxman S, Flood L, Foreman K, Forouzanfar MH, Fowkes FG, Franklin R, Fransen M, Freeman MK, Gabbe BJ, Gabriel SE, Gakidou E, Ganatra HA, Garcia B, Gaspari F, Gillum RF, Gmel G, Gosselin R, Grainger R, Groeger J, Guillemin F, Gunnell D, Gupta R, Haagsma J, Hagan H, Halasa YA, Hall W, Haring D, Haro JM, Harrison JE, Havmoeller R, Hay RJ, Higashi H, Hill C, Hoen B, Hoffman H, Hotez PJ, Hoy D, Huang JJ, Ibeanusi SE, Jacobsen KH, James SL, Jarvis D, Jasrasaria R, Jayaraman S, Johns N, Jonas JB, Karthikeyan G, Kassebaum N, Kawakami N, Keren A, Khoo JP, King CH, Knowlton LM, Kobusingye O, Koranteng A, Krishnamurthi R, Lalloo R, Laslett LL, Lathlean T, Leasher JL, Lee YY, Leigh J, Lim SS, Limb E, Lin JK, Lipnick M, Lipshultz SE, Liu W, Loane M, Ohno SL, Lyons R, Ma J, Mabweijano J, MacIntyre MF, Malekzadeh R, Mallinger L, Manivannan S, Marcenes W, March L, Margolis DJ, Marks GB, Marks R, Matsumori A, Matzopoulos R, Mayosi BM, McAnulty JH, McDermott MM, McGill N, McGrath J, Medina-Mora ME, Meltzer M, Mensah GA, Merriman TR, Meyer AC, Miglioli V, Miller M, Miller TR, Mitchell PB, Mocumbi AO, Moffitt TE, Mokdad AA, Monasta L, Montico M, Moradi-Lakeh M, Moran A, Morawska L, Mori R, Murdoch ME, Mwaniki MK, Naidoo K, Nair MN, Naldi L, Narayan KM, Nelson PK, Nelson RG, Nevitt MC, Newton CR, Nolte S, Norman P, Norman R, O’Donnell M, O’Hanlon S, Olives C, Omer SB, Ortblad K, Osborne R, Ozgediz D, Page A, Pahari B, Pandian JD, Rivero AP, Patten SB, Pearce N, Padilla RP, Perez-Ruiz F, Perico N, Pesudovs K, Phillips D, Phillips MR, Pierce K, Pion S, Polanczyk GV, Polinder S, Pope CA 3rd, Popova S, Porrini E, Pourmalek F, Prince M, Pullan RL, Ramaiah KD, Ranganathan D, Razavi H, Regan M, Rehm JT, Rein DB, Remuzzi G, Richardson K, Rivara FP, Roberts T, Robinson C, De Leòn FR, Ronfani L, Room R, Rosenfeld LC, Rushton L, Sacco RL, Saha S, Sampson U, Sanchez-Riera L, Sanman E, Schwebel DC, Scott JG, Segui-Gomez M, Shahraz S, Shepard DS, Shin H, Shivakoti R, Singh D, Singh GM, Singh JA, Singleton J, Sleet DA, Sliwa K, Smith E, Smith JL, Stapelberg NJ, Steer A, Steiner T, Stolk WA, Stovner LJ, Sudfeld C, Syed S, Tamburlini G, Tavakkoli M, Taylor HR, Taylor JA, Taylor WJ, Thomas B, Thomson WM, Thurston GD, Tleyjeh IM, Tonelli M, Towbin JA, Truelsen T, Tsilimbaris MK, Ubeda C, Undurraga EA, van der Werf MJ, van Os J, Vavilala MS, Venketasubramanian N, Wang M, Wang W, Watt K, Weatherall DJ, Weinstock MA, Weintraub R, Weisskopf MG, Weissman MM, White RA, Whiteford H, Wiersma ST, Wilkinson JD, Williams HC, Williams SR, Witt E, Wolfe F, Woolf AD, Wulf S, Yeh PH, Zaidi AK, Zheng ZJ, Zonies D, Lopez AD, Murray CJ, AlMazroa MA, Memish ZA. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012;380:2163-2196.
- 5. Borkum JM. Migraine triggers and oxidative stress: a narrative review and synthesis. Headache 2016;56:12-35.
- 6. Dahri M, Hashemilar M, Asghari-Jafarabadi M, Tarighat-Esfanjani A. Efficacy of coenzyme Q10 for the prevention of migraine in women: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur J Integr Med 2017;16:8-14.
- 7. Janoska M, Chorążka K, Domitrz I. Migraine frequency and its association with dyslipidemia in women. Neurol Neurochir Pol 2015;49:95-98.
- 8. Rist PM, Tzourio C, Kurth T. Associations between lipid levels and migraine: cross-sectional analysis in the epidemiology of vascular ageing study. Cephalalgia 2011;31:1459-1465.
- 9. Kurth T, Ridker PM, Buring JE. Migraine and biomarkers of cardiovascular disease in women. Cephalalgia 2008;28:49-56.
- 10. Bernecker C, Ragginer C, Fauler G, Horejsi R, Möller R, Zelzer S, Lechner A, Wallner-Blazek M, Weiss S, Fazekas F, Bahadori B, Truschnig-Wilders M, Gruber HJ. Oxidative stress is associated with migraine and migraine-related metabolic risk in females. Eur J Neurol 2011;18:1233-1239.
- 11. Neri M, Frustaci A, Milic M, Valdiglesias V, Fini M, Bonassi S, Barbanti P. A meta-analysis of biomarkers related to oxidative stress and nitric oxide pathway in migraine. Cephalalgia 2015;35:931-937.
- 12. Rozen TD, Oshinsky ML, Gebeline CA, Bradley KC, Young WB, Shechter AL, Silberstein SD. Open label trial of coenzyme Q10 as a migraine preventive. Cephalalgia 2002;22:137-141.
- 13. Sadeghi O, Nasiri M, Maghsoudi Z, Pahlavani N, Rezaie M, Askari G. Effects of pyridoxine supplementation on severity, frequency and duration of migraine attacks in migraine patients with aura: a double-blind randomized clinical trial study in Iran. Iran J Neurol 2015;14:74-80.
- 14. Montagna P, Cortelli P, Barbiroli B. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies in migraine. Cephalalgia 1994;14:184-193.
- 15. Ghavami A, Mohammadi H, Hadi A, Ziaei R, Nattagh-Eshtivani E, Sheykhrobat MV, Askari G. Effects of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on anthropometric indices in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Prev Med 2020;11:181.
- 16. Cordero MD, Cano-García FJ, Alcocer-Gómez E, De Miguel M, Sánchez-Alcázar JA. Oxidative stress correlates with headache symptoms in fibromyalgia: coenzyme Q10 effect on clinical improvement. PLoS One 2012;7:e35677.
- 17. Nattagh-Eshtivani E, Dahri M, Hashemilar M, Tarighat-Esfanjani A. The effect of Coenzyme Q10 supplementation on serum levels of lactate, pyruvate, matrix metalloproteinase 9 and nitric oxide in women with migraine. A double blind, placebo, controlled randomized clinical trial. Eur J Integr Med 2018;21:70-76.
- 18. Ndebele P. The Declaration of Helsinki, 50 years later. JAMA 2013;310:2145-2146.
- 19. Dahri M, Tarighat-Esfanjani A, Asghari-Jafarabadi M, Hashemilar M. Oral coenzyme Q10 supplementation in patients with migraine: effects on clinical features and inflammatory markers. Nutr Neurosci 2019;22:607-615.
- 20. Bilici M, Efe H, Köroğlu MA, Uydu HA, Bekaroğlu M, Değer O. Antioxidative enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in major depression: alterations by antidepressant treatments. J Affect Disord 2001;64:43-51.
- 21. Alp R, Selek S, Alp SI, Taşkin A, Koçyiğit A. Oxidative and antioxidative balance in patients of migraine. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2010;14:877-882.
- 22. Stuart S, Griffiths LR. A possible role for mitochondrial dysfunction in migraine. Mol Genet Genomics 2012;287:837-844.
- 23. Sparaco M, Feleppa M, Lipton RB, Rapoport AM, Bigal ME. Mitochondrial dysfunction and migraine: evidence and hypotheses. Cephalalgia 2006;26:361-372.
- 24. Merison K, Jacobs H. Diagnosis and treatment of childhood migraine. Curr Treat Options Neurol 2016;18:48.
- 25. Boćkowski L, Sobaniec W, Kułak W, Smigielska-Kuzia J. Serum and intraerythrocyte antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxides in children with migraine. Pharmacol Rep 2008;60:542-548.
- 26. Erol I, Alehan F, Aldemir D, Ogus E. Increased vulnerability to oxidative stress in pediatric migraine patients. Pediatr Neurol 2010;43:21-24.
- 27. Liu HT, Huang YC, Cheng SB, Huang YT, Lin PT. Effects of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on antioxidant capacity and inflammation in hepatocellular carcinoma patients after surgery: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Nutr J 2016;15:85.
- 28. Ahmadvand H, Mabuchi H, Nohara A, Kobayahi J, Kawashiri MA. Effects of coenzyme Q(10) on LDL oxidation in vitro. Acta Med Iran 2013;51:12-18.
- 29. Lee BJ, Huang YC, Chen SJ, Lin PT. Coenzyme Q10 supplementation reduces oxidative stress and increases antioxidant enzyme activity in patients with coronary artery disease. Nutrition 2012;28:250-255.
- 30. Farhangi MA, Alipour B, Jafarvand E, Khoshbaten M. Oral coenzyme Q10 supplementation in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: effects on serum vaspin, chemerin, pentraxin 3, insulin resistance and oxidative stress. Arch Med Res 2014;45:589-595.
- 31. Bigal ME, Kurth T, Santanello N, Buse D, Golden W, Robbins M, Lipton RB. Migraine and cardiovascular disease: a population-based study. Neurology 2010;74:628-635.
- 32. Gruber HJ, Bernecker C, Pailer S, Lechner A, Horejsi R, Möller R, Fazekas F, Truschnig-Wilders M. Lipid profile in normal weight migraineurs - evidence for cardiovascular risk. Eur J Neurol 2010;17:419-425.
- 33. Saberi A, Hatamian HR, Kazemnejad E, Ghorbannejad N. Hyperlipidemia in migraine: Is it more frequent in migraineurs? Iran J Neurol 2011;10:46-50.
- 34. Zahedi H, Eghtesadi S, Seifirad S, Rezaee N, Shidfar F, Heydari I, Golestan B, Jazayeri S. Effects of CoQ10 supplementation on lipid profiles and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Diabetes Metab Disord 2014;13:81.
- 35. Raygan F, Rezavandi Z, Dadkhah Tehrani S, Farrokhian A, Asemi Z. The effects of coenzyme Q10 administration on glucose homeostasis parameters, lipid profiles, biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in patients with metabolic syndrome. Eur J Nutr 2016;55:2357-2364.
- 36. Mori TA, Burke V, Puddey I, Irish A, Cowpland CA, Beilin L, Dogra G, Watts GF. The effects of [ω]3 fatty acids and coenzyme Q10 on blood pressure and heart rate in chronic kidney disease: a randomized controlled trial. J Hypertens 2009;27:1863-1872.
- 37. Ritu M, Manika M. Impact of intervention with Co-Enzyme Q10 on homocysteine levels of cardiac patients with established angiographic evidence. J Clin Trial Cardiol 2014;1:1-6.
- 38. Ferrante RJ, Andreassen OA, Dedeoglu A, Ferrante KL, Jenkins BG, Hersch SM, Beal MF. Therapeutic effects of coenzyme Q10 and remacemide in transgenic mouse models of Huntington’s disease. J Neurosci 2002;22:1592-1599.
- 39. Keith SW, Wang C, Fontaine KR, Cowan CD, Allison DB. BMI and headache among women: results from 11 epidemiologic datasets. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008;16:377-383.
- 40. Yu S, Liu R, Yang X, Zhao G, Qiao X, Feng J, Fang Y, Cao X, He M, Steiner TJ. Body mass index and migraine: a survey of the Chinese adult population. J Headache Pain 2012;13:531-536.
- 41. Peterlin BL, Rosso AL, Rapoport AM, Scher AI. Obesity and migraine: the effect of age, gender and adipose tissue distribution. Headache 2010;50:52-62.
- 42. Carmona MC, Lefebvre P, Lefebvre B, Galinier A, Bénani A, Jeanson Y, Louche K, Flajollet S, Ktorza A, Dacquet C, Pénicaud L, Casteilla L. Consortium of the French Ministry of Research and Technology: ‘Molecules and New Therapeutic Targets’. Coadministration of coenzyme Q prevents rosiglitazone-induced adipogenesis in ob/ob mice. Int J Obes 2009;33:204-211.
 , Atefeh Sarafan Sadeghi1
, Atefeh Sarafan Sadeghi1 , Naseh Pahlavani2
, Naseh Pahlavani2 , Elyas Nattagh-Eshtivani3
, Elyas Nattagh-Eshtivani3 , Mazyar Hashemilar4
, Mazyar Hashemilar4 , Mohammad Asghari-Jafarabadi5,6
, Mohammad Asghari-Jafarabadi5,6 , Hanieh Barghchi7
, Hanieh Barghchi7 , Ali Tarighat-Esfanjani8
, Ali Tarighat-Esfanjani8