ABSTRACT
Recently, mobile health care has been applied to manage diabetes requiring self-management. Health care by mobile applications (apps) has a great advantage when applied to patients with diabetes; the adherence to self-management activities for diabetes can be improved through mobile apps. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has cleared and approved the use of some mobile apps as medical devices for the management of diabetes since 2010. However, mobile apps may not be effective for all patients. We here report the effect of use of mobile-based diabetes care app (Healthy-note app) for 2 patients with diabetes, and discuss issues and strategies for effective mobile intervention. Further study is needed on improving patient's participation to increase the effect of management via a mobile app.
-
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Self-Management; Healthcare; Telehealth; Smartphone
INTRODUCTION
Mobile health care which is the use of mobile technology in health care and public health has been continuously developed in recent decades [
1]. Recently, it has been applied to manage various acute and chronic diseases, such as diabetes, obesity, mental health, and smoking secession, with diabetes being the most common disease among them [
2].
Self-management is very important for patients with diabetes, and health care provided via mobile applications (apps) has a great advantage when applied to patients with diabetes; the adherence to activities for the management of diabetes, such as regular medication and insulin injection, self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG), diet, and exercise, can be improved through mobile apps. One randomized controlled trial reported that traditional intervention methods could not provide adequate blood glucose control, while a mobile diabetes intervention method improved clinical outcomes [
3]. The fact that the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has provided clearance and approval for the use of some diabetes management apps as medical devices since 2010 [
4] implies that mobile health care is considered effective in the management of diabetes.
Hood et al. [
4] suggested that the contents of apps for diabetes care could be classified into 2 categories: monitoring tasks (diabetes-specific self-management tasks, weight and blood pressure tracking, etc.) and education. Education-related content is only provided by 16%–35% of total apps. It is important to provide not only monitoring functions but also feedback of the patient's own recordings. However, only a small number of apps provide content for personalized education.
We have evaluated the effect of use of the mobile app (Healthy-note app; CVnet, Suwon, Korea) on the management of diabetes. In the study with the Healthy-note app, the mobile intervention group showed improvements in hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) and total cholesterol levels, which was not observed in the control group (conventional intervention). The percentage of subjects who achieved the HbA1c treatment goal (< 7.0%) was significantly higher in the mobile intervention group than in the control group. However, even in the mobile intervention group, the clinical outcomes were different depending on compliance evaluated by the number of personal glucose recordings. The HbA1c level was only reduced in the good-user group compared with the poor-user and control groups [
5]. This suggested that mobile apps may not be effective for all patients with diabetes. We report the case of 2 patients who used mobile-based diabetes care that resulted in contrasting findings and discuss related issues and strategies for effective intervention.
CASE
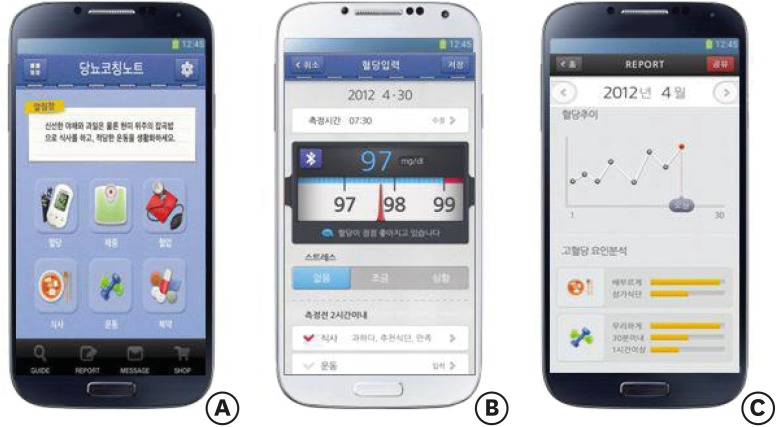
Out-patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) who visited the Diabetes Center at Kangbuk Samsung Hospital were instructed to conduct self-management activities for 6 months using the Healthy-note app. The Healthy-note app was designed to enable patients to record and monitor self-management activities (SMBG, diet, exercise, and medication), providing the patient with a self-learning function (
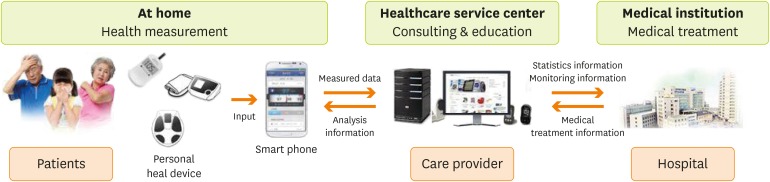
Figure 1). The professional care provider could send personally tailored messages to the patients and engage them in interactive communication through a messaging function (
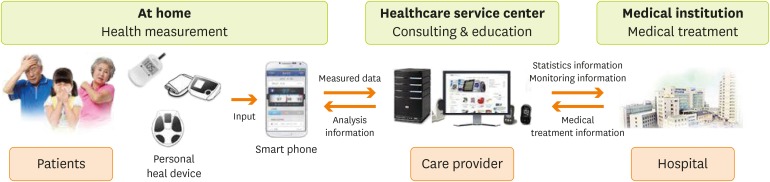
Figure 2).
Figure 1Features of Healthy-note app. (A) Main menu, (B) Blood glucose monitoring function (interfaced with a blood glucose monitoring device), and (C) A summary report on the status of glycemic control (Source: Yoo SH [
5]; reprinted with permission).
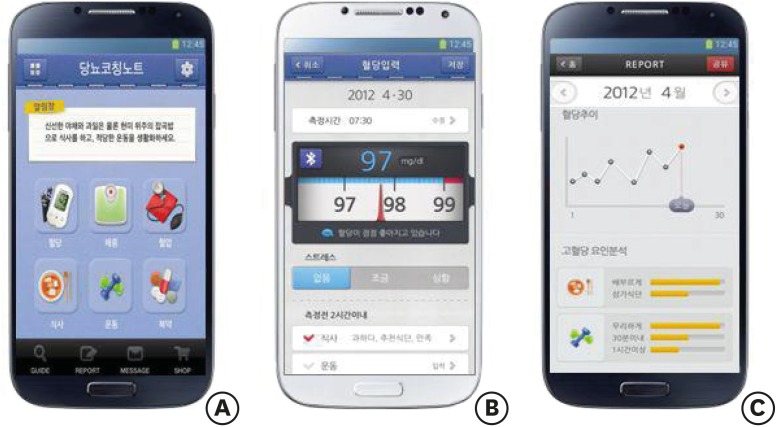
Figure 2Overall management system of the study (Source: Yoo SH [
5]; reprinted with permission).
Off-line education on diabetes management and instructions on how to use the Healthy-note app were given to subjects at the baseline of the study. The individual's goals for lifestyle modification were set with assistance from health professionals. The achievement level of each goal was evaluated using 4 levels (almost always, often, sometimes, and seldom) at 3 and 6 months after enrolling in this program. The study on this program was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Kangbuk Samsung Hospital (IRB No. KBC12093).
Case 1
Patient #1 was a 58-year-old man with a 12-year history of diabetes and a body mass index (BMI) of 31.5 kg/m
2. During the study period, he received a total of 10 messages containing medical information about hypoglycemic events, diet management, insulin therapy, and exercise. Patient-tailored advice was sent to remind the patient of his lifestyle modification goals and provide encouragement, information regarding blood glucose monitoring times, weight management, and coping with post-prandial hyperglycemia. The message confirmation rate was 70% (
Table 1).
Table 1Types and number of messages interactively transmitted between care provider and patient #1
Table 1
|
Message type |
No. of messages sent by the care provider |
No. of messages read by patient #1 |
|
Medical information |
5 |
3 |
|
Patient-tailored advice |
5 |
4 |
|
Technology-related information |
0 |
0 |
|
Total |
10 |
7 |
Two goals for participant's lifestyle modification set at baseline were as follows; one was “I'll walk or ride a bike for an hour for at least 5 days a week.” and the other goal was “I'll not miss the daily insulin injection.” The achievement of each goal was evaluated at the second visit, 3 months after engagement. It was found that he performed his goals well (level: almost always). The professional care provider adjusted his previous 2 goals to walking or riding a bike only. At the third visit at 6 months after engagement, he replied that the performance of his goal was well-achieved again. During the whole study period, he achieved his goals well.
The total number of recorded self-management activities was 235, and the details were described in
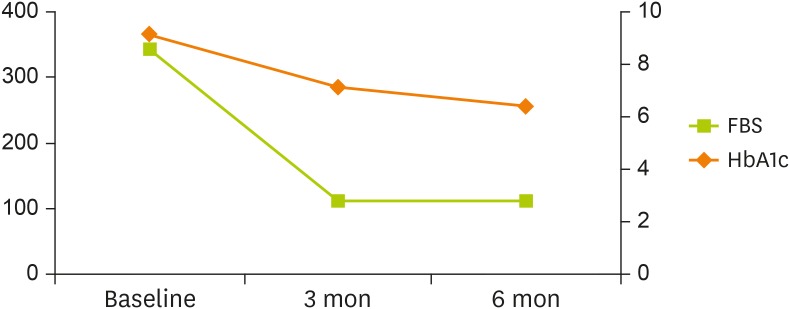
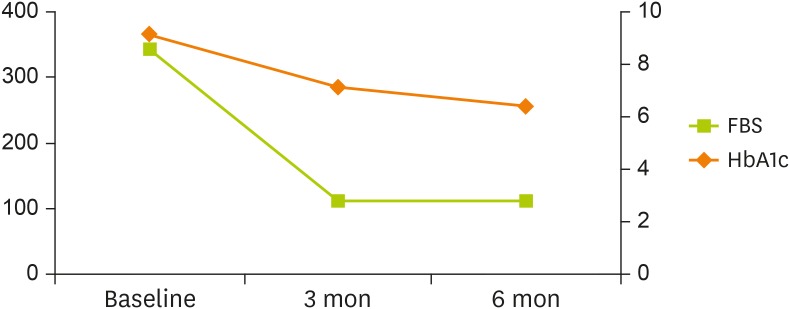
Table 2. HbA1c decreased from 9.1% to 6.4%, and fasting blood sugar (FBS) decreased from 343 mg/dL to 112 mg/dL (
Table 3,
Figure 3).
Table 2Types and number of self-management activities recorded by patient #1
Table 2
|
Type |
No. |
|
SMBG |
169 |
|
Exercise |
52 |
|
Diet |
14 |
|
Total |
235 |
Table 3Changes in metabolic parameters of patient #1
Table 3
|
Time |
HbA1c, % |
FBS, mg/dL |
Weight, kg |
BMI, kg/m2
|
|
Baseline |
9.1 |
343 |
79.8 |
31.5 |
|
3 mon |
7.1 |
112 |
82.1 |
32.4 |
|
6 mon |
6.4 |
112 |
82.0 |
32.4 |
Figure 3
Changes in FBS and HbA1c levels of patient #1 over 6 months.
FBS, fasting blood sugar; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c.
Case 2
Patient #2 was a 52-year-old man with a 13-year history of diabetes and a BMI of 25.2 kg/m
2. During the study period, a total of 16 messages was transmitted including FBS levels, diet management, and hypoglycemic events. The themes of the patient-tailored advice were as follows; reminding the patient of the goals for lifestyle modification and providing encouragement, information regarding blood glucose monitoring times, recommendation about more frequent monitoring of blood glucose, and coping with post-prandial hyperglycemia. A technology-related information message was sent to him for an update of the app. The message confirmation rate was 62.5% (
Table 4).
Table 4Types and number of messages interactively transmitted between care provider and patient #2
Table 4
|
Message type |
No. of messages sent by the care provider |
No. of messages read by patient #2 |
|
Medical information |
6 |
3 |
|
Patient-tailored advice |
9 |
6 |
|
Technology-related information |
1 |
1 |
|
Total |
16 |
10 |
Two goals for participant's lifestyle modification set at baseline were as follows; one goal was “I'll eat slowly.” and the other was “I'll cut down on smoking (less than 5 cigarettes a day).” The achievement of each goal was evaluated at the second visit. He was found to perform fairly (level: often). He was advised to make an effort to achieve the 2 goals continuously and include an additional goal: “I'll exercise after dinner for an hour, 3–4 times a week.” At the final evaluation, his performance status had worsened (level: sometimes) compared to the second visit.
The number of recorded self-management activities was 22, and the detailed counts were described in
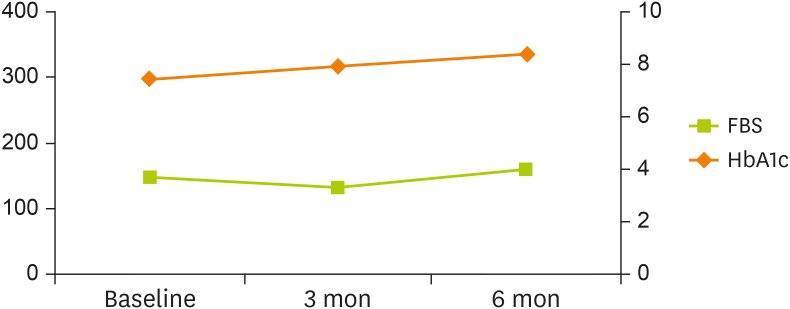
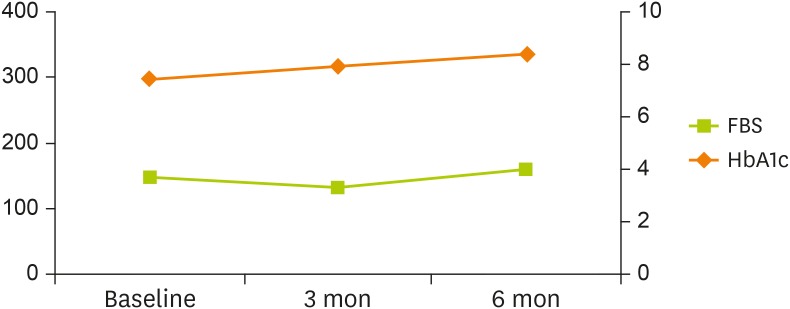
Table 5, showing a poor result. HbA1c increased from 7.4% to 8.4%, and FBS rose from 149 mg/dL to 159 mg/dL (
Table 6,
Figure 4).
Table 5Types and number of self-management activities recorded by patient #2
Table 5
|
Type |
No. |
|
SMBG |
27 |
|
Exercise |
0 |
|
Diet |
5 |
|
Total |
32 |
Table 6Changes in metabolic parameters of patient #2
Table 6
|
Time |
HbA1c, % |
FBS, mg/dL |
Weight, kg |
BMI, kg/m2
|
|
Baseline |
7.4 |
149 |
76.6 |
25.2 |
|
3 mon |
7.9 |
134 |
78.3 |
25.7 |
|
6 mon |
8.4 |
159 |
79.8 |
26.2 |
Figure 4
Changes in FBS and HbA1c levels of patient #2 over 6 months.
FBS, fasting blood sugar; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c.
DISCUSSION
The general characteristics of both patients were similar; both were obese and males. They were in their 50's and had suffered from diabetes for more than 10 years. Nevertheless, we found contrasting clinical results depending on the extent of participation and adherence to the use of the Healthy-note app. It is possible that participation and adherence of patients might affect clinical outcomes of which the evidence is limited in mobile health care.
The advantages of mobile care for diabetes are not only recording and monitoring blood glucose levels but helping to achieve lifestyle modifications. The Healthy-note app study showed significant changes in HbA1c levels based on performance level of lifestyle management goals, confirming that maintenance of modifying lifestyle activities is important for diabetes care [
5]. Similarly, patient #1 achieved his goals well throughout the study period and showed improvement in the HbA1c status, whereas patient #2 did not. Interaction with patients seems to be important to set feasible goals and provide continuous encouragement.
There is no doubt that the adherence of mobile-based intervention is affected by many factors: personal characteristics, behavioral patterns, social supports, specific events, and etc. However, there is limited information as to which specific factors affect substantially adherence to mobile health care. A meta-analysis on the effect of mobile-based intervention for diabetes showed that there were no differences in glycemic control according to personal characteristics or specific intervention strategies [
6]. Hence, it is meaningful to find ways to increase the use of mobile apps in clinical settings and improve the adherence to it. Such efforts may help achieve good clinical outcomes in the management of diabetes.
It was reported that improved glucose control for an extended time was achieved by the good compliance group with an achievement rate of over 80% of an initially recommended SMBG frequency compared with the poor compliance group [
7]. The intervention study using the Healthy-note app showed that metabolic parameters, including HbA1c, only improved in the good-user group, which corresponds with the previous study. During the follow-up period of 6 months after the completion of the intervention period by the care provider, the frequency of app usage gradually decreased. There was no significant difference in the frequency of app usage between the good-user and poor-user groups at the end of the follow-up period. In addition, HbA1c levels significantly increased in all the groups (good-user, poor-user, and control groups) compared to at the beginning of the follow-up period [
5]. These results suggested that appropriate intervention by the care provider played an important role in successful mobile-based diabetes intervention.
User-tailored interventions may be a good strategy for successful mobile-based diabetes care. Waki et al. [
8] demonstrated that a smartphone-based self-management support system was effective for the management of T2DM patients. They reported that the system provided a real-time report on nutritional intake and tailored advice based on the user's dietary recordings and blood glucose levels. These approaches may make the mobile diabetes intervention more effective and powerful. In our study, care providers analyzed the personal recordings and sent customized messages for each situation, such as hyper- or hypoglycemic events. However, integrative tailored messages reflecting dietary intake were not provided. This limitation was because a clinical dietitian was not included as a care provider.
Taken together, further study is required to improve patients' participations, which increases the efficacy of management via a mobile app. In particular, as the number of recorded dietary information was significantly lower compared with SMBG information in both cases, the method of diet recording needs to be upgraded for effective self-diet management via an app.
NOTES
-
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
REFERENCES
- 1. Free C, Phillips G, Felix L, Galli L, Patel V, Edwards P. The effectiveness of M-health technologies for improving health and health services: a systematic review protocol. BMC Res Notes 2010;3:250.
- 2. Fiordelli M, Diviani N, Schulz PJ. Mapping mHealth research: a decade of evolution. J Med Internet Res 2013;15:e95.
- 3. Quinn CC, Shardell MD, Terrin ML, Barr EA, Ballew SH, Gruber-Baldini AL. Cluster-randomized trial of a mobile phone personalized behavioral intervention for blood glucose control. Diabetes Care 2011;34:1934-1942.
- 4. Hood M, Wilson R, Corsica J, Bradley L, Chirinos D, Vivo A. What do we know about mobile applications for diabetes self-management? A review of reviews. J Behav Med 2016;39:981-994.
- 5. Yoo SH. Effects of smartphone application on diabetes management: randomized controlled trial [master's thesis]. Seoul: Ewha Womans University; 2014.
- 6. Liang X, Wang Q, Yang X, Cao J, Chen J, Mo X, Huang J, Wang L, Gu D. Effect of mobile phone intervention for diabetes on glycaemic control: a meta-analysis. Diabet Med 2011;28:455-463.
- 7. Cho JH, Chang SA, Kwon HS, Choi YH, Ko SH, Moon SD, Yoo SJ, Song KH, Son HS, Kim HS, Lee WC, Cha BY, Son HY, Yoon KH. Long-term effect of the internet-based glucose monitoring system on HbA1c reduction and glucose stability: a 30-month follow-up study for diabetes management with a ubiquitous medical care system. Diabetes Care 2006;29:2625-2631.
- 8. Waki K, Fujita H, Uchimura Y, Omae K, Aramaki E, Kato S, Lee H, Kobayashi H, Kadowaki T, Ohe K. DialBetics: a novel smartphone-based self-management support system for type 2 diabetes patients. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2014;8:209-215.