ABSTRACT
This analytical cross-sectional study examined the nutrient intakes, dietary compliance, dietary supplementation and traditional remedy usage in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients from selected tertiary hospitals in multi-racial Malaysia. We compared the different characteristics of T2DM patients with and without cardiovascular disease (CVD). Socio-demographic status, dietary intakes, dietary supplementation, traditional remedy use, medical history, anthropometric measurements and clinical characteristics were obtained from face-to-face interviews. A total of 313 patients who were treated for T2DM participated in this study, in which 36.1% of them had CVD. The mean age of study subjects was 55.7 ± 9.2 years; mean diabetes duration was 10.1 ± 8.1 years; 52.1% were females; and 47.0% were Malays. The mean total energy intake of the subjects was 1674 ± 694 kcal/day, and patients with CVD consumed higher total calories (p = 0.001). Likewise, the mean carbohydrate, protein and total fat intake of CVD patients were significantly higher than non-CVD patients (p < 0.05), while mean intakes of cholesterol, fibre, minerals and all vitamins were comparable between CVD and non-CVD patients. Regardless of CVD status, a notably high proportion of the subjects did not meet the recommendations of the Medical Nutrition Therapy Guidelines for Type 2 Diabetes for total energy, carbohydrate, protein, total fat, and fibre intakes. Meanwhile, 52.4% used at least one dietary supplement and 12.1% took single traditional remedy or in various combinations. Traditional remedies and supplement intake did not differ between CVD and non-CVD subjects. It is suggested that T2DM patients should be educated based on their personalized dietary intake, dietary supplementation and traditional remedy usage. The recommendations for T2DM patients shall be met to achieve the optimal metabolic goals and minimize the potential diabetic complications.
-
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Type 2 diabetes mellitus; Dietary compliance; Dietary supplementation; Traditional remedies
Introduction
The prevalence of diabetes mellitus (DM) is rapidly increasing worldwide. It is a complex and serious chronic disease associated with potentially preventable complications such as cardiovascular disease (CVD), retinopathy, neuropathy, and nephropathy [
1]. Globally, this chronic disease causes about 5% of all deaths each year. Absence of urgent action will further increase the DM deaths by more than 50% in the next ten years as alarmed by World Health Organization. Similarly in Malaysia, DM is a growing concern with its marked increase in prevalence rate. The prevalence of DM among adults 30 years old and above in Malaysia was elevated for nearly three-fold within 15 years from 8.3% in 1996 to 20.8% in 2011 [
2]. Over 60% of the world's population affected by DM, where most of the incidence was from Asia, the world's most populous region [
1,
3,
4]. It is foreseen that the number of individuals with DM in each Asian country will escalate substantially in coming decades. Malaysia ranked ninth among Asian countries, with high DM estimates (11.6% of comparative prevalence); and this figure is projected to reach 13.8% in year 2030 [
4].
The importance of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in the social and health context is basically due to it being an established risk factor for CVD, especially coronary artery disease (CAD), stroke and peripheral vascular disease (PVD), all of which represent the leading causes of mortality and disability in the industrialised countries and developing nations, contributing to the high public health expenses [
5]. In view of this, the potential vascular complications in diabetic patients should be evaluated early and treated at an early stage. Besides the classical genetic, lifestyle and treatment-related factors may interact with one another, producing a complex combination of side effects which ultimately dictate patients' health condition. Focus has long been directed towards the impact of single dietary components in nutritional epidemiology, such a "reductionist" approach can reveal the pivotal role of individual nutrients in the occurrence of disease including CVD.
Medical nutrition therapy (MNT) is an integral component of diabetes prevention, management, self-management education, and overall healthy lifestyle [
6]. The effectiveness of MNT in the management of DM has been well established and previous reviews have provided comprehensive recommendations for MNT in the management of DM [
7]. In accordance with the recommendations of the MNT Guidelines for Type 2 Diabetes [
8], energy requirement of a diabetic should be sufficient to attain and maintain a reasonable body weight for adult. Protein recommendations would be lower for individuals with evidence of nephropathy [
6]. Besides, the relationship between diet and DM has been focused on macronutrient content, proper micronutrient intake should also be achieved for optimal health. Moreover, vitamin and mineral intake should meet the established requirements for health.
Provided that the diet is adequate, patients with T2DM do not require dietary supplementation. Indeed, routine supplementation with antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, is not advisable due to the lack of evidence of efficacy and concern related to long-term safety [
6,
8]. Moreover, the use of traditional remedies could interact with the prescribed drugs. To date, there is lack of clinical evidences on the dietary supplementation, as well as the use of traditional medicine among T2DM patients of the multi-ethnic groups in Malaysia whose social and cultural backgrounds are different.
Compliance to the dietary prescription is viewed as important in the management of DM. It is also essential to investigate the use of dietary supplements and traditional remedies among T2DM patients in order to warrant a better insight of the current status of diabetics in Malaysia. With this framework, the aims of this study were to assess the nutrient intakes and dietary compliance based on the nutritional recommendations and guidelines for macro- and micronutrients. On top of that, we also studied the trends of using dietary supplementations and traditional remedies among the T2DM patients, with or without CVD for updating knowledge of patients, health care practitioners and researchers. Finally, the present study also determined the correlation between the dietary factors and CVD of the T2DM patients.
Materials and Methods
Sample selection and data collection
An analytical cross-sectional study utilised a systematic random sampling method was conducted in two Malaysian tertiary hospitals. Medical Specialist Clinic and Endocrinology Clinic at Hospital Serdang, a government-funded multi-specialty hospital located in the state of Selangor, Malaysia served as the clinical settings and source of participants for the present study. In addition, subjects were also recruited from Physician Clinic at Hospital Kuala Lumpur (HKL), the largest hospital under Ministry of Health Malaysia as well as one of the largest hospitals in Asia, which is situated in the heart of the capital city of Malaysia - Federal Territory of Kuala Lumpur. Patients with T2DM were evaluated in accordance with inclusion and exclusion criteria justified. T2DM patients who were at least 30 years of age and who were not involved in other studies were invited to participate in the study. The exclusion criteria were history of type 1 diabetes mellitus, gestational diabetes mellitus, haemorrhagic stroke, malignant disease or patients under dietary restrictions. Upon eligibility, informed consent was obtained from each patient. Subjects were interviewed and completed a standardised questionnaire that included sociodemographic backgrounds, aspects of personal medical profile, current dietary intakes, dietary supplementation and use of traditional remedies. The pre-tested questionnaires were available in three languages - English, Malay and Mandarin. All of the structured questionnaires were administered by interviewers for consistency and to clarify the questions as needed. Diagnosis of diseases was based on self-reports, confirmed by hospital medical records and further clinical examinations carried out by our adjudication committee members formed by physicians at the time of the survey. Patients' recent medical records on lipid profiles [total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and triglycerides] and glycaemic control comprised of glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c) and fasting plasma glucose (FPG) within past three months were also accessed.
Ethical approvals
The study protocol conforms to the Ethical Guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approvals to conduct this study were obtained from the Medical Research and Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM) and Ministry of Health Malaysia (Reference # NMRR-10-483-5703).
Anthropometric measurements
Anthropometric measurements including weight and height were taken using standard procedures and body mass index (BMI) was computed to establish the extent of obesity and excessive leanness. The WHO classification of BMI was used to classify the subjects as underweight (BMI < 18.5 kg/m
2); normal range (BMI 18.5 - 24.9 kg/m
2); overweight (BMI 25.0 - 29.9 kg/m
2); and obese (BMI > 30 kg/m
2) [
9].
Subjects' current dietary intakes were assessed using the interactive 24-hour dietary recall method on a face-to-face interviewed basis to avoid introducing measurement error. Study subjects were interviewed for their intakes of past 24-hour foods and beverages. Information obtained includes names of foods (brands name whenever possible), food preparation (ingredients and cooking techniques such as deep-frying, stirfrying, boiling, stewing, grilling, barbecue, roasting, and steaming), amounts of foods eaten, brands of foods, times the foods were consumed, type of meals or snacks, and where the food was consumed (home or eat out). A set of household measurement tools (glasses, cups, Chinese rice bowls, soup bowls, noodle bowls, plates, teaspoons, and tablespoons) was used to help subjects to estimate portions consumed and with the aid of the latest album of food pictures in Malaysia-Atlas of Food Exchanges & Portion Sizes [
10]. The album consists of actual standard portion size photographs of individual foods which were useful in assisting subjects to estimate amounts eaten as fractions or multiples of the illustrated reference portions. Furthermore, measurement visuals including drawings were also used by the subjects to facilitate quantification of the foods and beverages reported.
The foods consumed were recorded and entered into the Nutritionist Pro™ diet analysis software (Version 2.5, Axxya Systems, USA) for energy intake (EI) and nutrient analysis. This software contains several food databases including Nutrient Composition of Malaysian Foods, the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Continuing Survey of Food Intakes by Individuals (CSFII) Standard Reference Database, Canadian Nutrient File, and Mexico Food Database along with other over thousands of international food items (60% brand-name foods; 40% generic foods). For food items not available in Nutritionist Pro diet analysis software, other food databases such as the Food Composition Guide Singapore [
11], China Food Composition 2002 [
12], ASEAN Food Composition Tables [
13] and The Concise New Zealand Food Composition Tables [
14] were sought for total EI and nutrient contents.
For local complex mixed cooked dishes that were not available in any of the food databases, local well-established recipe books were used to identify at least two recipes for each dish. For each dish, it was ensured that the quantitative information on oils, fats, salt and serving size were available. Energy and nutrient content of these dishes were compared on the basis of food databases available and the average of these values was entered into the Nutritionist Pro software. For example, two recipes of curry gravy were obtained and the ingredients were analysed for energy and nutrient values (per 100 gram). The average values of the two recipes were then used as the standard for nutrient content of the curry. For processed and packaged foods, information on energy and nutrient content on their nutrition labels was entered into the software directly for analysis. For all foods consumed by the subjects, steps were taken to ensure that oils, fats and salt were accounted for. The macro- and micro-nutrient intakes reported were based exclusively on the contribution of foods and fluids consumed and did not include contribution from dietary supplements. It is of utmost important to note that data cleaning and quality control checks were carried out in the present study before dietary intake analysis was performed by Nutritionist Pro software. Total energy and nutrient intake were calculated by summing up energy or nutrients from all foods. Subsequently, the total energy and nutrient intake were compared with the nutrition recommendations for individuals with DM based on the Medical Nutrition Therapy Guidelines for Type 2 Diabetes [
8] for dietary adequacy assessment.
As adopted by U.S. Food and Nutrition Board, the term "Adequate Intake" (AI) refers to a recommended average daily nutrient intake level that appears sufficient to maintain a specified criterion based on observed or experimentally derived approximations or estimates of the nutrient intake by a group of people. Following the recommendations of the MNT Guidelines for Type 2 Diabetes [
8], the macronutrient contribution to the total EI should be in the ranges of 50-60% and 20-30% for carbohydrate and fat respectively, and 0.8-1.0 g/kg (T2DM patients < 60 years old) and 1.0-1.25 g/kg (T2DM patients ≥60 years old) for adequate protein intake, depending on individualization based on treatment goals, physiologic parameters, and medication usage [
6,
8].
Under-reporting of energy is a major concern in dietary assessment [
15]. The ratio between reported total EI and basal metabolic rate (BMR) was used to examine the possibility of under-reporting of energy. Basal metabolic rate was calculated using the equation established [
16] due to its relevance to the local context. An EI/BMR ratio below 1.2 was considered as inadequate for the maintenance of body weight to identify low energy reporters [
17].
Dietary supplement and traditional remedy intake
A dietary supplement was defined as a product intended to supplement the diet that contains one or more of the following dietary ingredients: a vitamin, a mineral, an herb or other botanical, an amino acid or a dietary substance for use by one to supplement the diet by increasing the total daily intake, or a concentrate, metabolite, constituent, extract, or a combination of the above ingredients. A series of questions about current intakes (past one month) of multivitamin and individual vitamin supplements, as well as other nutritional supplement and traditional remedy use was administered. Subjects who affirmed supplement and traditional herbs use were asked to provide information regarding type, frequency, dose and duration of use, and reasons for use, the brand name, and show the vitamin-mineral supplement and herb containers to the interviewer so that supplement and herb details could be recorded. If the container was not available, they were asked for the exact details of the product or to provide information with as much specificity as possible.
Statistical analyses
All statistical analyses were performed by using IBM SPSS statistics (Version 21.0, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Descriptive data were presented as frequencies and percentages for categorical variables, and as mean±standard deviation (SD) for continuous variables. Variables were compared between subjects with and without CVD, in which the association or difference between significant socio-demographics, clinical variables, dietary intake and dietary adequacy, dietary supplementations, traditional remedies, and the prevalence of CVD were explored by chi-square test and independent t-test. Statistical significance level was set at p < 0.05.
Results
Patient characteristics
Response rate was 100% where all the T2DM patients approached agreed and cooperated in the interviews, and complete data were obtained. A total of 313 patients with T2DM composed of 47.0% Malays, 25.6% Chinese and 27.5% Indians who fulfilled the eligibility criteria participated in the present research upon written informed consent. The prevalence of CVD among the subjects was 36.1%, with one or more cardiovascular events ever been experienced. The prevalence of CAD, cerebrovascular disease and PVD was 30.7%, 10.2% and 5.1%, respectively. Neuropathy (41.5%) was found to be the main microvascular complication among the subjects, followed by nephropathy (17.6%) and retinopathy (15.0%). Among all of the subjects, 60.7% of them reported using oral hypoglycemic agents alone, 31.3% on combination therapy of oral agents and insulin, and 8.0% on insulin monotherapy. This study also found the poor lipid profiles and glycaemic control status among the subjects (
Table 1).
Table 1 demonstrates the socio-demographic characteristics of the study subjects. Overall, the mean age of the subjects at the time of enrolment was 55.7 ± 9.2 years old with the range of duration being from 30 to 78 years, and majority of them fell in the groups of middle age and elderly (50-69.9 years). The average duration of T2DM of subjects was approximately 10 years, and the subjects with CVD were tended to have longer duration of T2DM (p = 0.021). The proportion of male and female was 47.9% and 52.1%, respectively. There was a significant difference between men and women in the prevalence of CVD, with the disease affected more men than women (p = 0.005). In terms of ethnicity, approximately half of the subjects were Malays, followed by Indians and Chinese. This statistically significant racial distribution reflected the country's racial distribution with Malays being the largest group in Malaysia. Majority of the subjects were married, had retired from work, of low educational status, and had completed non-tertiary education, respectively.
Anthropometric measurements
The mean BMI of the subjects was 29.0 ± 5.0 kg/m
2, and the mean BMI of the CVD patients (28.5 ± 4.2 kg/m
2) being lower than the non-CVD patients (29.2 ± 5.4 kg/m
2). With regards to BMI classifications, a total of 43.3% of them were overweight and 35.9% were obese. It is an alarming finding that only one-fifth (20.5%) of our subjects fell within the normal weight range (
Table 1).
The mean energy and nutrient intakes of the subjects are explicitly presented in
Table 2. On the whole, the mean total EI of the subjects was 1674 ± 694 kcal per day, and the subjects with CVD were known to consume higher calories (p = 0.001) than the non-CVD subjects. Likewise, the mean carbohydrate (p = 0.003), protein (p = 0.020) and fat intake (p = 0.006) of the T2DM patients with CVD were significantly higher than the non-CVD counterparts. The mean intakes of cholesterol, fibre, minerals and all vitamins were comparable between CVD and non-CVD groups. Distinct differences in the EI were seen among all patients with and without CVD, in which the intake of energy by CVD patients was found to be higher than the non-CVD group by about 264 kcal. The mean carbohydrate intake of the patients was approximately 230.2 g, which contributed to 55.6% of the total EI. T2DM patients with CVD had a significant higher mean carbohydrate intake than the non-CVD counterparts (p = 0.003). The mean protein intake of subjects was 65.8 g (15.7% of total EI), and the CVD patients had higher protein intake than the non-CVD patients (p = 0.02). Mean fat intake was estimated to be about 54.3 g (28.6% of total EI) for the entire studied population while a 9.8 g difference was noted between CVD and non-CVD patients.
The adequacy of energy and nutrient intakes of subjects were tabulated in
Table 3. The results showed that 14.7% and 18.2% of the subjects aged < 60 and ≥ 60 years old, respectively, were found to achieve the energy requirements. The majority of the subjects had inadequate EI (65.3% for subjects < 60 years old and 40.5% for subjects ≥ 60 years old). On the contrary, 20.0% of the subjects < 60 years old and 41.3% of the subjects ≥ 60 years old had excess EI. Similarly, protein intakes of the subjects for all age groups were mostly inadequate. Only 20.1% (< 60 years old) and 13.4% (≥ 60 years old) of the subjects achieved the recommended protein intake, whilst 31.4% and 20.6% of the subjects had exceed the acceptable range of protein intakes. The percentage of calories from proteins was not different among the CVD and non-CVD patients. The patients with and without CVD of all age groups had achieved similar carbohydrate intake.
Meanwhile, the results indicate that only 28.5% subjects met the recommendation for total fat intake; as much as 40.1% of subjects exceeded the suggested range of 20-30% total EI for fat intake. This unsatisfactory trend equally appeared in both CVD (39.3%) and non-CVD groups of study subjects (40.5%). According to the Malaysian Dietitians' Association, patients with T2DM are advised to consume less than 300 mg/d (for those with LDL-C < 2.6 mmol/L) and 200 mg/d (with LDL-C ≥ 2.6 mmol/L) of dietary cholesterol, respectively. The intakes of dietary cholesterol among the subjects were being apparently satisfactory, i.e. 84.8% (LDL-C < 2.6 mmol/L) and 74.1% (LDL-C ≥ 2.6 mmol/L) of them achieved the recommendations, while only 15.2% and 25.9% exceeded the optimal recommended levels, respectively. The desired level of fibre intake based on the MNT Guidelines for Type 2 Diabetes is 20-30 g/d. However, the fibre intake of majority of the subjects (89.4%) was below the recommended levels, and only ~10% of the subjects achieved the recommended level of fibre intake.
Dietary supplement and traditional remedy intakes
Table 4 details the use of dietary supplements and traditional remedies among the T2DM patients with and without CVD. The results showed that 52.4% of subjects used dietary supplements (either herbal or non-herbal), and 12.1% of them took single traditional remedy or in various combinations. Of the dietary supplements, vitamins were the most frequently taken (39.0%), in which 20.4%, 6.7%, 10.2%, 4.5%, 3.8% and 4.5% of the subjects consumed vitamin B
1, B
6, B
12, vitamin B complex, multivitamin, vitamin C, folic acid and other vitamins, respectively. This was followed by trace elements, whereby almost 10.9% of them took supplementation of minerals (i.e. calcium, iron and magnesium) and calcium (7.7%) was the most popular. Other than that, 16.6% of the subjects consumed various natural products, such as herbal supplements, evening primrose oil, gingko biloba, bamboo salt, shake, fish oil, cod liver oil, flax seed oil, grape seed oil, plant extracts (e.g. cranberry and blueberry extracts), bee pollen, apple cider, chlorophyl, spirulina, and pearl powder. The other 7.0% of the subjects have taken coenzyme Q
10, glucosamine, chondroitin, protein, fibre, alpha-lipid, lecithin, beta-carotene, transfer factor, glutathione accelerator, and stem cell enhancer. However, the intakes of traditional remedies and dietary supplements were not significantly different between the CVD and non-CVD subjects.
Discussion
The present study focused on total EI, macronutrients, as well as certain micronutrients, that are closely related to cardiovascular health in diabetics. Controlling body weight in reducing risks related to DM is of great importance. To this respect, nutrition recommendations usually start by considering energy balance and weight loss strategies [
6,
18]. The distribution of calories for the macronutrients among subjects was inconsistent with the recommendations of the Malaysian Dietitians' Association for a healthy diet for T2DM [
8]. Majority of the studied subjects failed to achieve the recommendation for total EI, with high percentage of subjects reported intake less than requirement, yet most of them were either overweight or obese. A comparison with an earlier local study by Moy and Abdul Rahman revealed the similar trend where the mean EI of the study achieved only about 72% of the recommended daily allowance (RDA) [
19]. The discrepancy between the inadequate EI and obesity status among the subjects could be due to the limitations of the 24-hour dietary recall method of dietary intake assessment, such as underestimation either from the participants or the interviewer; subjects did not give a true picture of their daily intake or social desirability response bias; and daily variation of subjects' diet. It is also likely that the subjects are on strict diet control, amounted to altered portions and type of foods consumed. As most subjects in this study are overweight and obese, total caloric intake must be appropriate to weight management goal, particularly among the CVD patients with higher total EI noticed.
Based on the BMR calculated, as a result, a high degree of under-reporting was found (65.0%). Low energy reporters, however, were not excluded from the present analysis as exclusion would have biased the data towards higher intakes [
20]. Rather, the aim of the study was to present the overall energy and nutrient intakes of all samples obtained. Indeed, actual EI and hence nutrient intakes are likely to be under-estimated as pointed out by a past study [
20]. Deliberate fabrication, failure to remember food items or whole eating events, lack of knowledge of the composition of mixed dishes and inability to estimate portion size accurately have all been considered as potential contributors to the under-reporting problem. In some cases, age, sex and BMI, as well as other demographic and psychological factors, such as embarrassment may also be the factors associated with low-energy reporting.
Carbohydrate intake for the recruited subjects accounted for 55.6% of daily energy intake in kilocalories. When compared with the recommendation by MNT Guidelines for Type 2 Diabetes, the recommended level of carbohydrate intake was fairly achieved (40.7%), whereas 27.6% were inadequate and 31.7% exceeded the recommendation for carbohydrate intake. The results were in agreement with the findings reported by Mirnalini and her co-researchers [
20] that patients with T2DM tend to have a lower carbohydrate intake than that of the general population. This trend is not unusual because patients were battling with hyperglycaemia, and the low-carbohydrate options that are readily available from the food supply offer an approach to glucose management. Of the three macronutrients (carbohydrate, protein and fat), carbohydrate intake may have the greatest influence on blood glucose, although the overall balance of micro- and macronutrients has implications for diabetic complications. This is because carbohydrate is the major insulin secretagogue, it is thus believed that providing a consistent carbohydrate intake spaced throughout the day helps diabetics maintain appropriate blood glucose levels and maximizes the effectiveness of drug therapy.
Most of the subjects did not meet the requirements for proteins. Majority of protein intakes were below the recommended levels across all age groups. DM greatly increases the chances of suffering from complications such as kidney disease, on top of other microvascular complications and CVD. In spite of the fact that low protein diets are still questionable in halting the progression of diabetic nephropathy, it was evident that protein restriction slows down the chronic kidney disease (CKD) [
21], as can be reviewed that restriction of protein positively affect urine albumin excretion and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in patients with incipient or manifest nephropathy [
22]. Therefore, the subjects with diabetic nephropathy have been recommended to be on low protein diets, and individuals with DM are also generally often advised to limit protein intake to protect their renal functions although there is conconsiderably insufficient clinical evidence and has created some doubt about the practical effectiveness of protein restriction in diabetic nephropathy prevention [
21,
23]. These have possibly resulting in the phenomenon that the protein intakes of the subjects in this study were mostly inadequate. Despite the speculation that excessive protein intake may be linked with the development of diabetic nephropathy, the current evidence suggests this is not a risk at intakes recommended by MNT Guidelines for Type 2 Diabetes [
8].
In our sample, it is alarming to note that carbohydrate intake has been replaced with fat, and has also resulted in a low protein diet, as indicated by the majority patients fallen into the excessive total fat recommended range. Nearly half of the subjects had an estimated total fat intake of more than the recommendation. Only 28.5% of the subjects met the recommendations for total fat. It implies that their lower intake of carbohydrate and protein foods indirectly increased foods with higher fat content. The high fat intake among subjects may also reflected by the prominent high fat contents of multicultural Malaysian cuisines as indicated by Malaysia food composition database [
24]. A diet high in dietary fat may increase calories, thereby increasing the risk of weight gain, insulin resistance, and worsening glucose control [
25]. These may explain the significant association of dietary total fat with higher CVD prevalence in this research. Additionally, high-fat diets increase postprandial lipemia and chylomicron remnants, both of which are associated with increased risk of CAD [
26]. Interestingly, it is pleased to see from the present findings that the average dietary cholesterol intake by a very high proportion of subjects was below the recommended levels. In fact, individuals do not need to consume sources of dietary cholesterol because the body makes more than enough for physiological and structural functions [
27], as such, cholesterol intake in the diet often targeted to be restricted [
8].
The American Diabetes Association, the American Dietetic Association and the Malaysian Dietitians' Association advocate that type 2 diabetics should consume adequate amounts of fibre from a variety of plant foods [
6,
8,
28]. Although there is no significant difference seen between CVD and fibre intake of the subjects studied, it has long been known that cardiovascular events are linked with fibre intakes as evident by abundant published investigations [
29,
30,
31,
32,
33]. It appeared through a variety of mechanisms, such as improving blood lipid profiles [
34,
35], lowering blood pressure [
35,
36,
37], and improving insulin sensitivity [
35,
38,
39] and fibrinolytic activity [
40]. These findings prompted worries to the subjects in the present study because the fibre intake of majority of them (89.4%) was below the recommended levels, and only about 10% of the remaining subjects achieved the recommended fibre intake. This may explain the insignificant difference of fibre intakes between CVD and non-CVD groups of subjects, as nearly all of the subjects had inadequate fibre intake. What is of great concern is that a diet adequate in fibre-containing foods usually has lower calories, fat, and refined sugar, and is also usually rich in micronutrients and phytochemicals that have additional health benefits. A fibre-rich meal is digested slower in the gastrointestinal tract, thus promoting satiety. These salubrious features of a high-fibre diet promote the treatment and prevention of overweight, obesity, T2DM and CVD [
35]. Nevertheless, the recommended intake of 20-30 g/day is not usually met because of low intake of fruits, vegetables, whole and high-fibre grain products, and legumes, which explain the inadequate fibre intake phenomenon among subjects in the current study. Palatability, limited food choices, and gastrointestinal side effects might be some of the potential barriers to achieving such high-fibre intakes [
18].
This part of study attempts to define the trends of use of dietary supplements and traditional remedies as well as to investigate their associations with CVD among Malaysian patients with T2DM. Dietary supplement and traditional remedy use is widespread among T2DM patients as can be seen that more than half of the studied subjects used dietary supplements and traditional remedies. Of particular to be highlighted, as much as 20.4% of the subjects used vitamin B
1, B
6, B
12, which is used most frequently among all the dietary supplements on the basis that one common cause of neurological disorders, such as peripheral neuropathy, is deficiency of B vitamins. Therefore, vitamin B
1, B
6, B
12 tablets are frequently used for preventing and treating peripheral neuropathy [
41]. This is further supported by the data in this study that about one third of the subjects diagnosed with peripheral neuropathy (33.1%) were prescribed vitamin B
1, B
6, B
12 tablets. Subjects are very likely to incorporate dietary supplements and traditional remedies into their treatment plans, may be in an attempt to improve their health and to prevent further illness. Nonetheless, reported dietary supplements and traditional remedies use for the treatment of T2DM and CVD in the present research were relatively uncommon. The analysis suggests that the subjects in this study do not seem to be using dietary supplements and traditional remedies specifically for their neurological disorders, such as peripheral neuropathy, is deficiency of B vitamins. Therefore, vitamin B1, B6, B12 tablets are frequently used for preventing and treating peripheral neuropathy [
41]. This is further supported by the data in this study that about one third of the subjects diagnosed with peripheral neuropathy (33.1%) were prescribed vitamin B1, B6, B12 tablets. Subjects are very likely to incorporate dietary supplements and traditional remedies into their treatment plans, may be in an attempt to improve their health and to prevent further illness. Nonetheless, reported dietary supplements and traditional remedies use for the treatment of T2DM and CVD in the present research were relatively uncommon. The analysis suggests that the subjects in this study do not seem to be using dietary supplements and traditional remedies specifically for their T2DM and CVD only; in reality, more towards holistic approach to general health care.
In actual fact, many dietary supplements and traditional remedies have been extensively reported to be currently being promoted as beneficial for the management of people with DM and its complications [
22]. These include supplements containing various dietary fibres, n-3 fatty acids, minerals, trace elements and some herbs. In the past few years, a number of controlled clinical studies have reported the effects of nutritional supplements on CVD risk [
42,
43,
44]. These studies have been conducted on post-MI subjects or subjects at high risk for CVD, although some studied healthy subjects. The clinical trials have failed to demonstrate a beneficial effect of antioxidant supplements on CVD morbidity and mortality. Similarly, the lack of efficacy was demonstrated consistently for different doses of various antioxidants in diverse population groups [
45,
46,
47,
48]. In agreement with these studies, the present data also does not justify the association between CVD and the routine use of nutritional supplements. In truth, the principal benefits of nutritional approaches to the treatment and prevention of DM are derived from the appropriate intake of usual foods. Because dietary supplements and traditional remedies have not been a component of any traditional dietary pattern, it is believed that longer term evaluation in formal clinical trials is required before offering firm recommendations.
This study has thrown up some considerable limitations in need of further investigation. Firstly, the causal effects between dietary status and CVD could not be established due to the nature of the cross-sectional study design which only provides a snapshot of time. Secondly, as with most observational studies relying on 24-hour dietary recall data, measurement error may be introduced by the under- or over-reporting of the amounts of foods usually eaten per day. However, in most cases, this type of error would be non-differential, biasing estimates to the null. The main limitation of our study is the use of a single 24-hour recall. Multiple 24-hour recalls would have provided better estimates of intake, but would have also increased respondent burden, which in turn may have contributed to decreased memory recall in the subjects. It is suggested that future studies using a combination of 24-hour dietary recall, food frequency questionnaire and food diary to further ascertain dietary assessment is highly encouraged. Thirdly, the Malaysia food composition database [
24] has not been updated for over 15 years and this may affect the accuracy of the estimation of nutrient intakes.
Some of the nutrient composition of raw food materials was used when the cooked food items were not available in the databases and this might introduce bias in estimation. Nonetheless, the database was used due to its relevance to the local context in terms of food items. In addition, it only provides a limited list of foods with dietary fat composition, making the analyses of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids an ambitious undertaking in this study. Besides dietary cholesterol and fatty acid contents, the published local database lacked information on dietary fibre because it provided only crude fibre data. This is outdated as crude fibre has been reported to contribute only one-seventh to one-half of total dietary fibre [
49]. So the food databases from other countries such as Singapore, China, and USA as described were particularly useful in providing information on dietary fibre as well as dietary cholesterol.
Conclusion
Taken overall, the energy and nutrient consumption of the subjects was unsatisfactory. Patients with CVD consumed statistically higher total calories. Likewise, the mean carbohydrate, protein and total fat intake of CVD patients were significantly higher than those of non-CVD patients, while mean intakes of cholesterol, fibre, minerals and all vitamins were comparable between CVD and non-CVD groups. Regardless of CVD status, a very high proportion of the subjects did not meet the recommendations of the MNT Guidelines for Type 2 Diabetes for total energy, carbohydrate, protein, total fat, and fibre intakes. Although numerous studies have attempted to identify the optimal mix of nutrients for meal plans of people with DM, it is unlikely that one such combination of nutrients exists. Therefore, it is reasonable to believe that in the management of DM and its complications, the combination of macro- and micronutrients with adequate intakes may be adjusted to meet the optimal metabolic goals (e.g., lipid profile, renal function), individual preferences and circumstances of the person with DM. Inevitably and not to be neglected, effective interventions combining nutrition education with behaviour-oriented counselling are needed to help patients acquire the skills, motivation, and support. Given the importance of dietary management and the scarcity of dietary intake data on patients with T2DM, this paper contributes to the knowledge on how well current dietary recommendations are being complied. Future studies should be designed to determine the behavioural and food selection factors that may contribute to the dietary status of the T2DM patients.
On the other hand, this study also discovered a wide variety of dietary supplements and traditional remedies were consumed among the T2DM patients and some subjects reported taking multiple types of supplements on a regular basis. Taken together, as much as 52.4% used at least one dietary supplement and 12.1% took single traditional remedy or in various combinations, albeit their intakes did not differ between those who suffered CVD and the rest of the non-CVD subjects. Traditional remedies have been used since centuries ago while dietary supplement is introduced quite recently. However, the supplement-drug interactions can lead to a better integration of complementary and mainstream medicine in the future. Until more is understood, patients should be advised of possible interactions and of the need to inform their physicians that they are using dietary supplements. Most importantly, physicians and pharmacists should be urged to request information about the use of supplements when prescribing medications.
Universiti Putra Malaysia
NOTES
-
All authors claim no conflict of interest in regard to the publication of these results.
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our sincere gratitude and appreciation to all the health care providers and patients with T2DM in HKL and Hospital Serdang for their contribution to this research. We are particularly thankful for financial support from the Research University Grant Scheme (RUGS), Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM). Also, we gratefully appreciate the excellent contributions of Dr. Khoo Hock Eng in revising our manuscript critically leading to the success of this manuscript. Lastly, we would like to thank Prof. Dr. Poh Bee Koon, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Chan Yoke Mun and Prof. Dr. Mirnalini Kandiah for providing us with useful dietary advices.
REFERENCES
- 1. International Diabetes Federation (BE). IDF Diabetes atlas. 5th ed. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation; 2011.
- 2. Ministry of Health Malaysia. The fourth national health and morbidity survey 2011 (NHMS IV 2011). Putrajaya: Ministry of Health Malaysia; 2011.
- 3. Chan JC, Malik V, Jia W, Kadowaki T, Yajnik CS, Yoon KH, Hu FB. Diabetes in Asia: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. JAMA 2009;301:2129-2140.
- 4. International Diabetes Federation (BE). IDF Diabetes atlas. 4th ed. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation; 2009.
- 5. Pellegrini E, Maurantonio M, Giannico IM, Simonini MS, Ganazzi D, Carulli L, D'Amico R, Baldini A, Loria P, Bertolotti M, Carulli N. Risk for cardiovascular events in an Italian population of patients with type 2 diabetes. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2011;21:885-892.
- 6. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes--2012. Diabetes Care 2012;35(Suppl 1):S11-S63.
- 7. Wheeler ML, Dunbar SA, Jaacks LM, Karmally W, Mayer-Davis EJ, Wylie-Rosett J, Yancy WS Jr. Macronutrients, food groups, and eating patterns in the management of diabetes: a systematic review of the literature, 2010. Diabetes Care 2012;35:434-445.
- 8. Malaysian Dietitians' Association. Medical nutrition therapy guidelines for type 2 diabetes. Petaling Jaya: Malaysian Dietitians' Association; 2005.
- 9. World Health Organization (CH). WHO technical report series 854. Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry. Report of a WHO Expert Committee. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1995.
- 10. Shahar S, Yusoff NA, Safii NS, Ghazali R, Ahmad R. Atlas of food exchanges & portion sizes. Kuala Lumpur: MDC Publishers Sdn Bhd; 2009.
- 11. Health Promotion Board (SG). Food composition guide Singapore. Singapore: Health Promotion Board; 2003.
- 12. China Institute of Nutrition and Food Safety. China Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. China food composition 2002 (Book 1). Beijing: Peking University Medical Press; 2002.
- 13. Pawastein P, Mahidon M. ASEAN Network of Food Data System. ASEAN food composition tables 2000. Phutthamonthon District: Mahidol University; 2000.
- 14. Athar N, Spriggs TW, Taptiklis E, Taylor G. The concise New Zealand food composition tables. 5th ed. Palmerston North: New Zealand Crop & Science Research and Ministry of Health; 2001.
- 15. Black AE, Goldberg GR, Jebb SA, Livingstone MB, Cole TJ, Prentice AM. Critical evaluation of energy intake data using fundamental principles of energy physiology: 2. Evaluating the results of published surveys. Eur J Clin Nutr 1991;45:583-599.
- 16. Ismail M, Chee S, Roslee R, Zawiah H. Predictive equations for the estimation of basal metabolic rate in Malaysian adults. Malays J Nutr 1998;4:73-80.
- 17. Goldberg GR, Black AE, Jebb SA, Cole TJ, Murgatroyd PR, Coward WA, Prentice AM. Critical evaluation of energy intake data using fundamental principles of energy physiology: 1. Derivation of cut-off limits to identify under-recording. Eur J Clin Nutr 1991;45:569-581.
- 18. American Diabetes Association. Bantle JP, Wylie-Rosett J, Albright AL, Apovian CM, Clark NG, Franz MJ, Hoogwerf BJ, Lichtenstein AH, Mayer-Davis E, Mooradian AD, Wheeler ML. Nutrition recommendations and interventions for diabetes: a position statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2008;31(Suppl 1):S61-S78.
- 19. Moy FM, Abdul Rahman S. Anthropometry and dietary intake of type 2 diabetes patients attending an outpatient clinic. Malays J Nutr 2002;8:63-73.
- 20. Mirnalini K Jr, Zalilah MS, Safiah MY, Tahir A, Siti Haslinda MD, Siti Rohana D, Khairul Zarina MY, Mohd Hasyami S, Normah H. Energy and nutrient intakes: findings from the Malaysian Adult Nutrition Survey (MANS). Malays J Nutr 2008;14:1-24.
- 21. Robertson L, Waugh N, Robertson A. Protein restriction for diabetic renal disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2007;CD002181.
- 22. Dämon S, Schätzer M, Höfler J, Tomasec G, Hoppichler F. Nutrition and diabetes mellitus: an overview of the current evidence. Wien Med Wochenschr 2011;161:282-288.
- 23. Aparicio M. Place of dietary protein restriction in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol Ther 2006;2(Suppl 1):S32-S38.
- 24. Tee ES, Mohd Ismail N, Mohd Nasir A, Khatijah I. Nutrient composition of Malaysian foods. 4th ed. Kuala Lumpur: Malaysian Food Composition Database Programme; 1997.
- 25. Riccardi G, Giacco R, Rivellese AA. Dietary fat, insulin sensitivity and the metabolic syndrome. Clin Nutr 2004;23:447-456.
- 26. Raymond JL, Mahan LK, Escott-Stump S. Krause's food & nutrition therapy. Philadelphia (PA): Saunders Elsevier; 2008.
- 27. Thomas B, Bishop J. Manual of dietetic practice. 4th ed. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing Ltd; 2007.
- 28. Marlett JA, McBurney MI, Slavin JL. American Dietetic Association. Position of the American Dietetic Association: health implications of dietary fiber. J Am Diet Assoc 2002;102:993-1000.
- 29. Bazzano LA, He J, Ogden LG, Loria CM, Whelton PK. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey I Epidemiologic Follow-up Study. Dietary fiber intake and reduced risk of coronary heart disease in US men and women: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey I Epidemiologic Follow-up Study. Arch Intern Med 2003;163:1897-1904.
- 30. Liu S, Buring JE, Sesso HD, Rimm EB, Willett WC, Manson JE. A prospective study of dietary fiber intake and risk of cardiovascular disease among women. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002;39:49-56.
- 31. Mozaffarian D, Kumanyika SK, Lemaitre RN, Olson JL, Burke GL, Siscovick DS. Cereal, fruit, and vegetable fiber intake and the risk of cardiovascular disease in elderly individuals. JAMA 2003;289:1659-1666.
- 32. Pereira MA, O'Reilly E, Augustsson K, Fraser GE, Goldbourt U, Heitmann BL, Hallmans G, Knekt P, Liu S, Pietinen P, Spiegelman D, Stevens J, Virtamo J, Willett WC, Ascherio A. Dietary fiber and risk of coronary heart disease: a pooled analysis of cohort studies. Arch Intern Med 2004;164:370-376.
- 33. Wallström P, Sonestedt E, Hlebowicz J, Ericson U, Drake I, Persson M, Gullberg B, Hedblad B, Wirfält E. Dietary fiber and saturated fat intake associations with cardiovascular disease differ by sex in the Malmö Diet and Cancer Cohort: a prospective study. PLoS One 2012;7:e31637.
- 34. Jenkins DJ, Kendall CW, Vuksan V, Vidgen E, Parker T, Faulkner D, Mehling CC, Garsetti M, Testolin G, Cunnane SC, Ryan MA, Corey PN. Soluble fiber intake at a dose approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for a claim of health benefits: serum lipid risk factors for cardiovascular disease assessed in a randomized controlled crossover trial. Am J Clin Nutr 2002;75:834-839.
- 35. Rizvi AA. Nutritional challenges in the elderly with diabetes. Int J Diabetes Mellit 2009;1:26-31.
- 36. Keenan JM, Pins JJ, Frazel C, Moran A, Turnquist L. Oat ingestion reduces systolic and diastolic blood pressure in patients with mild or borderline hypertension: a pilot trial. J Fam Pract 2002;51:369.
- 37. Vuksan V, Jenkins DJ, Spadafora P, Sievenpiper JL, Owen R, Vidgen E, Brighenti F, Josse R, Leiter LA, Bruce-Thompson C. Konjac-mannan (glucomannan) improves glycemia and other associated risk factors for coronary heart disease in type 2 diabetes. A randomized controlled metabolic trial. Diabetes Care 1999;22:913-919.
- 38. Fukagawa NK, Anderson JW, Hageman G, Young VR, Minaker KL. High-carbohydrate, high-fiber diets increase peripheral insulin sensitivity in healthy young and old adults. Am J Clin Nutr 1990;52:524-528.
- 39. Pereira MA, Jacobs DR Jr, Pins JJ, Raatz SK, Gross MD, Slavin JL, Seaquist ER. Effect of whole grains on insulin sensitivity in overweight hyperinsulinemic adults. Am J Clin Nutr 2002;75:848-855.
- 40. Pereira MA, Pins JJ. Dietary fiber and cardiovascular disease: experimental and epidemiologic advances. Curr Atheroscler Rep 2000;2:494-502.
- 41. MIMS Editorial Board. MIMS Malaysia: official drug reference of the Malaysian Medical Association. Selangor: UBM Medica Sdn Bhd; 2011.
- 42. de Gaetano G. Collaborative Group of the Primary Prevention Project. Low-dose aspirin and vitamin E in people at cardiovascular risk: a randomised trial in general practice. Collaborative Group of the Primary Prevention Project. Lancet 2001;357:89-95.
- 43. Lonn E, Yusuf S, Hoogwerf B, Pogue J, Yi Q, Zinman B, Bosch J, Dagenais G, Mann JF, Gerstein HC. HOPE Study. MICRO-HOPE Study. Effects of vitamin E on cardiovascular and microvascular outcomes in highrisk patients with diabetes: results of the HOPE study and MICRO-HOPE substudy. Diabetes Care 2002;25:1919-1927.
- 44. Hodis HN, Mack WJ, LaBree L, Mahrer PR, Sevanian A, Liu CR, Liu CH, Hwang J, Selzer RH, Azen SP. VEAPS Research Group. Alpha-tocopherol supplementation in healthy individuals reduces low-density lipoprotein oxidation but not atherosclerosis: the Vitamin E Atherosclerosis Prevention Study (VEAPS). Circulation 2002;106:1453-1459.
- 45. Heinecke JW. Clinical trials of vitamin E in coronary artery disease: is it time to reconsider the low-density lipoprotein oxidation hypothesis? Curr Atheroscler Rep 2003;5:83-87.
- 46. Gotto AM. Antioxidants, statins, and atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003;41:1205-1210.
- 47. Brown BG, Cheung MC, Lee AC, Zhao XQ, Chait A. Antioxidant vitamins and lipid therapy: end of a long romance? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2002;22:1535-1546.
- 48. Steinberg D, Witztum JL. Is the oxidative modification hypothesis relevant to human atherosclerosis? Do the antioxidant trials conducted to date refute the hypothesis? Circulation 2002;105:2107-2111.
- 49. Anderson J, Perryman S, Young L, Prior S. Dietary fibre [Internet]. Fort Collins (CO): Colorado State University Extension; 2011, cited 2014 september. Available from www.ext.colostate.edu/pubs/foodnut/09333.html
Table 1Socio-demographic and clinical characteristics of the subjects (n = 313)
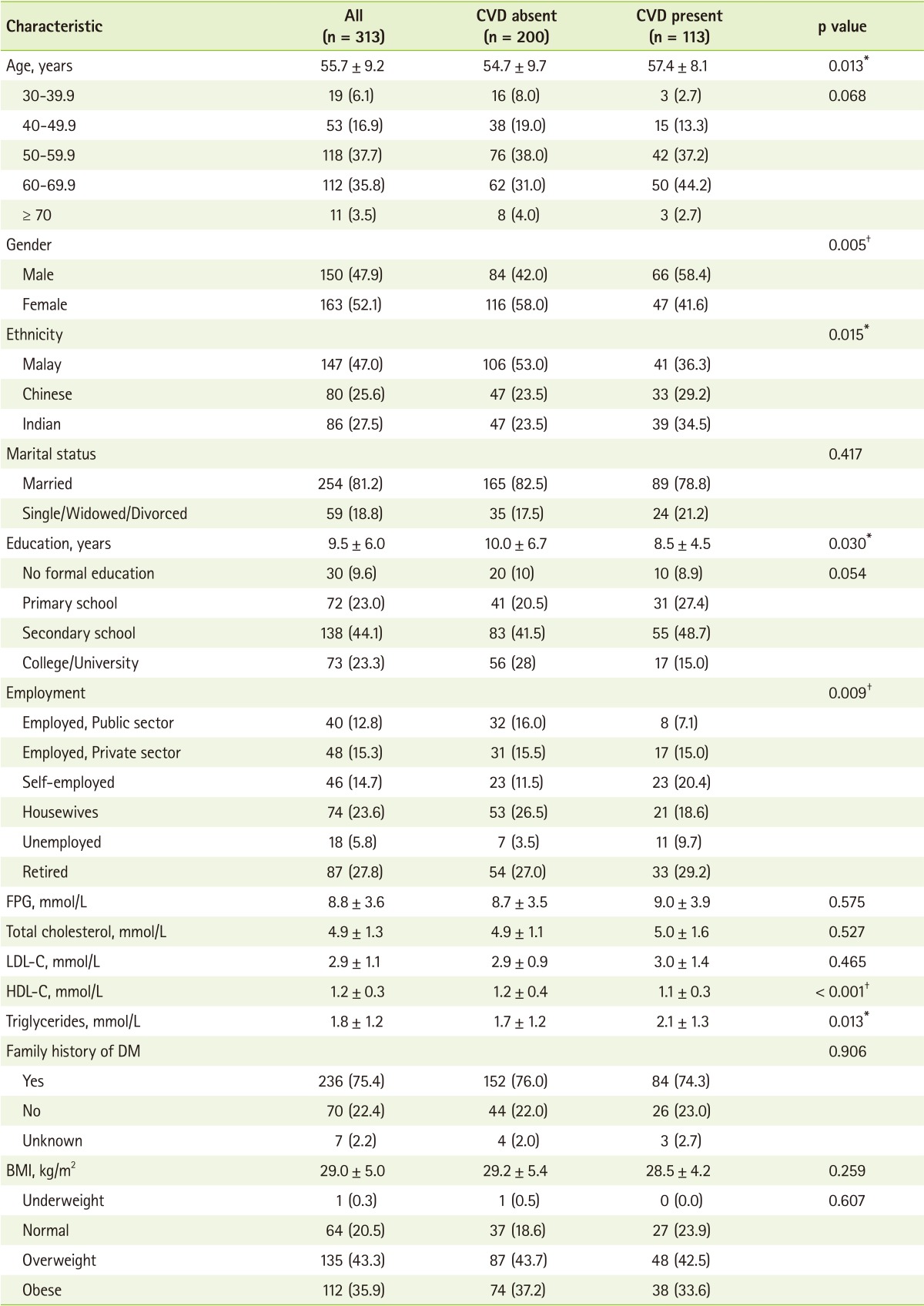
Table 2Mean daily dietary intake of the subjects as a whole and stratified by the presence of CVD (n = 313)
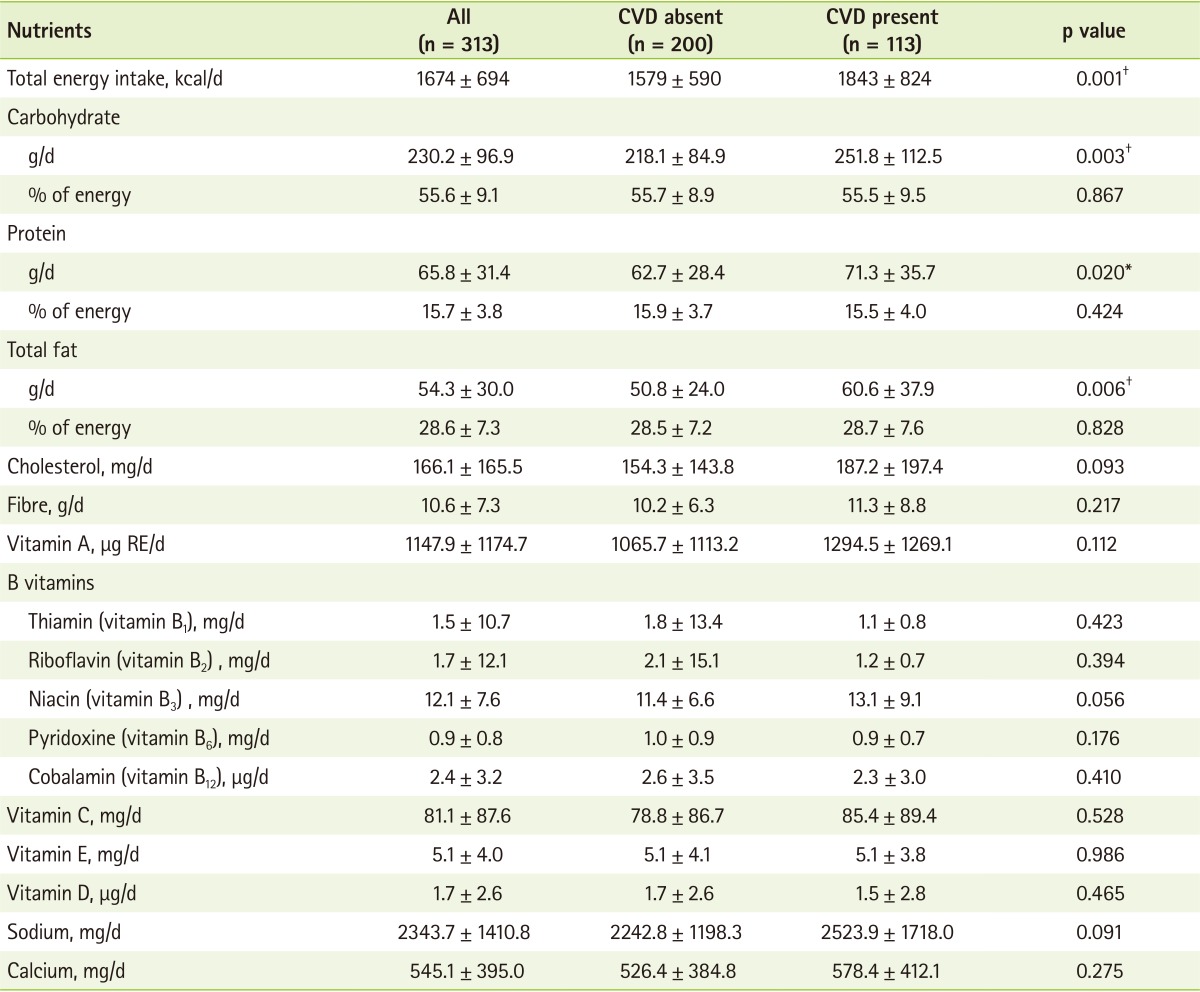
Table 3Adequacy of selected nutrient intakes of the subjects†
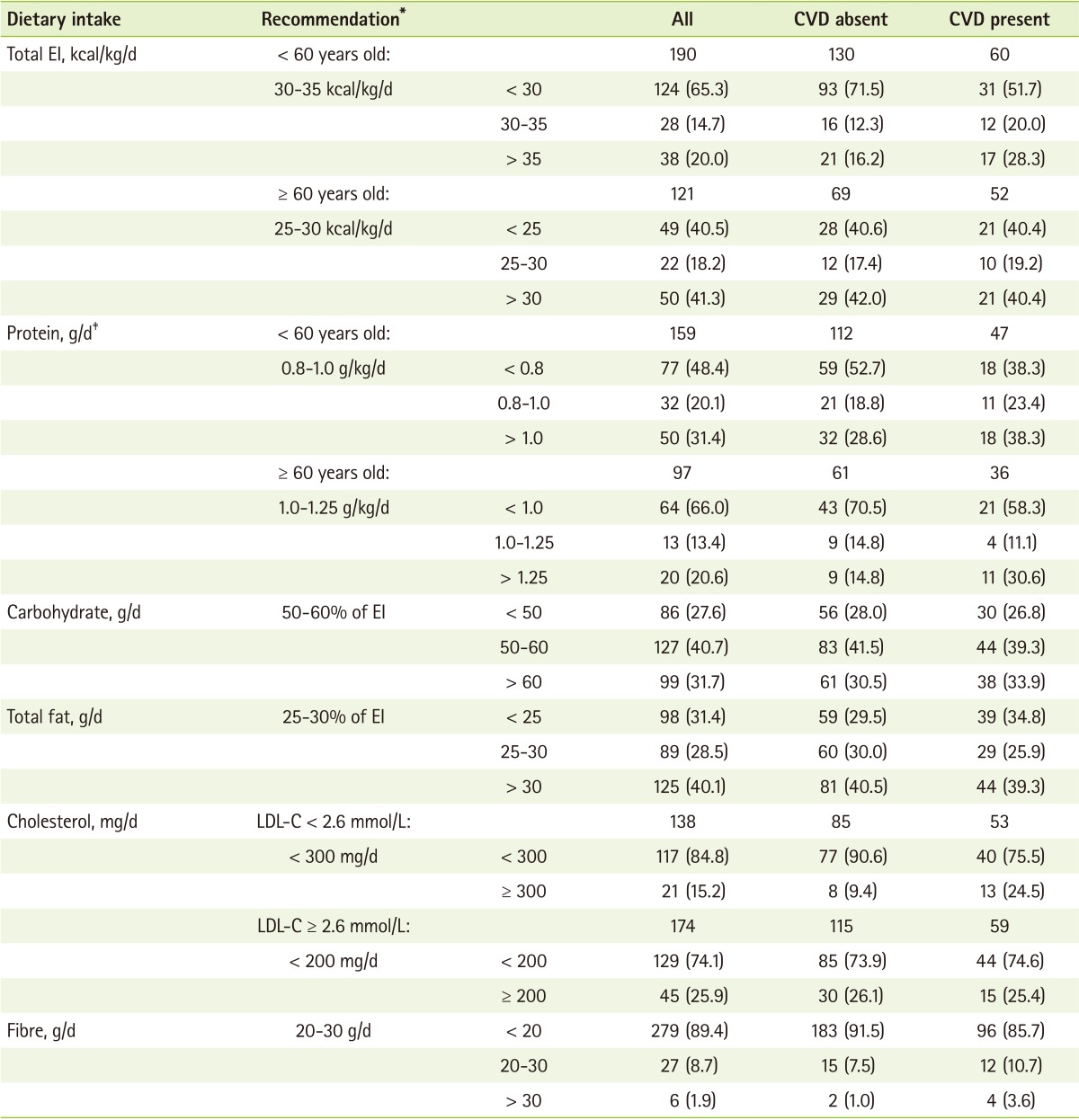
Table 4Dietary supplement and traditional remedy intakes of the subjects (n = 313)*†‡