ABSTRACT
Polymorphisms in the melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R) gene with occurrence and progression of chronic diseases such as obesity and cardiovascular disease (CVD) have long been addressed but there is a lack of evidence for complex interrelationships, including direct and indirect effects of these variables. This review specifically focuses on studying the effects of healthy diet interaction and MC4R polymorphisms on the development of CVD. The quantity and quality of carbohydrates and proteins consumed are related to obesity susceptibility and cardiometabolic risk factors. A healthy dietary pattern such as a Mediterranean dietary can modulate the association between MC4R polymorphisms (rs17782313) and the risk of CVDs. Also, the Nordic diet can reduce lipid profiles such as low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and total cholesterol levels. On the other hand, MC4R interaction with the dietary inflammatory index decreases high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and increases LDL-C and triglyceride (TG) levels. Additionally, the DASH diet decreases TG, atherogenic index of plasma, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and serum glucose. The interaction between MC4R genes and diets plays an important role in the development of CVD. Adherence to healthy diets such as the Mediterranean, Nordic, Anti-inflammatory, and Dash diets might be an efficient strategy to prevent CVD. The potential for personalized diets to be developed for the treatment and prevention of CVD and its related comorbidities is expected to expand as this field develops.
-
Keywords: MC4 receptor; Melanocortin-4 receptor; Diet; Dietary pattern; Cardiovascular disease
INTRODUCTION
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a considerable cause of death worldwide. By 2030, CVD incidence is assumed to reach more than 23 million people around the world [
1]. Blood pressure, dyslipidemia, obesity, and type 2 diabetes are CVD risk factors that have been affected by genetic and environmental factors [
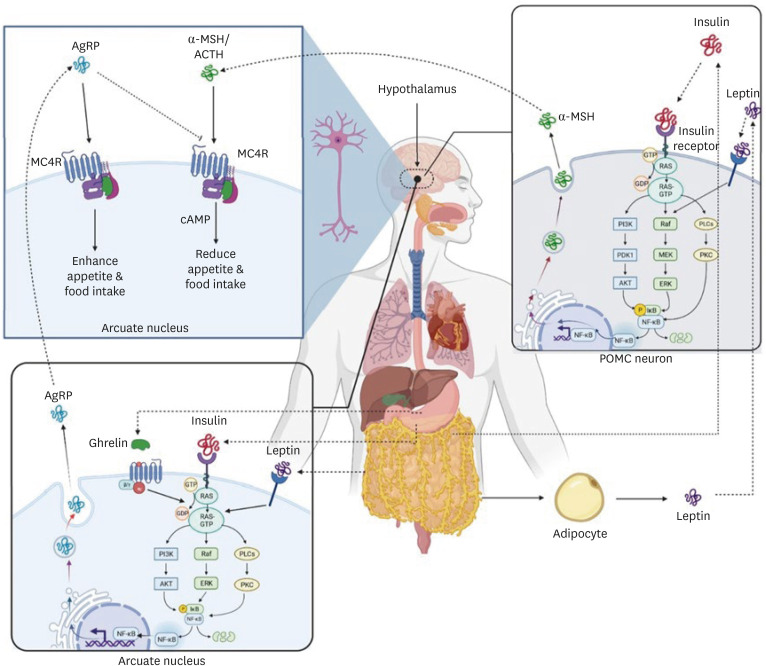
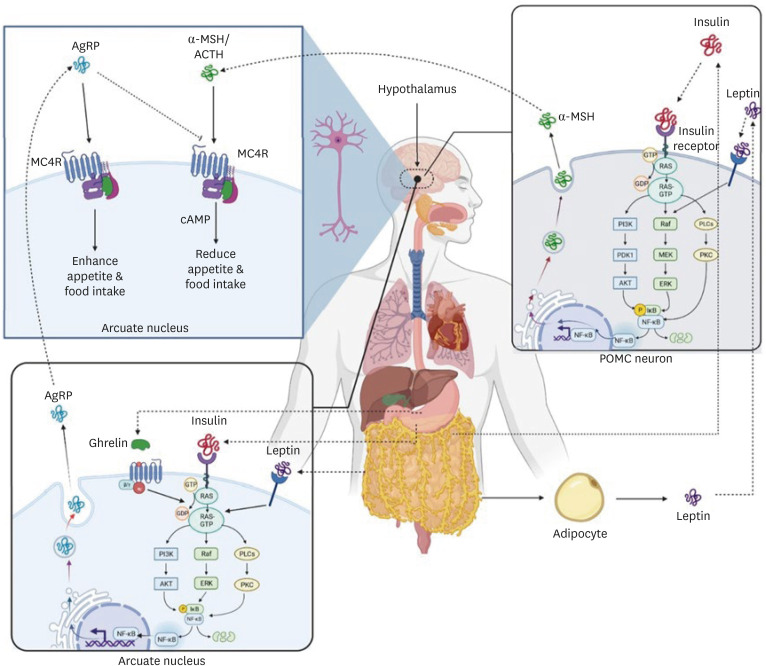
2]. The melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R) is a plasma G protein-coupled receptor that expresses in the hypothalamus and plays an essential function in controlling food intake through the two neuropeptide α-melanocyte stimulating hormone (α-MSH) and agouti-related protein (AgRP) that secreted by two different neuronal cells (
Figure 1) [
3]. These neuropeptides control food consumption and energy intake by stimulation and inhibition of the MC4R. MC4R is stimulated by α-MSH, which decreases appetite and food consumption. In contrast, AgRP inhibits MC4R and increases food intake (
Figure 1). Leptin, insulin, PYY3-36, and ghrelin control appetite by MC4R stimulators and inhibitors. Leptin is a hormone released from lipocytes that suppresses hunger by acting on anorectic pro-opiomelanocortin neurons and stimulating α-MSH in the hypothalamus (
Figure 1). Insulin is another stimulator released from the pancreas (beta cells) and stimulates α-MSH secretion through a pathway similar to leptin. In another way, the PYY that is secreted from the small intestine and colon inhibits AgRP neurons, so satiety is promoted [
4]. In contrast, Ghrelin sends signals to AgRP neurons and stimulates the secretion of AgRP. Ghrelin is secreted during hunger from the stomach and increases appetite [
5]. Therefore, various factors, including hormonal and genetic, can affect the melanocortin receptor and food intake. The MC4R gene is located in chromosome 18q.21.3 with 996 base pairs which express in the hypothalamus and control appetite [
6]. Mutation in the MC4R gene may alter the ligand-binding ability between α-MSH or AgRP and MC4R and influence food intake. The number of identified mutations in the human MC4R gene is more than 130 mutations. Among these mutations, the most common single nucleotide polymorphism is rs17782313, which has the most impact on the melanocortin system. MC4R rs17782313 is associated with increased energy consumption and overeating and also increased CVD risk factors [
7]. The relationship between the MC4R rs17782313 risk allele (minor C allele) and CVD risk factors has been shown in several studies. Therefore, finding effective methods to modulate the MC4R rs17782313 is useful in managing CVD and its risk factors.
Figure 1
α-MSH and AgRP control food consumption and energy intake by stimulation and inhibition of the melanocortin 4 receptor. MC4R is stimulated by α-MSH, which reduces appetite and food intake. In contrast, AgRP inhibits MC4R and increases food intake. Leptin secreted by adipocytes that decreases food intake by acting on anorectic POMC neurons and stimulating α-MSH in the hypothalamus. Insulin secreted by beta cells in the pancreas and stimulates α-MSH secretion through a pathway similar to leptin. In contrast, Ghrelin sends signals to AgRP neurons and stimulates the secretion of AgRP. Ghrelin is released during hunger from the gastrointestinal tract and increases appetite.
AgRP, agouti-related protein; α-MSH, α-melanocyte stimulating hormone; ACTH, adrenocorticotropic hormone MC4R, melanocortin 4 receptor; NF, nuclear factor; POMC, pro-opiomelanocortin.
There is a close relationship between genes and environmental factors that affect CVD. Genome-wide association studies have emphasized the importance of considering gene-environment interactions in discovering new genetic variants. Environmental factors, such as diet, can affect the genetic risk of obesity and CVDs, and gene-diet interactions have been identified in several studies [
8]. Dietary patterns may modulate the association of gene polymorphisms with CVD [
9,
10].
The effect of the MC4R gene-diet interactions on CVD has been concentrated in several studies. However, there has not been a review on the impact of a healthy diet on MC4R single nucleotide polymorphisms. Our aim of this narrative review study is to express and discuss the interactions between MC4R rs17782313 polymorphism and dietary patterns and also, we want to investigate whether these diets can modulate MC4R mutations associated with CVD risk factors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This narrative review aimed to investigate the association between the MC4R rs17782313 polymorphism and dietary patterns on the risk of CVD. The search strategy for this review was entirely internet-based. Scopus, PubMed, WOS, and Google Scholar were searched from February 18 2024 until March 25, 2024 using the combination of the following keywords: Melanocortin 4 Receptor [title/abstract], MC4R [title/abstract], diet*[title/abstract], nutr*[title/abstract] and cardiovascular disease [title/abstract]. To identify additional studies, the reference list of articles has been reviewed manually.
DIETARY PATTERNS INTERACTED WITH MC4R RS117782313
High carbohydrate dietary pattern
There is no exact global definition for a carbohydrate diet and its carbohydrate content. Different studies have expressed different standards. On average, a high-carbohydrate diet contains 55% or more carbohydrates in their diet [
11]. The glycemic index (GI) and glycemic load (GL) are used to measure the contribution of carbohydrate quality and quantity. Low GI and GL diets, induce glucose and insulin to release slowly after intake, reduce intake, prolonged satiety stimulation, reduce lipogenesis, and also decrease fat storage by high fat oxidation [
12]. It limits the basal metabolic rate (BMR) reduction in the body when you are fast. Therefore, it may increase obesity risks. In contrast, diets with a high GL or GI induce a rapid rise in blood glucose because of quick digestion and absorption. It also causes fluctuations in glucose and insulin, leading to the early return of hunger and calorie intake is excessive.
Khodarahmi et al. [
13] in a cross-sectional study of 147 men and 140 women showed that higher dietary GI and GL consumption was significantly related to lower high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) (p = 0.029) and higher low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) (p = 0.042) levels (
Table 1). Alizadeh et al. [
14] in another cross-sectional study of 282 women with MC4R rs17782313, reported that high intake of carbohydrates significantly increased waist circumference)WC(and body mass index (BMI) among C allele carriers. Lower HDL-C and higher LDL-C are associated with increased risk of CVD [
15]. Inadequate levels of HDL-C cause plaques forming in the blood. They may block arteries flowing to the heart and cause heart attack [
16]. In contrast, high LDL-C levels increase plaque forming by transporting cholesterol to the arteries [
17]. Moreover, increased carbohydrate intake reduces BMR due to the interaction of MC4R polymorphism [
14]. Decreased BMR leads to obesity and its comorbidities including CVD [
18]. This obesity-susceptibility gene may influence obesity and its related cardiovascular risk factors through the quality and quantity of ingested carbohydrates, suggesting that these factors should be targeted in the treatment of obesity and other chronic diseases [
13]. WC is a good indicator of fat accumulation around the middle of the body. This index is related to high blood pressure and high blood fat levels. These are risk factors for developing CVD [
19]. Therefore, a diet with a high intake of carbohydrates may be related to a higher risk of CVD in individuals by modulating MC4R rs17782313 polymorphism.
Table 1A review of studies that examined the effect of interaction between MC4R rs17782313 and diets.
Table 1
|
Authors |
Article title |
Type of study |
Genetic polymorphism type |
Population, gender, disease |
Age, body mass index |
Association |
Main outcome |
|
Khodarahmi et al. [13] (2022) |
The Role of Dietary Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load in Mediating Genetic Susceptibility via MC4R s17782313 Genotypes to Affect Cardiometabolic Risk Factors among Apparently Healthy Obese Individuals |
Cross-sectional |
rs17782313 (CC) |
287 males and females, healthy |
20–50 ≥ 30 kg/m2
|
Negative |
↓Basal metabolic rate and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
|
↑Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
|
Alizadeh et al. [14] (2022) |
Interaction of MC4R rs17782313 Variants and Dietary Carbohydrate Quantity and Quality on Basal Metabolic Rate and General and Central Obesity in Overweight/Obese Women: A Cross-Sectional Study |
Cross-sectional |
rs17782313 (CC & TC) |
282 females, healthy |
18–56 ≥ 25 kg/m2
|
Negative |
↑Waist circumference and body mass index |
|
Adamska-Patruno et al. [15] (2021) |
An Association Between Diet and MC4R Genetic Polymorphism, in Relation to Obesity and Metabolic Parameters-A Cross Sectional Population-Based Study |
Cross-sectional |
rs17782313 (CC) |
1,549, males and females, type 2 diabetes |
18–79 > 25 kg/m2
|
Negative |
↓Subcutaneous fat content (SAT) |
|
↑Body mass index, body fat content, visceral fat content (VAT), and VAT/SAT ratios |
|
Mohammadi et al. [16] (2020) |
The Interaction Between Dietary Non-Enzymatic Antioxidant Capacity (NEAC) With Variants of Melanocortin-4 Receptor (MC4R) 18q21.23-rs17782313 Locus on Hypothalamic Hormones and Cardio-Metabolic Risk Factors in Obese Individuals From Iran |
Cross-sectional |
rs17782313 (CC) |
287 males and females, healthy |
20–50 ≥ 30 kg/m2
|
Positive & negative |
↓High-density lipoprotein cholesterol, quantitative insulin sensitivity check index, insulin, serum glucose, α-melanocyte stimulating hormone, and triglyceride |
|
ElhamKia et al. [17] (2022) |
The Interaction Between Dietary Total Antioxidant Capacity and MC4R Gene and HOMA-IR in Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Overweight and Obese Women |
Cross-sectional |
rs17782313 (CC & TC) |
237 females, healthy |
18–50, 25–40 kg/m2
|
Not significant |
No significant associations were found with lipid profile and metabolic parameters. |
|
Khodarahmi et al. [18] (2020) |
Dietary Quality Indices Modifies the Effects of Melanocortin-4 Receptor (MC4R) rs17782313 Polymorphism on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors and Hypothalamic Hormones in Obese Adults |
Cross-sectional |
rs17782313 (CC & TC) |
188 males and females, healthy |
20–50 ≥ 30 kg/m2
|
Positive |
↓Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and serum glucose levels |
|
Zarei et al. [19] (2022) |
The Interaction Between Alternative Healthy Eating Index and MC4R rs17782313 Gene Variants on Central and General Obesity Indices in Women: A Cross‐Sectional Study |
Cross-sectional |
rs17782313 (CC) |
291 females, healthy |
18–48 ≥ 25 kg/m2
|
Positive |
↓Visceral fat area, fat mass, body mass index, and hip circumference |
|
Khodarahmi et al. [20] (2020) |
Melanocortin-4 Receptor (MC4R) rs17782313 Polymorphism Interacts With Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension (DASH) and Mediterranean Dietary Score (MDS) to Affect Hypothalamic Hormones and Cardio-Metabolic risk Factors Among Obese Individuals |
Cross-sectional |
rs17782313 (CC) |
288 males and females, healthy |
20–50 ≥ 30 kg/m2
|
Positive |
↓Systolic blood pressure, atherogenic index of plasma, serum glucose, and triglyceride levels |
|
Ortega-Azorín et al. [21] (2012) |
Associations of the FTO rs9939609 and the MC4R rs17782313 Polymorphisms With Type 2 Diabetes Are Modulated by Diet, Being Higher When Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Pattern Is Low |
Case-control |
rs17782313 (CC) |
7,052, male and female mean BMI 29.9 kg/m2
|
Mean age 70, type 2 diabetes |
Positive |
The MC4R rs17782313 interacted with the Mediterranean diet in its relation to type 2 diabetes. |
|
Koochakpoor et al. [22] (2016) |
Effect of Interactions of Polymorphisms in the Melanocortin‐4 Receptor Gene With Dietary Factors on the Risk of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes |
Systematic review |
rs17782313 (CC) |
Not clear, male and female |
Not clear, type 2 diabetes |
Positive |
Mediterranean diet interacted with MC4R rs17782313 on the risk of type 2 diabetes. |
|
Rasaei et al. [23] (2023) |
Investigation the Interaction of Dietary Fat Quality Indices and the MC4R Gene in Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Overweight and Obese Women |
Cross-sectional |
rs17782313 (CC) |
279 females, healthy |
18–68, 25–40 kg/m2
|
Negative |
↑Homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance index |
|
Aoun et al. [24] (2022) |
The Interaction Between Genetic Polymorphisms in FTO, MC4R and MTHFR Genes and Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in Relation to Obesity |
Cross-sectional |
rs17782313 (CC & TC) |
392 males and females, healthy |
Not clear |
No significant |
No significant association with waist circumference, waist-hip ratio, and body mass index |
|
Mohammadi et al. [25] (2020) |
Dietary Patterns Interact With the Variations of 18q21. 23 rs17782313 Locus on the Regulation of Hypothalamic-Pituitary Axis Hormones and Cardio-Metabolic Risk Factors in Obesity |
Cross-sectional |
rs17782313 (CC) |
288 males and females, healthy |
20–50 ≥ 30 kg/m2
|
Negative |
↑Systolic blood pressure and agouti-related protein levels |
|
Hosseininasab et al. [9] (2022) |
Are There Any Interactions Between Modified Nordic-Style Diet Score and MC4R Polymorphism on Cardiovascular Risk Factors Among Overweight and Obese Women? |
Cross-sectional |
rs17782313 (CC & TC) |
282 females, healthy |
18–48 ≥ 25 kg/m2
|
Positive |
↓Visceral fat level, total cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels |
|
Yarizadeh et al. [10] (2021) |
The Interaction Between the Dietary Inflammatory Index and MC4R Gene Variants on Cardiovascular Risk Factors |
Cross-sectional |
rs17782313 (CC) |
266 females, healthy |
18–56, 25–45 kg/m2
|
Positive |
↑Higher high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels |
|
↓Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglyceride levels |
|
Yarizadeh et al. [26] (2020) |
The Interaction Between Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension and MC4R Gene Variant in Predicting Cardiovascular Risk Factors |
Cross-sectional |
rs17782313 (CC) |
266 females, healthy |
18–50, 25–40 kg/m2
|
Positive |
↓Systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure |
High protein dietary pattern
Proteins are a favorable source of energy and amino acids that constitute a part of our daily energy intake [
20]. A normal protein diet includes 10%–15% of total daily energy intake. However, a high protein diet (HPD) contains more than 18%. Even some high-protein diets provide 47% of daily energy intake from protein [
20]. The proteins of the diet are produced from both animal and plant sources. Animal sources of proteins include dairy, eggs, meat, and fish, and also, plant sources include soya products, grains, legumes, seeds, and nuts [
21]. Some types of HPDs may be adhered to by people around the world such as low carbohydrate high protein ketogenic diet [
22], Zone diet [
23], etc.
Some studies investigated gene-protein interactions. In a cross-sectional study with 1,549 subjects, the association between dietary protein consumption and MC4R rs17782313 was assessed. For participants with CC genotypes who had higher protein consumption (more than 18% of daily energy intake), subcutaneous fat content (SAT) (P < 0.001) was lower. On the other hand, they had higher BMI (p = 0.03), body fat content (p = 0.001), visceral fat content (VAT) (p < 0.001), and VAT/SAT ratios (p < 0.001) [
24]. Studies have shown that BMI, body fat content, and VAT lead to cardiovascular events [
25,
26]. VAT may cause insulin resistance and metabolic disturbances that increase the risk of type 2 diabetes and CVD [
27]. Also, higher VAT/SAT ratios are associated with the risk factors of CVD, independently [
28]. Therefore, high protein consumption may increase the risk of CVD in CC genotype carriers of MC4R rs17782313 polymorphism.
The dietary non-enzymatic antioxidant capacity (NEAC) includes the intake of special foods classified as nuts, legumes, vegetables, fruits, tea, and olive oil. These ingredients are full of antioxidants in this dietary pattern. High intake of foods that are rich in antioxidants including seafood, vegetables, nuts, fruits, and olive oil are significantly correlated with high HDL-C and low LDL-C. Dietary total antioxidant capacity (DTAC) is another index to estimate the cumulative effect of antioxidants and provide information about the synergistic effect between different antioxidants in the diet [
28]. Some studies conducted that a diet with high consumption of antioxidants can modulate carbohydrate and lipid metabolism due to the regulation of appetite, high thermogenesis, and reduction of insulin resistance [
29].
Mohammadi et al. [
16] in their cross-sectional study evaluated the association between MC4R rs17782313 and dietary NEAC. There was a significant relationship between HDL-C (p = 0.03), quantitative insulin sensitivity check index (QUICKI) (p = 0.04), insulin (p = 0.04), serum glucose (p = 0.01), α-MSH (p = 0.04), and TG. More adherence to dietary NEAC is related to decreased HDL-C levels. It is a harmful result because inadequate HDL-C levels increase the risk of heart attack as explained earlier [
16]. On the other hand, more adherence to NEAC, decreased QUICKI, insulin, serum glucose, α- MSH, and TG. Insulin resistance and higher insulin levels in the blood cause endothelial dysfunction and lead to cardiovascular events including coronary heart disease and atherosclerosis. Also, High glucose levels in serum after some time, damage blood vessels and increase the risk of cardiovascular events [
30]. Increased fat tissue and hyperleptinemia cause hypothalamus resistance to α-MSH in obese individuals. Therefore, α-MSH levels increase in blood circulation and can lead to metabolic disorders and obesity. High TG levels increase the risk of CVD and mortality caused by cardiovascular events. TG and its metabolites increase the formation of foam cells and promote atherosclerosis. Furthermore, ElhamKia et al. [
17] in their cross-sectional study of 237 women with BMI ≥ 25 reported that the HOMA-IR (homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance) index, LDL-C, and TG were inversely related to DTAC values but not significant [
31].
Dietary indices are appropriate tools that indicate the association between healthy lifestyle patterns and show overall diet quality [
32]. One of the indicators for assessing the quality of diet is Diet Quality Index-International (DQI-I). This index is used in countries that experience different stages of nutrition transition. Another diet quality index is the Healthy Eating Index (HEI) which the United States Department of Agriculture constructed it to assess the quality of diet [
33]. In both indexes, high scores show high nutrient-dense food consumption and also, lower micronutrient inadequacy intake [
34]. Alternative Healthy Eating Index (AHEI) is known as a reliable predictor of health and staving off chronic diseases and inflammation by emphasizing plant-based protein, healthy oils, whole grains, and limiting processed meats [
35].
In a cross-sectional study of 92 female and 96 male participants who were healthy and obese, Khodarahmi et al. [
18] constructed HEI and DQI-I by taking a validated food frequency questionnaire (FFQ). They showed that there was a significant gene-diet correlation between HEI and MC4R rs17782313 (p < 0.05) in modulating LDL-C levels through a female group. They also found that low adherence to HEI in participants with heterozygotes allele of MC4R rs17782313 caused an increased level of LDL-C. Moreover, in males, there was a significant correlation between HEI, DQI-I, and rs17782313 on SBP, DBP, and serum glucose levels (p < 0.05). They showed that low adherence to HEI and DQI-I had a significant association with increased SBP, DBP, and serum glucose levels. Analyzing 291 overweight and obese women with MC4R rs17782313, Zarei et al. [
19] reported that there was a significant relationship between higher AHEI and lower visceral fat area, fat mass, BMI, and hip circumference. Elevated SBP and DBP independently increase the risk of adverse cardiovascular events such as coronary heart disease and also, a higher risk of mortality. However, high serum glucose levels over time, damage blood vessels and increase the risk of heart failure, heart attack, and stroke [
35]. So, the interaction between MC4R rs17782313 and dietary quality indices decreases the risk of CVD.
The Mediterranean diet (MD) is a well-known healthy eating pattern worldwide. MD is a plant-based diet rich in vegetables, fruits, nuts, legumes, extra-virgin olive oil, whole grains, dairy products, and fish. It is rich in a variety of nutrients including vitamin E, ascorbic acid, beta carotene, fiber, polyphenols, and minerals which protect the cardiovascular system by reducing blood cholesterol due to the lack of saturated lipids [
36]. More adherence to MD increases total antioxidant capacity levels which have a beneficial role in CVD. MD also improves the quality of life [
37].
In a cross-sectional study of 288 healthy obese adults (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m
2), the MD score was assessed by a 147-item FFQ, and interaction between MD and MC4R rs17782313 was evaluated. Lower adherence to MD was related to high levels of α-MSH in the male group with the CT genotype [
20]. It increased fat tissue and hyperleptinemia cause hypothalamus resistance to α-MSH. So, α-MSH increases in the blood circulation of obese people. Several studies have investigated the interaction between the MD and MC4R rs17782313 on cardiovascular risk factors. A well-known risk factor for CVD is type 2 diabetes mellitus which increases mortality and morbidity of CVD [
38]. Ortega-Azorin et al. [
21] in their case-control study on 7,052 subjects with a high risk of CVD (the number of type 2 diabetes cases is 3,430 and non-diabetic cases is 3,622), found that lower adherence to MD increased the risk of type 2 diabetes in carriers of MC4R rs17782313. MD components (vegetables, fiber, fruits, and olive oil) appear to reduce insulin resistance [
39,
40]. Also, a systematic review concluded that adherence to MD interacts with MC4R rs17782313 and decreases the risk of type 2 diabetes [
22]. Furthermore, high dietary fat quality in MD is an important parameter that prevents CVD. On the other hand, MD is rich in omega-3 fatty acids [
41]. Analyzing 279 overweight and obese women, Rasaei et al. [
23] reported that dietary fat quality is associated with insulin resistance. A higher omega-6/omega-3 ratio increases the HOMA-IR index (p = 0.009) among participants with CC genotype. This study had an opposite effect with MD, and this diet can reverse this process towards improving insulin resistance. Insulin resistance with the production of abnormal cytokines plays an essential role in cardiac fibrosis, hypertrophy, and dysfunction in diabetic cardiomyopathy patients. Another study assessed the diet quality of 288 obese adults and found that the opposite diet to MD, including mayonnaise, pizza, snacks, high-fat dairy products, red or processed meat, sweets and desserts, and sweet beverages interacts with MC4R rs17782313. This study concluded that this dietary pattern increased SBP (p = 0.04) and AgRP (p = 0.03) levels by interacting with MC4R rs17782313 [
42]. Therefore, the MD can decrease the risk of CVD by modulating the rs17782313 variant of MC4R, but more studies are needed to understand its mechanism. In contrast, Aoun et al. [
24] found no significant association between MD and MC4R rs17782313 on WC, waist-hip ratio, and BMI. There were some limitations in anthropometric measurements, which may have affected the results of this study.
The ND is a health-promoting diet consumed in Nordic countries and includes fish, lean meat, low-fat dairy products, vegetables, fruits, and whole grains. ND is similar to the Mediterranean diet but differs in the consumption of canola oil instead of olive oil. Consuming n-6, n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and polyphenols in ND modulates inflammatory-related genes in metabolically active tissues.
Having a healthy plant-based diet like ND can reduce the risk of obesity and CVD in people with genetic risk factors. Hosseininasab et al. [
9] in their cross-sectional study on 282 women, calculated a modified Nordic-style diet score (MND) by an FFQ containing 147 food items. This study indicated a significant interaction between MND score and MC4R rs17782313 with the C allele on cardiovascular risk factors. There was negative interaction between rs17782313 genotypes and moderate MND score on LDL-C (p = 0.01) and total cholesterol levels (p = 0.01) in the crude and adjusted model. Also, in the high MND score group, VAT (p = 0.03) was decreased significantly. The mechanism of this gene-diet interaction is still unclear, and more studies are needed, but according to previous studies, the ND significantly reduced LDL-C and total cholesterol levels [
43]. Environmental factors interact with genes. So, the ND can hold beneficial effects on the MC4R gene.
MC4R gene polymorphisms are risk factors for obesity and inflammation. Data have shown a synergistic effect between genes and dietary factors that have an important function in CVD. An anti-inflammatory diet means avoiding pro-inflammatory ingredients like sugary drinks, and processed meat, and consuming anti-inflammatory foods like green leafy vegetables and fruits [
44].
An anti-inflammatory diet plays an essential role in reducing CVD risk factors and related mortality [
10]. A comparative cross-sectional study on 266 overweight or obese women, calculated the dietary inflammatory index (DII) score by an FFQ with 147 items and assessed the interaction between DII and MC4R rs17782313 on the risk of CVD. There was a significant relationship between higher DII scores and lower HDL-C (p < 0.001) levels in the crude model. Also, after adjusting, there was a significant interaction between the higher DII score and MC4R rs17782313 on low HDL-C (p = 0.01) and high TG (p = 0.04) levels. Furthermore, a positive significant interaction between the high DII score and CT genotypes of rs17782313 on total cholesterol levels (p = 0.04) was observed [
10]. MC4R mRNAs up-regulation, along with interleukin-6 in the hypothalamic arcuate, promotes lipid intake and fat collection in white adipose [
45]. Therefore, along with inflammation, dyslipidemia can also occur. Several studies have shown the association between DII score and CVD and its risk factors [
46,
47]. An important risk factor for CVD is inflammation. Therefore, an anti-inflammatory diet may have an essential role in decreasing the risk of CVD.
Dietary approaches to stop hypertension (DASH) is recommended to reduce blood pressure and is considered an important nutritional device. The DASH diet consists of vegetables, fruits, nuts, low-fat dairy products, whole grains, and reduced intake of red meat, processed meats, sodium, and sweets. Also, this healthy diet is rich in fiber, calcium, magnesium, and potassium through consuming fruits and vegetables that have cardio-protector effects.
Studies revealed a significant interaction between adherence to the DASH diet and MC4R rs17782313 polymorphism [
20,
26]. Yarizadeh et al. [
26] in their cross-sectional study assessed the dietary patterns of 266 overweight and obese individuals. They calculated the DASH diet score by a semi-quantitative 147-item FFQ and interaction between the DASH diet and MC4R rs17782313 polymorphism. The results indicated that high adherence to the DASH diet reduced SBP (p = 0.03) and DBP (p = 0.02) in the CC group. Another cross-sectional study on the interaction between the DASH diet and MC4R rs17782313 evaluated this gene-diet interaction on cardiometabolic risk factors. This study which has 288 healthy subjects with obesity, showed a significant association between adherence to the DASH diet and MC4R rs17782313. The DASH diet reduced TG (p = 0.02), serum glucose (p = 0.021), AIP (p = 0.045), and SBP (p = 0.023) levels among females. Also, serum glucose levels were lower in men (p = 0.037) [
20]. AIP is composed of HDL-C and TG. It is a marker for evaluating the risk of CVD. However, for males with the CC genotype, more adherence to the DASH diet was significantly associated with serum glucose (P < 0.05). Further, the lowest adherence to the DASH diet among females with the CC genotype was significantly related to a higher AgRP plasma level (p < 0.05) [
20]. There is not any reported mechanism for this interaction [
20]. Suppression of MC4R due to high AgRP plasma levels leads to increased food intake and higher CVD risk factors. However, it seems that the healthy food groups of the Dash diet may have favorable modulating effects on the rs17782313 genotype. Several studies considered the positive effect of the Dash diet on gene variants [
48]. Despite these studies, it can be concluded that the DASH diet reduces the risk of CVD in risk allele carriers by modulating genes.
CONCLUSION
Gene-environment interaction has an important function in the development of obesity and CVD. Dietary patterns as an environmental factor can modulate MC4R gene polymorphisms. Healthy dietary patterns such as MD, ND, anti-inflammatory diet, and DASH diet have cardioprotective effects by MC4R rs17782313 interaction. Adherence to the MD, ND, anti-inflammatory, and DASH diet may decrease the risk of CVD by affecting the MC4R gene. However, more nutrigenetic, nutrigenomic, and epigenetic studies are required to identify the association between dietary patterns and genes.
NOTES
-
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
-
Author Contributions:
Conceptualization: Mohammadhasani K, Bahari H.
Data curation: Fard MV.
Investigation: Fard MV.
Methodology: Fard MV, Yadegari M.
Project administration: Bahari H, Barati M.
Writing - original draft: Mohammadhasani K, fard MV.
Writing - review & editing: Nattagh-Eshtivani E, Rashidmayvan M.
REFERENCES
- 1. Hariri N, Nasseri E, Houshiar-Rad A, Zayeri F, Bondarianzadeh D. Association between Alternative Healthy Eating Index and 10-year risk of cardiovascular diseases in male-employees in the public sector in Tehran, 1391. Iran J Nutr Sci Food Technol 2013;8:41-50.
- 2. Carbone S, Canada JM, Billingsley HE, Siddiqui MS, Elagizi A, et al. Obesity paradox in cardiovascular disease: where do we stand? Vasc Health Risk Manag 2019;15:89-100.
- 3. Williams KW, Elmquist JK. From neuroanatomy to behavior: central integration of peripheral signals regulating feeding behavior. Nat Neurosci 2012;15:1350-1355.
- 4. Steinert RE, Feinle-Bisset C, Asarian L, Horowitz M, Beglinger C, et al. Ghrelin, CCK, GLP-1, and PYY (3–36): secretory controls and physiological roles in eating and glycemia in health, obesity, and after RYGB. Physiol Rev 2017;97:411-463.
- 5. Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, et al. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999;402:656-660.
- 6. Sharma S, Garfield AS, Shah B, Kleyn P, Ichetovkin I, et al. Current mechanistic and pharmacodynamic understanding of melanocortin-4 receptor activation. Molecules 2019;24:1892.
- 7. Yim KS. Changes of plasma cardiovascular disease risk factors according to the health practice and dietary habits in healthy male university students. Korean J Community Nutr 1998;3:685-694.
- 8. Heianza Y, Qi L. Impact of genes and environment on obesity and cardiovascular disease. Endocrinology 2019;160:81-100.
- 9. Hosseininasab D, Mirzababaei A, Abaj F, Firoozi R, Clark CC, et al. Are there any interactions between modified Nordic-style diet score and MC4R polymorphism on cardiovascular risk factors among overweight and obese women? A cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr Disord 2022;22:221.
- 10. Yarizadeh H, Mirzababaei A, Ghodoosi N, Pooyan S, Djafarian K, et al. The interaction between the dietary inflammatory index and MC4R gene variants on cardiovascular risk factors. Clin Nutr 2021;40:488-495.
- 11. Jung CH, Choi KM. Impact of high-carbohydrate diet on metabolic parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes. Nutrients 2017;9:322.
- 12. Silva KC, Neri Nobre L, Emanuelle de Castro Ferreira Vicente S, Lopes Moreira L, do Carmo Lessa A, et al. Influence of glycemic index and glycemic load of the diet on the risk of overweight and adiposity in childhood. Rev Paul Pediatr 2016;34:293-300.
- 13. Khodarahmi M, Siri G, Mohammadi M, Farhangi MA, Aleseidi S. The role of dietary glycemic index and glycemic load in mediating genetic susceptibility via MC4R s17782313 genotypes to affect cardiometabolic risk factors among apparently healthy obese individuals. BioMed Res Int 2022;2022:3044545.
- 14. Alizadeh S, Pooyan S, Mirzababaei A, Arghavani H, Hasani H, et al. Interaction of MC4R rs17782313 variants and dietary carbohydrate quantity and quality on basal metabolic rate and general and central obesity in overweight/obese women: a cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr Disord 2022;22:121.
- 15. Adamska-Patruno E, Bauer W, Bielska D, Fiedorczuk J, Moroz M, et al. An association between diet and MC4R genetic polymorphism, in relation to obesity and metabolic parameters—a cross sectional population-based study. Int J Mol Sci 2021;22:12044.
- 16. Mohammadi M, Khodarahmi M, Kahroba H, Farhangi MA, Vajdi M. The interaction between dietary non-enzymatic antioxidant capacity (NEAC) with variants of Melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) 18q21.23-rs17782313 locus on hypothalamic hormones and cardio-metabolic risk factors in obese individuals from Iran. Nutr Neurosci 2020;23:824-837.
- 17. ElhamKia M, Setayesh L, Yarizadeh H, Pooyan S, Veisy Z, et al. The interaction between dietary total antioxidant capacity and MC4R gene and HOMA-IR in metabolically healthy and unhealthy overweight and obese women. Nutr Metab Insights 2022;15:11786388221105984.
- 18. Khodarahmi M, Kahroba H, Jafarabadi MA, Mesgari-Abbasi M, Farhangi MA. Dietary quality indices modifies the effects of melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) rs17782313 polymorphism on cardio-metabolic risk factors and hypothalamic hormones in obese adults. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 2020;20:57.
- 19. Zarei M, Shiraseb F, Mirzababaei A, Mirzaei K. The interaction between Alternative Healthy Eating Index and MC4R rs17782313 gene variants on central and general obesity indices in women: A cross-sectional study. J Hum Nutr Diet 2022;35:634-650.
- 20. Khodarahmi M, Jafarabadi MA, Farhangi MA. Melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) rs17782313 polymorphism interacts with dietary approach to stop hypertension (DASH) and Mediterranean dietary score (MDS) to affect hypothalamic hormones and cardio-metabolic risk factors among obese individuals. Genes Nutr 2020;15:13.
- 21. Ortega-Azorín C, Sorlí JV, Asensio EM, Coltell O, Martínez-González MÁ, et al. Associations of the FTO rs9939609 and the MC4R rs17782313 polymorphisms with type 2 diabetes are modulated by diet, being higher when adherence to the Mediterranean diet pattern is low. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2012;11:137.
- 22. Koochakpoor G, Hosseini-Esfahani F, Daneshpour MS, Hosseini SA, Mirmiran P. Effect of interactions of polymorphisms in the Melanocortin-4 receptor gene with dietary factors on the risk of obesity and Type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. Diabet Med 2016;33:1026-1034.
- 23. Rasaei N, Fallah M, Nemati M, Gholami F, Ghaffarian-Ensaf R, et al. Investigation the interaction of dietary fat quality indices and the MC4R gene in metabolically healthy and unhealthy overweight and obese women. Sci Rep 2023;13:12183.
- 24. Aoun C, Hajj A, Hajj F, Papazian T, Rabbaa Khabbaz L. The interaction between genetic polymorphisms in FTO, MC4R and MTHFR genes and adherence to the Mediterranean diet in relation to obesity. Gene 2022;809:146037.
- 25. Mohammadi M, Khodarahmi M, Kahroba H, Farhangi MA. Dietary patterns interact with the variations of 18q21.23 rs17782313 locus on regulation of hypothalamic-pituitary axis hormones and cardio-metabolic risk factors in obesity. Eat Weight Disord 2020;25:1447-1459.
- 26. Yarizadeh H, Bahiraee A, Asadi S, Maddahi NS, Setayesh L, et al. The interaction between dietary approaches to stop hypertension and MC4R gene variant in predicting cardiovascular risk factors. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 2020;1-9.
- 27. Bartlett J, Predazzi IM, Williams SM, Bush WS, Kim Y, et al. Is isolated low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol a cardiovascular disease risk factor? New insights from the Framingham offspring study. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 2016;9:206-212.
- 28. Bortolotti M. Metabolic effects of dietary proteins. Lausanne: Université de Lausanne, Faculté de biologie et médecine; 2010.
- 29. Lonnie M, Hooker E, Brunstrom JM, Corfe BM, Green MA, et al. Protein for life: Review of optimal protein intake, sustainable dietary sources and the effect on appetite in ageing adults. Nutrients 2018;10:360.
- 30. Thomas EL, Fitzpatrick JA, Malik SJ, Taylor-Robinson SD, Bell JD. Whole body fat: content and distribution. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 2013;73:56-80.
- 31. Kaess BM, Pedley A, Massaro JM, Murabito J, Hoffmann U, et al. The ratio of visceral to subcutaneous fat, a metric of body fat distribution, is a unique correlate of cardiometabolic risk. Diabetologia 2012;55:2622-2630.
- 32. Puchau B, Zulet MA, de Echávarri AG, Hermsdorff HH, Martínez JA. Dietary total antioxidant capacity is negatively associated with some metabolic syndrome features in healthy young adults. Nutrition 2010;26:534-541.
- 33. Adan RA, Tiesjema B, Hillebrand JJ, la Fleur SE, Kas MJ, et al. The MC4 receptor and control of appetite. Br J Pharmacol 2006;149:815-827.
- 34. Meydani M, Hasan ST. Dietary polyphenols and obesity. Nutrients 2010;2:737-751.
- 35. Capes SE, Hunt D, Malmberg K, Pathak P, Gerstein HC. Stress hyperglycemia and prognosis of stroke in nondiabetic and diabetic patients: a systematic overview. Stroke 2001;32:2426-2432.
- 36. Kim S, Haines PS, Siega-Riz AM, Popkin BM. The Diet Quality Index-International (DQI-I) provides an effective tool for cross-national comparison of diet quality as illustrated by China and the United States. J Nutr 2003;133:3476-3484.
- 37. Guenther PM, Kirkpatrick SI, Reedy J, Krebs-Smith SM, Buckman DW, et al. The Healthy Eating Index-2010 is a valid and reliable measure of diet quality according to the 2010 Dietary Guidelines for Americans. J Nutr 2014;144:399-407.
- 38. Chiuve SE, Fung TT, Rimm EB, Hu FB, McCullough ML, et al. Alternative dietary indices both strongly predict risk of chronic disease. J Nutr 2012;142:1009-1018.
- 39. George ES, Kucianski T, Mayr HL, Moschonis G, Tierney AC, et al. A Mediterranean diet model in Australia: strategies for translating the traditional Mediterranean diet into a multicultural setting. Nutrients 2018;10:465.
- 40. Panagiotakos DB, Pitsavos C, Polychronopoulos E, Chrysohoou C, Zampelas A, et al. Can a Mediterranean diet moderate the development and clinical progression of coronary heart disease? A systematic review. Med Sci Monit 2004;10:RA193-RA198.
- 41. Bonaccio M, Di Castelnuovo A, Bonanni A, Costanzo S, De Lucia F, et al. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet is associated with a better health-related quality of life: a possible role of high dietary antioxidant content. BMJ Open 2013;3:e003003.
- 42. Eichelmann F, Schwingshackl L, Fedirko V, Aleksandrova K. Effect of plant-based diets on obesity-related inflammatory profiles: a systematic review and meta-analysis of intervention trials. Obes Rev 2016;17:1067-1079.
- 43. Calder PC. n-3 fatty acids, inflammation and immunity: new mechanisms to explain old actions. Proc Nutr Soc 2013;72:326-336.
- 44. Kreutzer C, Peters S, Schulte DM, Fangmann D, Türk K, et al. Hypothalamic inflammation in human obesity is mediated by environmental and genetic factors. Diabetes 2017;66:2407-2415.
- 45. Medzhitov R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 2008;454:428-435.
- 46. Nogueiras R, Wiedmer P, Perez-Tilve D, Veyrat-Durebex C, Keogh JM, et al. The central melanocortin system directly controls peripheral lipid metabolism. J Clin Invest 2007;117:3475-3488.
- 47. Garcia-Arellano A, Ramallal R, Ruiz-Canela M, Salas-Salvadó J, Corella D, et al. Dietary inflammatory index and incidence of cardiovascular disease in the PREDIMED study. Nutrients 2015;7:4124-4138.
- 48. Houston MC, Harper KJ. Potassium, magnesium, and calcium: their role in both the cause and treatment of hypertension. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 2008;10(Suppl 2):3-11.
 , Mohammad Vahedi Fard1,*
, Mohammad Vahedi Fard1,* , Mehran Yadegari1
, Mehran Yadegari1 , Mehdi Barati2
, Mehdi Barati2 , Hossein Bahari3
, Hossein Bahari3 , Elyas Nattagh-Eshtivani1
, Elyas Nattagh-Eshtivani1 , Mohammad Rashidmayvan1
, Mohammad Rashidmayvan1