ABSTRACT
Ischemic stroke and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) are representative geriatric diseases with a rapidly increasing prevalence worldwide. Recent studies have reported an association between ischemic stroke neuropathology and AD neuropathology. Ischemic stroke shares some similar characteristics with AD, such as glia activation-induced neuroinflammation, amyloid beta accumulation, and neuronal cell loss, as well as some common risk factors with AD progression. Although there are considerable similarities in neuropathology between ischemic stroke and AD, no studies have ever compared specific genetic changes of brain cortex between ischemic stroke and AD. Therefore, in this study, I compared the cerebral cortex transcriptome profile of 5xFAD mice, an AD mouse model, with those of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) mice, an ischemic stroke mouse model. The data showed that the expression of many genes with important functional implications in MCAO mouse brain cortex were related to synaptic dysfunction and neuronal cell death in 5xFAD mouse model. In addition, changes in various protein-coding RNAs involved in synaptic plasticity, amyloid beta accumulation, neurogenesis, neuronal differentiation, glial activation, inflammation and neurite outgrowth were observed. The findings could serve as an important basis for further studies to elucidate the pathophysiology of AD in patients with ischemic stroke.
-
Keywords: Ischemic stroke; Dementia; Middle cerebral artery occlusion; 5xFAD model; RNA sequencing
INTRODUCTION
Ischemic stroke is a leading cause of global mortality [
1] and can also result in disability and reduced quality of life [
2]. It is characterized by brain infarction caused by the occlusion of cerebral blood flow [
3,
4] and is also correlated with the onset of dementia such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD) [
5,
6].
AD has several hallmarks, including excessive deposition of amyloid beta, neuronal intracellular neurofibrillary tangles, and neuronal loss in cognition related brain regions such as the hippocampus and cortex [
7,
8].
The incidences of stoke and AD are simultaneously increasing internationally [
9,
10]. A recent meta-analysis identified the concurrent increase in the number of patients with stroke and AD [
11]. A previous study demonstrated that over 80% of patients with AD experienced ischemic stroke caused by amyloid deposition in cerebral blood vessels [
12]. Furthermore, a study demonstrated the high risk of AD onset in an ischemic stroke model with cerebral amyloid angiopathy [
13].
Considering previous reports, dementia appears to share common risk factors with stroke [
14] and leads to increased risks for death following ischemic stroke [
15,
16,
17,
18].
A recent clinical study reported that mortality after ischemic stroke increased with the onset of AD [
19]. Several studies have reported that stroke can cause dementia accompanied by cognitive impairment, neuronal cell damage, mitochondrial dysfunction, and glia activation [
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25]. Although there is much evidence on the relationship between ischemic stroke and AD, the genetic mechanisms shared between 2 diseases are not completely understood. In this study, I compared the cerebral cortex transcriptomes from middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) mice, a mouse model of ischemic stroke [
26], with those from 5xFAD mice, an AD mouse model [
27]. I identified that the function of commonly altered RNAs was associated with neuronal cell death, glia inflammation, and synaptic dysfunction in AD and ischemic stroke brains. These findings are thought to provide important basic data for broadening the understanding of the AD-like neuropathology in ischemic stroke patients by understanding the effect of RNA commonly expressed in both diseases.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Data used to analyze the transcriptome of 5xFAD and MCAO mouse models
To compare the common transcriptomic profile between MCAO mouse brain cortex and 5xFAD mouse brain cortex, I obtained RNA sequencing data from the cerebral cortex of 8-month-old male 5xFAD mice from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database with the accession number of GSE168137 [
28]. I also obtained RNA sequencing data from the cerebral cortex of 3-month-old male ischemic stroke MCAO mice (GSE137482) [
1].
The RNA sequencing data obtained from the ischemic stroke and AD models were screened for low-quality sequencing reads using Trimmomatic [
29] (
Figure 1A). The trimmed sequences were matched to the mouse genome (mm10) using the spliced transcript alignment to a reference aligner [
30]. The Cuffnorm value was used to examine normalized values of fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads (FPKM) based on the GENCODE annotation (Release M17, GRCm38.p6 [
31]) (
Figure 1A). Transcripts with an average FPKM value of < 1 or transcripts not detected in any sample were excluded from additional analysis (
Figure 1A). A t-test was used to sort transcripts with a significantly different expression between MCAO and 5xFAD groups. The commonly altered mRNAs between the cortex of MCAO and 5xFAD groups were selected for further functional analysis.
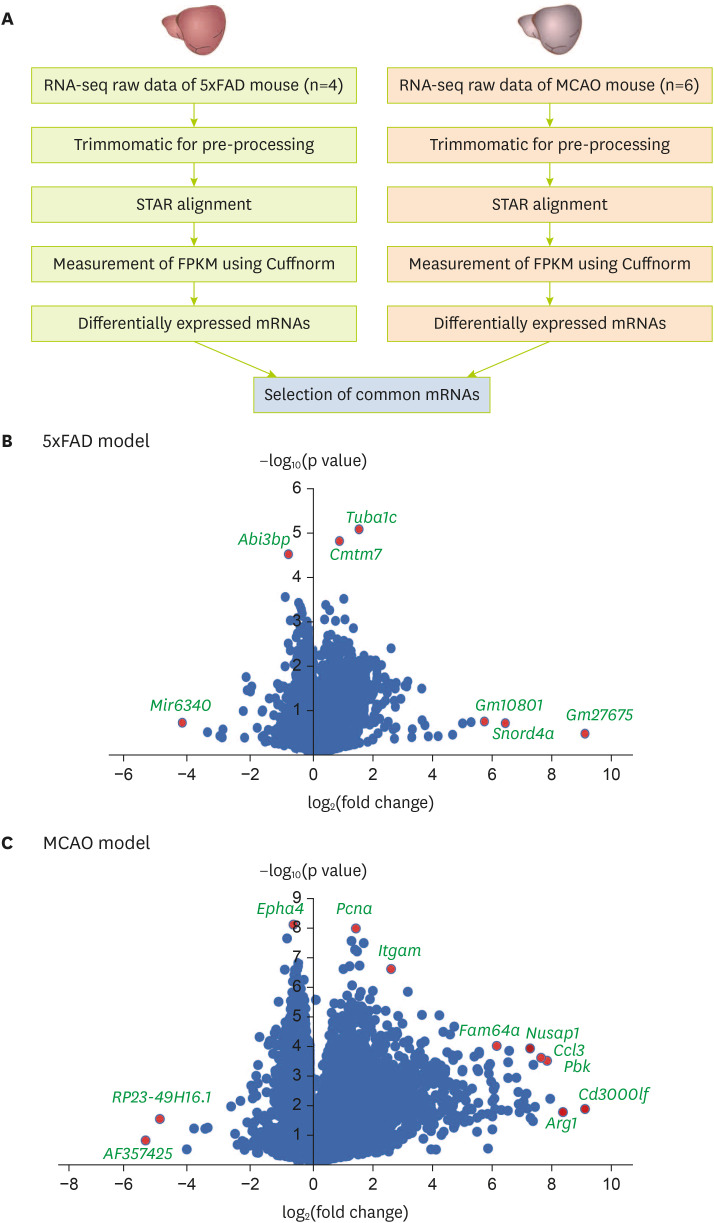
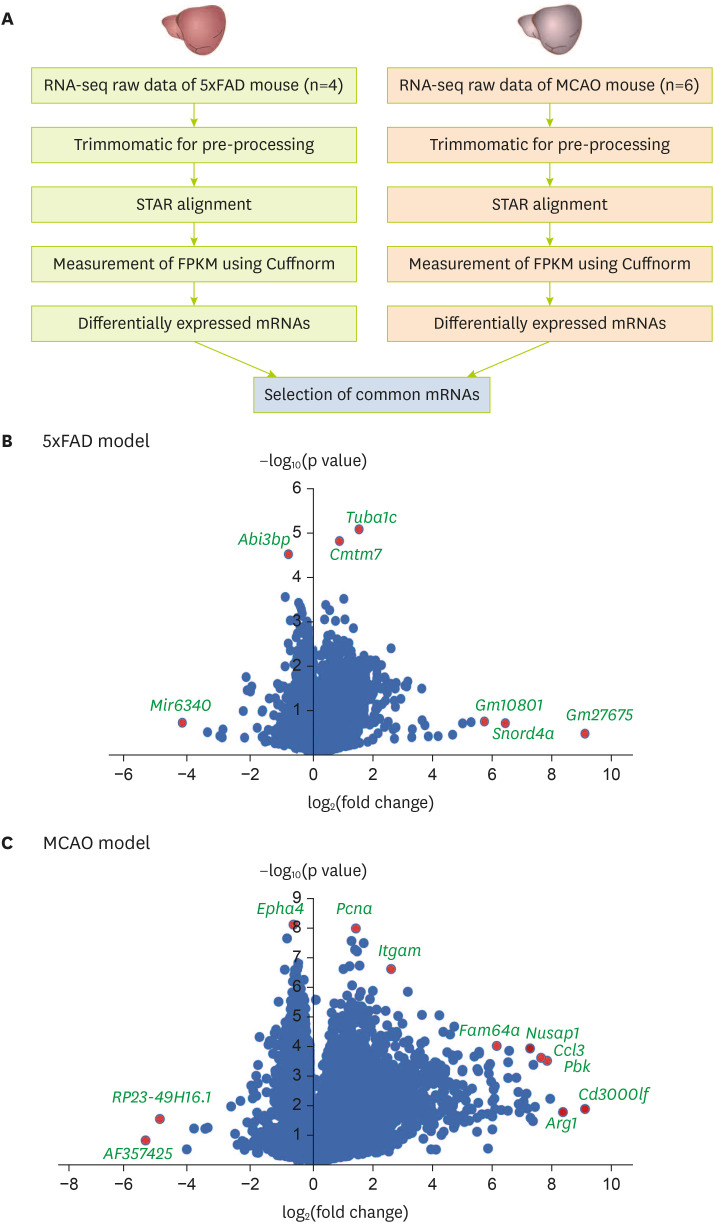
Figure 1
Analysis of transcriptomic data from the brain cortex of MCAO and 5xFAD mouse models. (A) Analysis of transcriptome data. Volcano plots of (B) the 5xFAD group and (C) the MCAO group. The X-axis represents the log2-transformed fold change in both the groups, and the Y-axis represents the −log10(p value) value. Red dots show significantly altered genes.
MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion; STAR, spliced transcript alignment to a reference; FPKM, fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads.
Functional analysis of mRNAs
For the functional analysis, significant expression changes based on a p value of ≤ 0.05 were selected in the MCAO and 5xFAD groups. Among them, the commonly changed genes with the same direction in the MCAO and 5xFAD groups were chosen. This filtering resulted in 231 significantly increased genes and 128 significantly decreased genes in both groups. These 359 genes as common genes in both groups were used for the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis and gene ontology (GO) analysis with the Molecular Signatures Database [
32]. For the same group of genes, functional annotation clustering was conducted using the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) clustering tool [
33].
RESULTS
The transcriptome data from 4 5xFAD model brain cortex and 6 MCAO brain cortex were analyzed. For the RNA sequencing analysis of cerebral cortex from 8-month-old 5xFAD mice, data from the publicly available dataset of the GEO database (GSE168137) were analyzed. For the RNA sequencing analysis of cerebral cortex from 3-month-old MCAO mice, the data from the publicly available dataset of the GEO database (GSE137482) were analyzed.
After analyzing and comparing the 2 group’s RNA sequencing data (
Figure 1A, see Materials and Methods), the genes with high expression with significant fold change in each group were sorted and displayed using volcano plot graphs (
Figure 1B and C).
I sorted 864 significant genes in 5xFAD mouse brain cortex and 5061 significant genes in MCAO mouse brain cortex with a p value of ≤ 0.05. In addition, there were 401 significant genes with a p value ≤ 0.05 shared between groups.
As depicted in the volcano plot of the 5xFAD model (
Figure 1B), the expression levels of
Mir6340,
Abi3bp,
Tuba1c,
Cmtm7,
Gm10801,
Snord4a, and
Gm27675 were significantly distinguished in 5xFAD mouse brain cortex compared with those in control brain cortex (
Figure 1B).
In the volcano plot of the MCAO model (
Figure 1C),
Epha4,
Pcna,
Itgam,
RP23-49h16.1,
AF357425,
Fam64a,
Nusap1,
Ccl3,
Pbk,
Arg1, and
Cd3000lf were significantly distinguished in their expression when comparing MCAO mouse brain cortex with control brain cortex (
Figure 1C).
To identify commonly altered genes shared by 5xFAD and MCAO mouse groups, genes with a pvalue of ≤ 0.05 in both 5xFAD and MCAO mouse brain cortex were reselected.
In addition, 231 increased genes and 128 decreased genes were identified in both groups (
Supplementary Table 1).
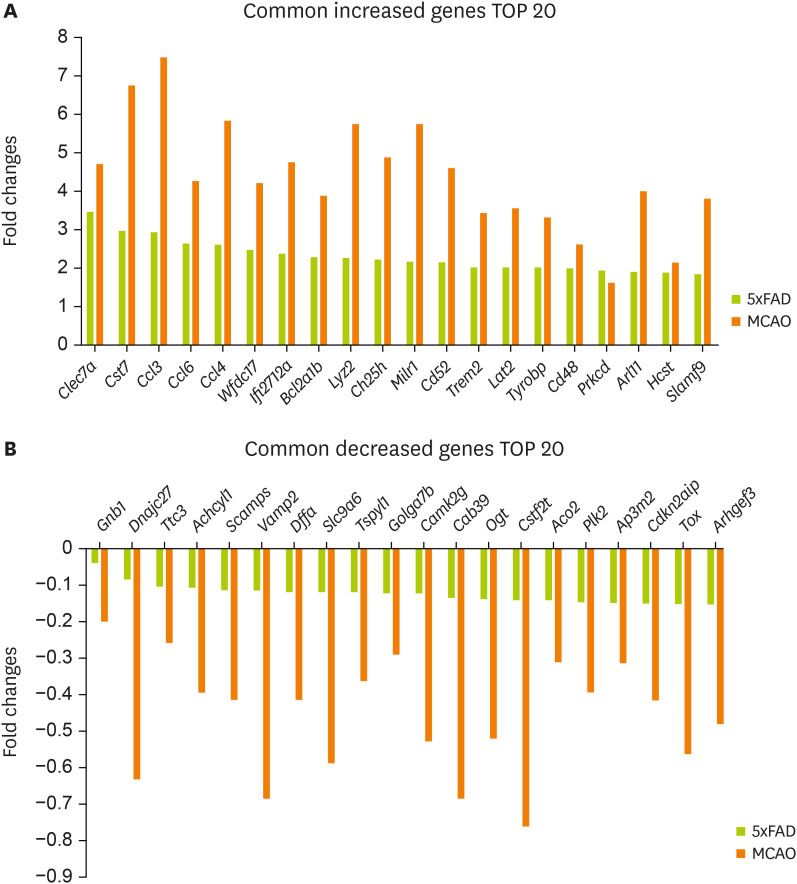
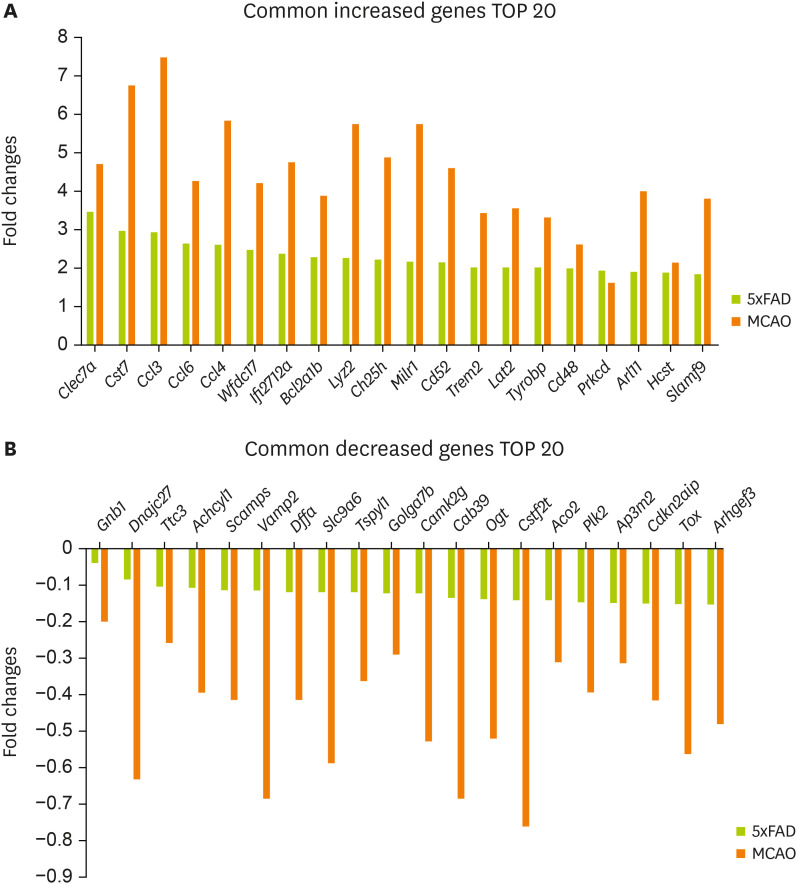
Figure 2A shows the 20 most commonly increased genes:
Clec7a,
Cst7,
Ccl3,
Ccl6,
Ccl4,
Wfdc17,
Ifi2712a,
Bcl2a1b,
Lyz2,
Ch25h,
Milr1,
Cd52,
Trem2,
Lat2,
Tyrobp,
Cd48,
Prkcd,
Arl11,
Hcst, and
Slamf9.
Figure 2B shows the 20 most commonly decreased genes:
Gnb1,
Dnajc27,
Ttc3,
Achcyl1,
Scamps,
Vamp2,
Dffa,
Slc9a6,
Tspyl1,
Golga7b,
Camk2g,
Cab39,
Ogt,
Cstf2t,
Aco2,
Plk2,
Ap3m2,
Cdkn2aip,
Tox, and
Arhgef3.
Figure 2
Selected genes with significant expression changes in the mouse brain cortex of MCAO and 5xFAD models. Common genes with a significant expression change in both MCAO and 5xFAD mouse cerebral cortex. Graphs for 20 most commonly (A) increased genes and (B) decreased genes.
MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion.
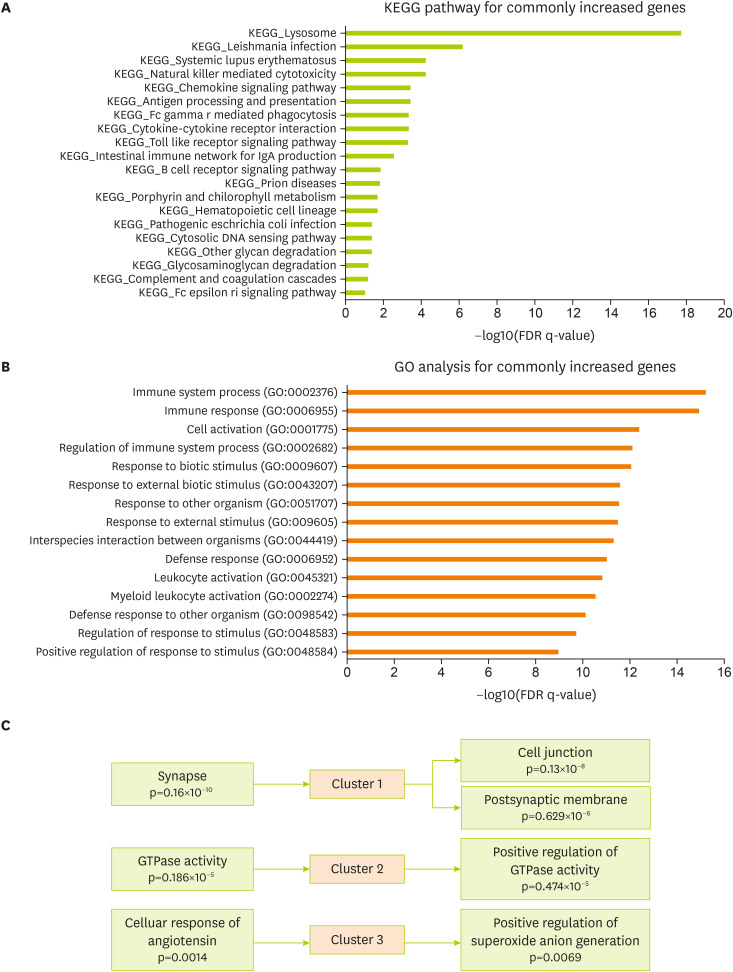
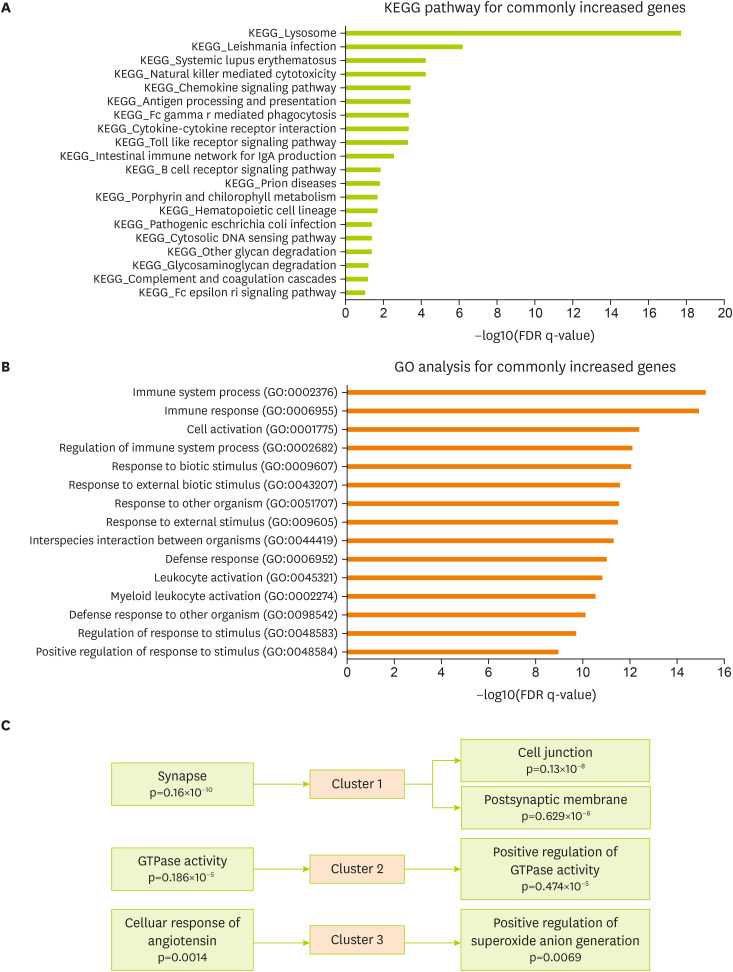
To verify related cellular pathways associated with commonly changed genes in the brain cortex of the 5xFAD and MCAO models, the KEGG pathway was analyzed using the MsigDB program (
Figure 3A). KEGG analysis data for commonly increased genes showed a significant enrichment in the molecular signaling of lysosome, natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity, chemokine signaling, antigen processing, cytokine interaction, toll-like receptor signaling, IgA production, and B-cell receptor signaling in the 5xFAD and MCAO groups (
Figure 3A). Next, I performed GO analysis for genes commonly increased in both groups (The Gene Ontology Consortium, 2017). The significantly enriched terms included those related to immune response, cell activation, response to biotic stimulus, response to external stimulus, defense response, leukocyte activation, and defense response to other organisms (
Figure 3B). In addition, I performed a functional clustering analysis of the increased genes using the DAVID functional annotation tool [
33] (
Figure 3C). Highly enriched clusters were linked to synapses, cell junctions, postsynaptic membranes, GTPase activity, cell response of angiotensin, and positive regulation of superoxide anion generation for the commonly changed genes in 5xFAD and MACO mouse brain cortex (
Figure 3C).
Figure 3
Functional analysis of the commonly increased genes between the MCAO and 5xFAD groups. (A) KEGG pathway analysis of commonly increased genes—significantly altered pathways based on FDR q-value. (B) GO analysis of commonly increased genes. Top 15 GO terms based on FDR q-value. (C) DAVID functional annotation clustering. The top 3 clusters with a significant change are presented.
MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; FDR, false discovery rate; DAVID, Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery; GO, gene ontology.
Based on the analyzed data, common characteristics were found between the genes expressed in the cerebral cortex of AD and the genes in the ischemic stroke mouse model.
DISCUSSION
In this study, I analyzed genes commonly expressed in 5xFAD and MCAO mouse cerebral cortex. Volcano plot shows significant gene expression in 5xFAD and MCAO mouse cerebral cortex. It is found that the expression of the
Tuba1c gene, which promotes cell proliferation and regulates immune cell infiltration under inflammation conditions [
34,
35], was significantly distinguished in 5xFAD brain cortex. In addition, the expression of
Cmtm7, which is associated with immune B-cell antigen receptor regulation [
36] and increased risk of obesity [
37], was significantly distinguished in 5xFAD brain cortex. These findings suggest that the cerebral cortex in 5xFAD mice may accelerate immune cell infiltration and activate inflammatory responses.
In the MCAO mouse brain cortex, enhanced expression of
Epha4, which regulates neuronal differentiation and promotes neurogenesis by interacting with platelet-derived growth factor receptor B was identified [
38]. Expression of
Nusap1, which is a microtubule-associated protein related to mitosis and activates glioblastoma [
39], was also significantly distinguished in the MCAO mouse brain cortex. In addition, the expression of
Ccl3, which is a major immune and neurogenesis regulator and plays a role in neuroendocrine function, activates migration of leukocyte, and impairs synaptic plasticity, leading to memory loss [
40,
41], was significantly distinguished in the MCAO mouse brain cortex.
In the MCAO mouse model, expression of
Cd3000lf, which leads to microglia activation and severe neuroinflammation [
42], was significantly distinguished. Considering these findings, it is thought that the MCAO cerebral cortex had several features such as microglia activation, neuroinflammation, immune cell infiltration, impaired neurogenesis, and synaptic dysfunction.
MCAO cerebral cortex shows alterations shared with AD pathology-related genes (
Figure 2). The increased expression of
Clec7a and
Cst7 in the MCAO brain cortex is also routinely found in the microglia of AD brain tissue [
43,
44]. The increased expression of chemokine
Ccl6 and
Ccl4 observed in the MCAO mouse brain cortex have also been identified in activated microglia and astrocytes in various neurological diseases such as ischemic stroke, AD, and multiple sclerosis [
45,
46,
47]. Furthermore, increased
Wfdc17 gene expression in MCAO and 5xFAD mouse cerebral cortex implicates immune cell infiltration and immune cell activation [
48].
The increased cholesterol 25-hydroxylase expression observed in MCAO mouse brain cortex is also related to impaired cholesterol metabolism in AD [
49]. The
Trem2 gene, which is related to microglia activation under amyloid beta toxicity in AD brain [
50] was increased in the MCAO and AD mouse brain cortex in this study. Increased
Slamf9 gene expression in the MCAO mouse brain cortex also regulates lymphocytic activation in AD brain [
51].
The expression of
Scamps gene, which controls synaptic plasticity [
52], was decreased in MCAO and AD mouse brain cortex. Additionally, the expression of
Vamp2 gene, which is reduced in the hippocampus region and entorhinal cortex and is related to memory formation [
53], was reduced in both MCAO and AD mouse brain cortex.
Ogt gene, which regulates postsynaptic plasticity, is reduced in AD brain tissue [
54,
55]. MCAO and 5xFAD brain cortex showed decreased expression of
Ogt gene. Decreased
Aco2 gene expression in MCAO brain cortex is related to AD and cognitive decline with mitochondrial dysfunction [
56].
MCAO ischemic stroke brain cortical tissue appears to share characteristics with AD pathology, such as cognitive decline, synaptic dysfunction, lymphocyte activation, glia activation, poor cholesterol metabolism, and inflammation.
KEGG and GO data from this study showed high enrichment of genes related to immune and inflammatory responses, as well as cytokine interaction, in both 5xFAD and MCAO mouse brain cortical tissues. DAVID functional annotation data also suggested a high relationship with inflammatory response, synaptic plasticity, and Rho GTPase, in both 5xFAD and MCAO mouse brain cortical tissues.
Several studies have mentioned that AD brain tissue shows greater activation of immune cells, such as natural killer cells [
57,
58], and elevated leukocyte infiltration and trafficking [
59], leading to memory loss [
60]. Synaptic loss is a primary feature of AD [
61,
62] and is related to postsynaptic density loss in AD brains [
63].
Furthermore, the activation of Rho GTPase is observed in AD brains [
64] and is related to synaptic stability maintenance and neuronal cell death [
65].
Considering previous literature and the findings of this study, I conclude that changes in the cerebral cortex caused by ischemic stroke and AD both result in increased immune response, glia activation, neuronal cell death, inflammation, and Rho GTPase; suppressed synaptic plasticity, neurogenesis, and cholesterol homeostasis; and impaired cognitive function. This suggests that further studies on AD-like cognitive decline after ischemic stroke are necessary for determining the best treatment for memory loss in patients with ischemic stroke.
NOTES
-
Conflict of Interest: The author declares that they have no competing interests.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was funded by grants from the Basic Science Research Program, through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2022R1A2C1006125 to Juhyun Song).
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary Table 1
The list of common increased and decreased genes in both groups
cnr-11-159-s001.xls
REFERENCES
- 1. Androvic P, Kirdajova D, Tureckova J, Zucha D, Rohlova E, Abaffy P, Kriska J, Valny M, Anderova M, Kubista M, Valihrach L. Decoding the transcriptional response to ischemic stroke in young and aged mouse brain. Cell Rep 2020;31:107777.
- 2. Norrving B, Barrick J, Davalos A, Dichgans M, Cordonnier C, Guekht A, Kutluk K, Mikulik R, Wardlaw J, Richard E, Nabavi D, Molina C, Bath PM, Stibrant Sunnerhagen K, Rudd A, Drummond A, Planas A, Caso V. Action plan for stroke in Europe 2018-2030. Eur Stroke J 2018;3:309-336.
- 3. Koistinaho M, Koistinaho J. Interactions between Alzheimer’s disease and cerebral ischemia--focus on inflammation. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 2005;48:240-250.
- 4. Shi J, Gu JH, Dai CL, Gu J, Jin X, Sun J, Iqbal K, Liu F, Gong CX. O-GlcNAcylation regulates ischemia-induced neuronal apoptosis through AKT signaling. Sci Rep 2015;5:14500.
- 5. Querfurth HW, LaFerla FM. Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 2010;362:329-344.
- 6. Hachinski V, Einhäupl K, Ganten D, Alladi S, Brayne C, Stephan BC, Sweeney MD, Zlokovic B, Iturria-Medina Y, Iadecola C, Nishimura N, Schaffer CB, Whitehead SN, Black SE, Østergaard L, Wardlaw J, Greenberg S, Friberg L, Norrving B, Rowe B, Joanette Y, Hacke W, Kuller L, Dichgans M, Endres M, Khachaturian ZS. Preventing dementia by preventing stroke: the Berlin Manifesto. Alzheimers Dement 2019;15:961-984.
- 7. Gandy S, DeKosky ST. Toward the treatment and prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: rational strategies and recent progress. Annu Rev Med 2013;64:367-383.
- 8. Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer’s disease results from the cerebral accumulation and cytotoxicity of amyloid beta-protein. J Alzheimers Dis 2001;3:75-80.
- 9. GBD 2017 US Neurological Disorders Collaborators. Feigin VL, Vos T, Alahdab F, Amit AM, Bärnighausen TW, Beghi E, Beheshti M, Chavan PP, Criqui MH, Desai R, Dhamminda Dharmaratne S, Dorsey ER, Wilder Eagan A, Elgendy IY, Filip I, Giampaoli S, Giussani G, Hafezi-Nejad N, Hole MK, Ikeda T, Owens Johnson C, Kalani R, Khatab K, Khubchandani J, Kim D, Koroshetz WJ, Krishnamoorthy V, Krishnamurthi RV, Liu X, Lo WD, Logroscino G, Mensah GA, Miller TR, Mohammed S, Mokdad AH, Moradi-Lakeh M, Morrison SD, Shivamurthy VK, Naghavi M, Nichols E, Norrving B, Odell CM, Pupillo E, Radfar A, Roth GA, Shafieesabet A, Sheikh A, Sheikhbahaei S, Shin JI, Singh JA, Steiner TJ, Stovner LJ, Wallin MT, Weiss J, Wu C, Zunt JR, Adelson JD, Murray CJ. Burden of neurological disorders across the US from 1990-2017: a Global Burden of Disease study. JAMA Neurol 2021;78:165-176.
- 10. Seshadri S, Wolf PA. Lifetime risk of stroke and dementia: current concepts, and estimates from the Framingham Study. Lancet Neurol 2007;6:1106-1114.
- 11. Waziry R, Chibnik LB, Bos D, Ikram MK, Hofman A. Risk of hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke in patients with Alzheimer disease: a synthesis of the literature. Neurology 2020;94:265-272.
- 12. Attems J, Jellinger KA, Lintner F. Alzheimer’s disease pathology influences severity and topographical distribution of cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Acta Neuropathol 2005;110:222-231.
- 13. Costa AS, Pinho J, Kučikienė D, Reich A, Schulz JB, Reetz K. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in amyloid-positive patients from a memory clinic cohort. J Alzheimers Dis 2021;79:1661-1672.
- 14. Fonarow GC, Reeves MJ, Zhao X, Olson DM, Smith EE, Saver JL, Schwamm LH. Get With the Guidelines-Stroke Steering Committee and Investigators. Age-related differences in characteristics, performance measures, treatment trends, and outcomes in patients with ischemic stroke. Circulation 2010;121:879-891.
- 15. Desmond DW, Moroney JT, Sano M, Stern Y. Mortality in patients with dementia after ischemic stroke. Neurology 2002;59:537-543.
- 16. Hénon H, Durieu I, Lebert F, Pasquier F, Leys D. Influence of prestroke dementia on early and delayed mortality in stroke patients. J Neurol 2003;250:10-16.
- 17. Saposnik G, Kapral MK, Cote R, Rochon PA, Wang J, Raptis S, Mamdani M, Black SE. Is pre-existing dementia an independent predictor of outcome after stroke? A propensity score-matched analysis. J Neurol 2012;259:2366-2375.
- 18. Saposnik G, Cote R, Rochon PA, Mamdani M, Liu Y, Raptis S, Kapral MK, Black SE. Registry of the Canadian Stroke Network. Stroke Outcome Research Canada (SORCan) Working Group. Care and outcomes in patients with ischemic stroke with and without preexisting dementia. Neurology 2011;77:1664-1673.
- 19. Zupanic E, von Euler M, Winblad B, Xu H, Secnik J, Kramberger MG, Religa D, Norrving B, Garcia-Ptacek S. Mortality after ischemic stroke in patients with Alzheimer’s disease dementia and other dementia disorders. J Alzheimers Dis 2021;81:1253-1261.
- 20. Moskowitz MA, Lo EH, Iadecola C. The science of stroke: mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron 2010;67:181-198.
- 21. de la Torre JC. Cerebral hemodynamics and vascular risk factors: setting the stage for Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2012;32:553-567.
- 22. Kalaria RN. The role of cerebral ischemia in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 2000;21:321-330.
- 23. Diener HC, Sacco RL, Yusuf S, Cotton D, Ounpuu S, Lawton WA, Palesch Y, Martin RH, Albers GW, Bath P, Bornstein N, Chan BP, Chen ST, Cunha L, Dahlöf B, De Keyser J, Donnan GA, Estol C, Gorelick P, Gu V, Hermansson K, Hilbrich L, Kaste M, Lu C, Machnig T, Pais P, Roberts R, Skvortsova V, Teal P, Toni D, VanderMaelen C, Voigt T, Weber M, Yoon BW. Prevention Regimen for Effectively Avoiding Second Strokes (PRoFESS) study group. Effects of aspirin plus extended-release dipyridamole versus clopidogrel and telmisartan on disability and cognitive function after recurrent stroke in patients with ischaemic stroke in the Prevention Regimen for Effectively Avoiding Second Strokes (PRoFESS) trial: a double-blind, active and placebo-controlled study. Lancet Neurol 2008;7:875-884.
- 24. Yu H, Yang C, Chen S, Huang Y, Liu C, Liu J, Yin W. Comparison of the glycopattern alterations of mitochondrial proteins in cerebral cortex between rat Alzheimer’s disease and the cerebral ischemia model. Sci Rep 2017;7:39948.
- 25. Chin Y, Kishi M, Sekino M, Nakajo F, Abe Y, Terazono Y, Hiroyuki O, Kato F, Koizumi S, Gachet C, Hisatsune T. Involvement of glial P2Y1 receptors in cognitive deficit after focal cerebral stroke in a rodent model. J Neuroinflammation 2013;10:95.
- 26. Yamauchi K, Imai T, Shimazawa M, Iwama T, Hara H. Effects of ticagrelor in a mouse model of ischemic stroke. Sci Rep 2017;7:12088.
- 27. Eimer WA, Vassar R. Neuron loss in the 5XFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease correlates with intraneuronal Aβ42 accumulation and Caspase-3 activation. Mol Neurodegener 2013;8:2.
- 28. Forner S, Kawauchi S, Balderrama-Gutierrez G, Kramár EA, Matheos DP, Phan J, Javonillo DI, Tran KM, Hingco E, da Cunha C, Rezaie N, Alcantara JA, Baglietto-Vargas D, Jansen C, Neumann J, Wood MA, MacGregor GR, Mortazavi A, Tenner AJ, LaFerla FM, Green KN. Systematic phenotyping and characterization of the 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Data 2021;8:270.
- 29. Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B. Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014;30:2114-2120.
- 30. Dobin A, Davis CA, Schlesinger F, Drenkow J, Zaleski C, Jha S, Batut P, Chaisson M, Gingeras TR. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013;29:15-21.
- 31. Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G, Kim D, Kelley DR, Pimentel H, Salzberg SL, Rinn JL, Pachter L. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc 2012;7:562-578.
- 32. Liberzon A, Subramanian A, Pinchback R, Thorvaldsdóttir H, Tamayo P, Mesirov JP. Molecular signatures database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics 2011;27:1739-1740.
- 33. Huang W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 2009;4:44-57.
- 34. Gui S, Chen P, Liu Y, Chen Q, Cheng T, Lv S, Zhou T, Song Z, Xiao J, He W, Yuan S, Cheng Z. TUBA1C expression promotes proliferation by regulating the cell cycle and indicates poor prognosis in glioma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2021;577:130-138.
- 35. Zhu H, Hu X, Gu L, Jian Z, Li L, Hu S, Qiu S, Xiong X. TUBA1C is a prognostic marker in low-grade glioma and correlates with immune cell infiltration in the tumor microenvironment. Front Genet 2021;12:759953.
- 36. Zhang Y, Wang JY, Han W. A role for CMTM7 in BCR expression and survival in B-1a but not B-2 cells. Int Immunol 2014;26:47-57.
- 37. Zhu Q, Xue K, Guo HW, Deng FF, Yang YH. Interaction of the CMTM7 rs347134 polymorphism with dietary patterns and the risk of obesity in Han Chinese male children. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020;17:1515.
- 38. Chen Q, Song H, Liu C, Xu J, Wei C, Wang W, Han F. The interaction of EphA4 with PDGFRβ regulates proliferation and neuronal differentiation of neural progenitor cells in vitro and promotes neurogenesis in vivo
. Front Aging Neurosci 2020;12:7.
- 39. Zhao Y, He J, Li Y, Lv S, Cui H. NUSAP1 potentiates chemoresistance in glioblastoma through its SAP domain to stabilize ATR. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2020;5:44.
- 40. Chui R, Dorovini-Zis K. Regulation of CCL2 and CCL3 expression in human brain endothelial cells by cytokines and lipopolysaccharide. J Neuroinflammation 2010;7:1.
- 41. Marciniak E, Faivre E, Dutar P, Alves Pires C, Demeyer D, Caillierez R, Laloux C, Buée L, Blum D, Humez S. The chemokine MIP-1α/CCL3 impairs mouse hippocampal synaptic transmission, plasticity and memory. Sci Rep 2015;5:15862.
- 42. Keswani T, Roland J, Herbert F, Delcroix-Genete D, Bauderlique-Le Roy H, Gaayeb L, Cazenave PA, Pied S. Expression of CD300lf by microglia contributes to resistance to cerebral malaria by impeding the neuroinflammation. Genes Immun 2020;21:45-62.
- 43. Visan I. Alzheimer’s disease microglia. Nat Immunol 2017;18:876.
- 44. Ofengeim D, Mazzitelli S, Ito Y, DeWitt JP, Mifflin L, Zou C, Das S, Adiconis X, Chen H, Zhu H, Kelliher MA, Levin JZ, Yuan J. RIPK1 mediates a disease-associated microglial response in Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2017;114:E8788-E8797.
- 45. Kanno M, Suzuki S, Fujiwara T, Yokoyama A, Sakamoto A, Takahashi H, Imai Y, Tanaka J. Functional expression of CCL6 by rat microglia: a possible role of CCL6 in cell-cell communication. J Neuroimmunol 2005;167:72-80.
- 46. Cowell RM, Xu H, Galasso JM, Silverstein FS. Hypoxic-ischemic injury induces macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha expression in immature rat brain. Stroke 2002;33:795-801.
- 47. Zhu M, Allard JS, Zhang Y, Perez E, Spangler EL, Becker KG, Rapp PR. Age-related brain expression and regulation of the chemokine CCL4/MIP-1β in APP/PS1 double-transgenic mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2014;73:362-374.
- 48. Kan MJ, Lee JE, Wilson JG, Everhart AL, Brown CM, Hoofnagle AN, Jansen M, Vitek MP, Gunn MD, Colton CA. Arginine deprivation and immune suppression in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 2015;35:5969-5982.
- 49. Shibata N, Kawarai T, Lee JH, Lee HS, Shibata E, Sato C, Liang Y, Duara R, Mayeux RP, St George-Hyslop PH, Rogaeva E. Association studies of cholesterol metabolism genes (CH25H, ABCA1 and CH24H) in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 2006;391:142-146.
- 50. Carmona S, Zahs K, Wu E, Dakin K, Bras J, Guerreiro R. The role of TREM2 in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Lancet Neurol 2018;17:721-730.
- 51. Rothman SM, Tanis KQ, Gandhi P, Malkov V, Marcus J, Pearson M, Stevens R, Gilliland J, Ware C, Mahadomrongkul V, O’Loughlin E, Zeballos G, Smith R, Howell BJ, Klappenbach J, Kennedy M, Mirescu C. Human Alzheimer’s disease gene expression signatures and immune profile in APP mouse models: a discrete transcriptomic view of Aβ plaque pathology. J Neuroinflammation 2018;15:256.
- 52. Law AH, Chow CM, Jiang L. Secretory carrier membrane proteins. Protoplasma 2012;249:269-283.
- 53. Sze CI, Bi H, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Filley CM, Martin LJ. Selective regional loss of exocytotic presynaptic vesicle proteins in Alzheimer’s disease brains. J Neurol Sci 2000;175:81-90.
- 54. Vosseller K, Trinidad JC, Chalkley RJ, Specht CG, Thalhammer A, Lynn AJ, Snedecor JO, Guan S, Medzihradszky KF, Maltby DA, Schoepfer R, Burlingame AL. O-linked N-acetylglucosamine proteomics of postsynaptic density preparations using lectin weak affinity chromatography and mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics 2006;5:923-934.
- 55. Wani WY, Chatham JC, Darley-Usmar V, McMahon LL, Zhang J. O-GlcNAcylation and neurodegeneration. Brain Res Bull 2017;133:80-87.
- 56. Mangialasche F, Baglioni M, Cecchetti R, Kivipelto M, Ruggiero C, Piobbico D, Kussmaul L, Monastero R, Brancorsini S, Mecocci P. Lymphocytic mitochondrial aconitase activity is reduced in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. J Alzheimers Dis 2015;44:649-660.
- 57. Bettcher BM, Tansey MG, Dorothée G, Heneka MT. Peripheral and central immune system crosstalk in Alzheimer disease - a research prospectus. Nat Rev Neurol 2021;17:689-701.
- 58. Zhang Y, Fung IT, Sankar P, Chen X, Robison LS, Ye L, D’Souza SS, Salinero AE, Kuentzel ML, Chittur SV, Zhang W, Zuloaga KL, Yang Q. Depletion of NK cells improves cognitive function in the Alzheimer disease mouse model. J Immunol 2020;205:502-510.
- 59. Pietronigro E, Zenaro E, Constantin G. Imaging of leukocyte trafficking in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Immunol 2016;7:33.
- 60. Das R, Chinnathambi S. Microglial priming of antigen presentation and adaptive stimulation in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 2019;76:3681-3694.
- 61. Jackson J, Jambrina E, Li J, Marston H, Menzies F, Phillips K, Gilmour G. Targeting the synapse in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Neurosci 2019;13:735.
- 62. Jack CR Jr, Knopman DS, Jagust WJ, Shaw LM, Aisen PS, Weiner MW, Petersen RC, Trojanowski JQ. Hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers of the Alzheimer’s pathological cascade. Lancet Neurol 2010;9:119-128.
- 63. Gong Y, Lippa CF. Review: disruption of the postsynaptic density in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative dementias. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen 2010;25:547-555.
- 64. Aguilar BJ, Zhu Y, Lu Q. Rho GTPases as therapeutic targets in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 2017;9:97.
- 65. Rajaei S, Karima S, Sepasi Tehrani H, Shateri S, Mahmoodi Baram S, Mahdavi M, Mokhtari F, Alimohammadi A, Tafakhori A, Amiri A, Aghamollaii V, Fatemi H, Rajabibazl M, Kobarfard F, Gorji A. Conformational change and GTPase activity of human tubulin: a comparative study on Alzheimer’s disease and healthy brain. J Neurochem 2020;155:207-224.