ABSTRACT
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) associated with liver failure is accompanied by hyperammonemia, severe inflammation, depression, anxiety, and memory deficits as well as liver injury. Recent studies have focused on the liver-brain-inflammation axis to identify a therapeutic solution for patients with HE. Lipocalin-2 is an inflammation-related glycoprotein that is secreted by various organs and is involved in cellular mechanisms including iron homeostasis, glucose metabolism, cell death, neurite outgrowth, and neurogenesis. In this study, we investigated that the roles of lipocalin-2 both in the brain cortex of mice with HE and in Neuro-2a (N2A) cells. We detected elevated levels of lipocalin-2 both in the plasma and liver in a bile duct ligation mouse model of HE. We confirmed changes in cytokine expression, such as interleukin-1β, cyclooxygenase 2 expression, and iron metabolism related to gene expression through AKT-mediated signaling both in the brain cortex of mice with HE and N2A cells. Our data showed negative effects of hepatic lipocalin-2 on cell survival, iron homeostasis, and neurite outgrowth in N2A cells. Thus, we suggest that regulation of lipocalin-2 in the brain in HE may be a critical therapeutic approach to alleviate neuropathological problems focused on the liver-brain axis.
-
Keywords: Hepatic encephalopathy (HE); Lipocalin-2; Hyperammonemia; Neuron; Brain inflammation
INTRODUCTION
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE), which is caused by liver failure and portosystemic shunting, is accompanied by neurological or psychiatric dysfunction as well as hyperammonemia, severe inflammation, and cholinergic neuronal dysfunction [
1,
2]. In addition, patients with HE exhibit various neurological features such as cognitive impairment, personality changes, sleep disturbances, motor abnormalities, depressive symptoms, brain edema, and brain atrophy [
3,
4,
5,
6]. In the central nervous system (CNS), hyperammonemia leads to astrocyte swelling [
7], an impaired glutamate system [
8], and mitochondrial dysfunction [
9] and ultimately contributes to glial and neuronal dysfunction. A bile duct ligation (BDL) model is commonly used as a mouse model of HE; this model exhibits memory impairment, decreased brain cholinergic activity, hyperammonemia, increased blood-brain barrier permeability, and motor dysfunction [
10,
11,
12,
13,
14]. In this study, we used a BDL mouse model to evaluate for neurological changes in HE.
Recent studies have highlighted the liver-brain-inflammation axis to elucidate the neurological alterations caused by liver failure [
15,
16]. Several studies have mentioned that increased levels of endotoxin and pro-inflammatory cytokines in blood plasma cause depressive-like behavior and memory loss [
17,
18,
19,
20]. Liver failure with liver inflammation is associated with Kupffer cell activation and high secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-6 [
21,
22,
23]. Some studies have reported that TNF-α is a crucial factor related to sleep disturbances, fatigue, and depressive symptoms [
24,
25]. The liver is innervated by vagal nerve afferents, and cytokines secreted by the liver can activate these [
26,
27]. Inflammatory mediators such as cytokines and chemokines in the blood regulate immune cell infiltration and induce behavioral changes in the brains of BDL model mice [
28,
29].
Lipocalin-2, which is also known as neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), is an approximately 25-kDa glycoprotein [
30] that is expressed in human neutrophils [
31]. Lipocalin-2 also modulates complex cellular mechanisms including innate immune responses [
32], cell proliferation [
33], cellular apoptosis [
34], pathogen clearance [
35], metabolism homeostasis [
36], tumor metastasis [
37], and iron metabolism [
32]. In addition, lipocalin-2 modulates metabolic responses such as hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and glucose metabolism through nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) signaling [
38].
In the CNS, the lipocalin-2 receptor is highly expressed in neurons, microglia, and astrocytes [
39], and lipocalin-2 has been shown to control iron accumulation, amyloid beta (Aβ) accumulation, and astrocyte function in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) model brains [
40,
41]. A current study reports that lipocalin-2 is a critical inflammatory mediator that controls the interaction between neurons and microglia and is involved in cognitive function [
42].
Lipocalin-2 is known to regulate inflammatory responses through TNF receptor 2-mediated phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT, NF-κB [
43], and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) activation [
44]. High levels of hepatic lipocalin-2 are found in liver failure models and promote liver fibrosis by mediating by pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines [
45,
46]. One study mentions that hepatic lipocalin-2 is considered a prognostic factor in patients with liver failure and alcoholic hepatitis [
47].
Thus, we investigated the function and specific pathway of lipocalin-2 in the brains of mice in a BDL mouse model of HE. We also confirmed alterations in several inflammatory mediators in neuronal cells by lipocalin-2 treatment. In this study, we emphasized the importance of hepatic lipocalin-2 for neuronal cell function in the brain in HE, focusing on the liver-brain axis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
BDL surgery
Twelve-week-old wild-type C57BL/6J male mice (Koatech, Pyeongtaek, Korea) were housed in the Laboratory Animal Research Center, Chonnam National University (CNU), under a 16-hour light/8-hour dark cycle at 23°C with 60% humidity and given ad libitum access to water and food. Mice underwent BDL or a sham operation. BDL was performed using 5-0 black silk suture under 2% isoflurane anesthesia. Experiments were conducted two weeks postoperatively. The experiments were conducted following the recommendations of “96 Guidance for Animal Experiments” by the Animal Committee at CNU. The animal experimental protocol was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee at CNU (CNU IACUC-H-2022-8).
Cell cultures and treatment conditions
The Neuro-2a (N2A) cell line was cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 1 mM sodium pyruvate, and 100 U/mL penicillin-streptomycin. Cells were cultured at 5% CO2 at 37°C. The culture media was changed once every 2 days. We induced differentiation of N2A cells by adding 20 μM all-trans retinoic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) to DMEM containing 2% FBS, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, and 100 U/mL penicillin-streptomycin culture media. N2A cells were treated with or without 1 μg/mL mouse recombinant lipocalin-2 (50060-M08H; Sino Biological, Chesterbrook,PA, USA) and 30 mM NH4Cl (A9434; Sigma-Aldrich) for 24 hours.
RNA isolation and analysis
Total RNA was isolated using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions, and used as template to synthesize cDNA with TOPscript RT DryMix (dT18 plus; Enzynomics, Daejeon, Korea). The cDNAs were analyzed using the Applied Biosystems StepOnePlus real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) and Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Applied Biosystems). Based on the obtained cycle threshold values, the mRNA expression was calculated using the 2
−ΔΔCT method. All primers are listed in
Supplementary Table 1. Data were normalized to L32 (mouse) expression, which was determined using 5′-TCTGGTGAAGCCCAAGATGG-3′ (forward) and 5′-CTCTGGGTTTCCGCCAGT-3′ (reverse) primers.
The N2A cells and brain tissue were lysed in ice-cold radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer (Translab, Carpentersville, IL, USA) for 15 minutes on ice. The protein concentration of protein extract was quantified using a bicinchoninic acid protein assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Protein (50–70 μg) was separated on 10%–12% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and the protein was transferred onto polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF; Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA) membranes activated with absolute methanol. The PVDF membranes were incubated with 5% bovine albumin (GenDEPOT, Katy, TX, USA) and 5% skim milk (BD Bioscience, San Jose, CA, USA) in 1× Tris buffered saline with Tween 20 buffer for 1 hour and 30 minutes at room temperature. After incubation, the membranes were incubated with the following primary antibodies (1:1,000 dilution) overnight at 4°C: anti-p AKT (9271s; Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA), anti-AKT (UST4691p; Cell Signaling Technology), and anti-β-actin (MAB8929; AbFrontier, Seoul, Korea).
After the primary antibody incubation, the membranes were incubated with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labeled secondary antibody (1:5,000 dilution) for 2 hours at room temperature. The membranes were visualized using an enhanced chemiluminescence solution (Thermo Fisher Scientific) with Fusion Solo software (Vilber, Collégien, France). Protein expression was analyzed using ImageJ (provided from National Institutes of Health), the protein level was normalized to the β-actin protein level, and the phosphorylation of protein was normalized to the total form of the protein.
Lipocalin-2 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
Mouse plasma samples were analyzed using a sandwich ELISA to measure lipocalin-2 levels (MLCN20; R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA). All assays were performed as recommended by the manufacturers. Mouse plasma was mixed with 1X assay diluent and incubated for 2.5 hours at room temperature. After incubation, biotin conjugate was added to each sample, and the mixture was incubated for one hour at room temperature with gentle shaking. After incubation, 1X streptavidin-HRP solution was added to each sample, and they were incubated 45 minutes at room temperature with gentle shaking. After incubation, 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine substrate was added to each well, and they were incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature in the dark. After incubation, stop solution was added to each well, and lipocalin-2 was measured at 450 nm using an Epoch microplate reader.
Statistical analysis
All data are presented as the group mean ± standard error of the mean. Statistical analysis was conducted using unpaired 2-tailed t-test with Welch’s correction in Prism 8 (GraphPad Software Inc, La Jolla, CA, USA). Data were considered significant at p < 0.05, p < 0.01, and p < 0.005.
RESULTS
Lipocalin-2 levels are increased in the livers of BDL model mice
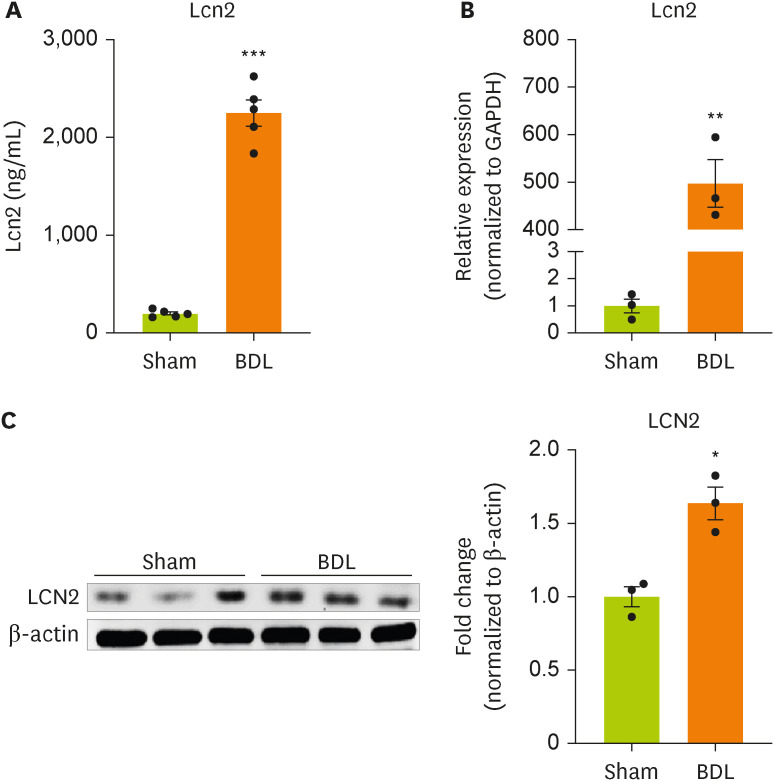
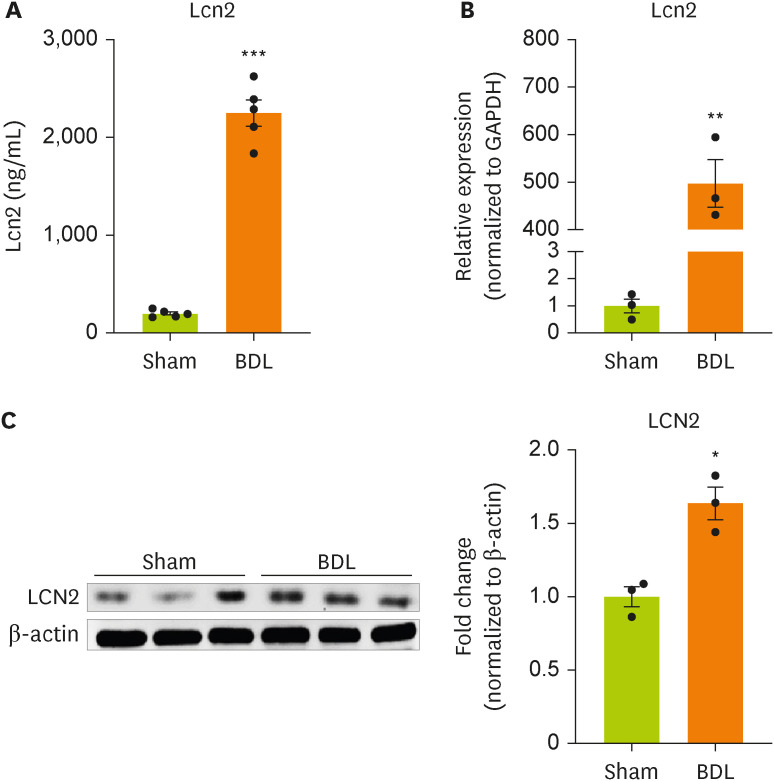
Changes in the concentration of plasma lipocalin-2 after BDL surgery were evaluated using ELISA (
Figure 1A). BDL surgery significantly increased the concentration of lipocalin in the blood of model mice compared with sham-operated mice. We examined whether BDL surgery regulated the gene and protein expression of lipocalin-2 in the impaired liver (
Figure 1B and 1C). BDL surgery increased the expression of lipocalin-2 mRNA and protein in liver tissue from model mice compared with sham-operated mice.
Figure 1
Lipocalin-2 gene expression is increased in the livers of BDL model mice.
(A) Lipocalin-2 levels measured by ELISA in sham-operated or BDL-treated mice. (B) RT-qPCR analysis of the total RNA isolated from liver tissues from sham-operated or BDL-treated mice. (C) Western blot analyses showing the expression of lipocalin-2 in liver tissues from sham-operated or BDL-treated mice. Data are reported as the mean ± standard deviation. All data were analyzed by 2-tailed Student’s t-test.
BDL, bile duct ligation; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction; Lcn2, lipocalin-2.
*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
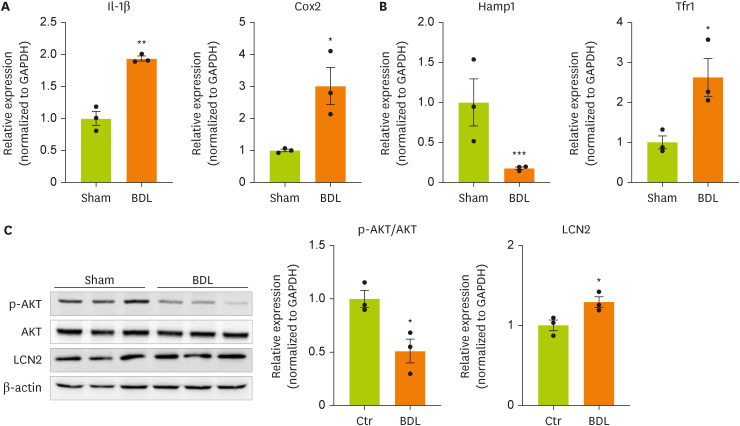
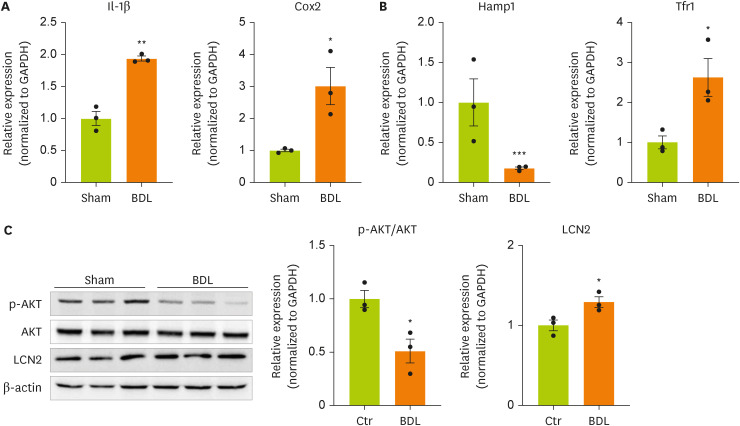
Lipocalin-2 signaling is activated in the brain cortices of BDL model mice.
We next examined the expression of genes and proteins related to inflammation, insulin resistance, and iron metabolism, which are known target genes of lipocalin-2, in the brain cortices of model mice. We measured the expression of inflammation-related genes in the brain cortices of BDL model mice (
Figure 2A). The gene expression of
IL-1β and cyclooxygenase-2 (
Cox-2) was confirmed to be increased by BDL surgery. This result indicates that inflammation is increased in the brain cortices of BDL model mice. BDL surgery decreased the expression of hepcidin antimicrobial peptide 1 (
Hamp1), a gene related to insulin resistance, and significantly increased the expression of transferrin receptor 1 (
Tfr1), which is related to iron metabolism (
Figure 2B). We measured the phosphorylation of AKT using western blot (
Figure 2C,
Supplementary Figure 1). BDL surgery induced insulin resistance through dephosphorylation of AKT (serine 473) in the cortex. Therefore, an increased concentration of lipocalin-2 induced by BDL surgery was confirmed to regulate the expression of the target genes of lipocalin-2.
Figure 2
Cytokine and iron metabolism gene expression and AKT phosphorylation are increased in the brain cortices in BDL model mice.
(A, B) RT-qPCR analysis of total RNA isolated from cortex tissues from sham-operated or BDL-treated mice. (C) Western blot analyses showing the expression of AKT and p-AKT in cortex tissues from sham-operated or BDL-treated mice. Data are reported as the mean ± standard deviation. All data were analyzed by 2-tailed Student’s t-test.
BDL, bile duct ligation; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction; Il, interleukin; Cox2, cyclooxygenase 2; Hamp1, hepcidin antimicrobial peptide 1; Tfr1, transferrin receptor 1; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; LCN2, lipocalin-2; Ctr, control.
*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
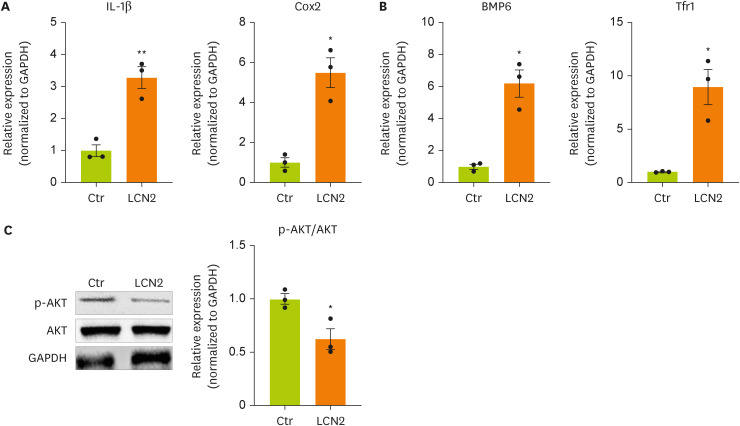
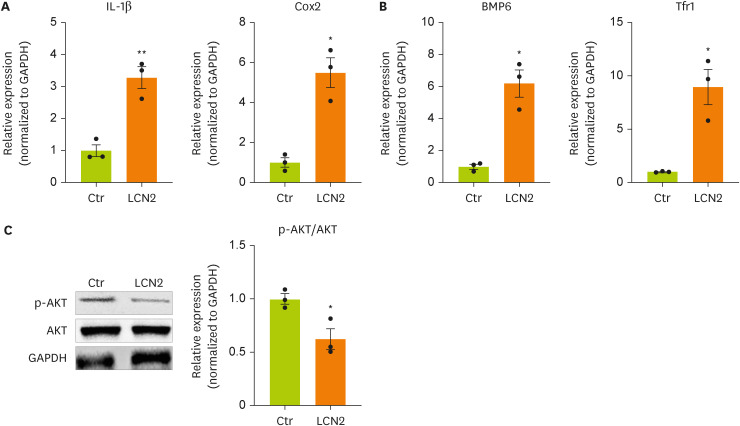
Lipocalin-2 regulates neuronal cell function through the AKT pathway
To induce an in vitro model of BDL surgery, neurons were treated with lipocalin-2. To determine whether lipocalin-2 regulates the intracellular metabolism of neuronal cells, we measured the mRNA and protein expression of factors related to inflammation, insulin resistance, and iron metabolism. The mRNA expression of
IL-1β and
Cox-2 in neuronal cells was increased by lipocalin-2 treatment (
Figure 3A). The mRNA expression of bone morphogenetic protein 6 (
Bmp6), which is related to insulin resistance, and
Tfr1, which is related to iron metabolism, in neuronal cells was increased by lipocalin-2 (
Figure 3B). We also confirmed dephosphorylation of AKT in neuronal cells by lipocalin-2 (
Figure 3C). These results indicate that lipocalin-2 regulates intracellular metabolism such as inflammation, insulin resistance, and iron metabolism in neuronal cells.
Figure 3
Cytokine and iron metabolism gene expression and AKT phosphorylation are increased by lipocalin-2 treatment in N2A cells.
(A, B) RT-qPCR analysis of the total RNA isolated from N2A cells. (C) Western blot analyses showing the expression of AKT and p-AKT in N2A cells. Data are reported as the mean ± standard deviation. All data were analyzed by 2-tailed Student’s t-test.
N2A, Neuro-2a; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction; Il, interleukin; Cox2, cyclooxygenase 2; Bmp6, bone morphogenetic protein 6; Tfr1, transferrin receptor 1; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; LCN2, lipocalin-2; Ctr, control.
*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
DISCUSSION
Herein, we investigated the roles of lipocalin-2 secreted by the liver in the brain HE using a BDL mouse model. First, we found elevated expression of lipocalin-2 both in the blood plasma and liver in BDL model mice compared with normal mice. According to a recent study, liver fibrosis caused by BDL causes inflammation, severe oxidative stress, and cellular apoptosis related to lipocalin-2 [
48]. One study reported that lipocalin-2 induced the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β through NF-κB activation in hepatocytes in liver disease [
49]. Another study mentioned that elevated serum levels of lipocalin-2 were due to increased secretion by the liver and led to IL-6 secretory signaling [
50]. Furthermore, increased levels of lipocalin-2 in plasma are linked to chronic liver failure and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and have the potential to predict liver recovery [
51,
52]. Elevated levels of lipocalin-2 in blood plasma are associated with some neurological diseases such as Parkinson’s disease [
53]. Furthermore, hepatic lipocalin-2 is increased in liver damage models and promotes inflammatory cytokines [
45,
46]. Given this evidence, elevated levels of lipocalin-2 both in the blood and liver may be related to liver dysfunction, increased inflammatory responses mediated by cytokines, and neurological changes.
Next, we observed significantly increased expression of
IL-1β, Cox2, and
Tfr1, reduced expression of
Tfr1, and reduced phosphorylation of AKT in the brain cortices of BDL model mice. One current study found elevated mRNA levels of lipocalin-2 in the brain cortex accompanied by hyperammonemia in HE [
54]. In the CNS, IL-1β is a major pro-inflammatory cytokine that aggravates inflammatory and immune responses [
55]. Increased levels of IL-1β disturb neuronal differentiation [
56], cell proliferation, neurite outgrowth, and apoptosis [
57,
58] in the brain [
59]. In addition, IL-1β can stimulate Cox2 activation in CNS cells and is involved in pain hypersensitivity [
60,
61,
62,
63]. Cox-2 is a major regulator of increased prostaglandin E2 (PGE
2) synthesis after an inflammatory response in cells [
60] through G protein-coupled receptors [
64,
65]. Increased expression of Cox2 in the CNS accelerates inflammation [
60] and is related to the neuropathogenesis of AD through the NF-κB pathway [
66,
67].
Based on our data, we assume that there is an increased inflammatory response, immune response, apoptosis, and pain hypersensitivity as well as reduced neuronal differentiation and suppressed neurite outgrowth in the brain cortices of BDL model mice. In the CNS, the PI3K/AKT pathway is a crucial signaling pathway that regulates inflammatory responses in CNS cells [
68] and is involved in neuronal differentiation [
69]. In addition, NF-κB signaling is induced by PI3K/AKT [
70,
71]. The PI3K/AKT pathway regulates the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and IL-1β in dendritic cells [
72], microglia [
73], and neurons [
74], production of anti-inflammatory cytokines [
75], and neuronal cell survival [
76].
Some studies have reported that lipocalin-2 promotes activation of PI3K/AKT signaling and induces cell proliferation [
77], and its promoter has a binding site for NF-κB [
78]. One study reported that lipocalin-2 attenuated the activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway and subsequently led to inhibition of cell proliferation [
79]. Based on this evidence, we speculate that lipocalin-2 may attenuate neuronal differentiation and increase neuroinflammation through increased secretion of inflammatory cytokines in the brain by suppression of AKT-mediated signaling.
Hamp1 is a small hormone peptide that is produced by hepatocytes and regulates iron metabolism [
80]. Hepcidin modulates iron absorption through iron homeostasis [
74]. Furthermore, the level of hepcidin has been correlated with liver dysfunction [
81]. One recent study showed that the overexpression of hepcidin in astrocytes inhibited brain damage due to Aβ toxicity [
80]. Aβ is a major pathological factor in AD [
82], and excessive accumulation and aggregation of Aβ cause memory impairment and cognitive dysfunction [
83]. Another study reported that hepcidin was strongly related to iron accumulation in the brain in AD and affected the progression of its neuropathogenesis [
84]. Our data showed that reduced levels of the
Hamp1 gene in the brain cortices of BDL model mice might be linked to a reduced cell protective effect and impaired iron metabolism in the brain in HE.
Finally, we confirmed increased levels of Il-1β, Cox-2, Bmp6, and Tfr1, reduced activation of AKT phosphorylation, and attenuation of the
Hamp1 gene in N2A cells after lipocalin-2 treatment. To mimic hepatic lipocalin-2 from passing from the blood circulation into the brain, we treated N2A cells with lipocalin synthesized protein. The increased levels of IL-1β and Cox-2 observed in N2A cells are similar to the expression patterns of these factors in the brain cortex. Bmp6 is considered a neurotrophic factor [
85] and negative regulator of neurogenesis in the brains of patients with AD [
86]. One study observed high levels of Bmp6 in the dentate gyrus accompanied by reduced neurogenesis and excessive Aβ plaque accumulation [
87], which are involved in memory formation and synaptic failure in patients with AD [
88]. Moreover, the
Tfr1 gene regulates iron overload and ferroptosis [
89,
90,
91]. Some studies have illustrated that increased expression of Tfr1 attenuates neurite outgrowth [
92], impairs iron homeostasis [
93], disrupts the dopamine system [
94], and contributes to poor motor coordination [
95]. Another study reported that Tfr1 could modulate iron-mediated immune responses through the NF-κB pathway [
96]. Considering our data and previous reports, lipocalin-2 may reduce neurite outgrowth and dysregulate iron-dependent mechanisms, inflammatory responses, and cell death in neurons by increasing the expression of
Bmp6 and
Tfr1 genes.
Although there are many limitations to fully elucidating the roles of lipocalin-2 in the brain in HE, we can conclude several points in this study. First, HE causes elevated levels of lipocalin-2 both in the blood circulation and in the liver. Second, hepatic lipocalin-2 may control inflammatory responses by regulating IL-1β secretion, pain hyperactivity by regulating Cox-2 expression, and iron metabolism by controlling Trf1 expression through AKT-mediated signaling in the brain cortex. Third, hepatic lipocalin-2 may accelerate inflammatory responses and cell death and dysregulate neurite outgrowth through iron-dependent mechanisms through AKT-mediated signaling in neurons.
Thus, the modulation of lipocalin-2 signaling in the brain may be a key target for treating neuropathological and neuropsychiatric issues in the brain in HE. Further studies on the roles of lipocalin-2 both in the brain and liver in liver failure are needed to identify the critical mechanisms of action of lipocalin-2. We also highlighted that lipocalin-2 is a cardinal protein to illustrate the mechanism of the liver-brain axis in patients with HE.
National Research Foundation of Koreahttps://doi.org/10.13039/501100003725
NRF-2022R1A2C1006125
Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospitalhttps://doi.org/10.13039/501100019780
HCRI 22019
NOTES
-
Funding: This study was supported by grant NRF-2022R1A2C1006125 (Juhyun Song) from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), Republic of Korea, and HCRI 22019 from the Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital Institute for Biomedical Science, Korea (Juhyun Song). The authors acknowledged Biorender.com in creating the figures.
-
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
-
Author Contributions:
Conceptualization: Jo D, Jung YS, Song J.
Data curation: Jo D, Jung YS, Song J.
Formal analysis: Jo D, Jung YS, Song J.
Funding acquisition: Song J.
Investigation: Jo D, Jung YS, Song J.
Project administration: Jo D, Jung YS, Song J.
Writing - original draft: Jo D, Song J.
Writing - review & editing: Song J.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary Figure 1
The protein level of lipocalin-2 is increased in BDL model mice cortex.
cnr-12-154-s002.ppt
REFERENCES
- 1. Ferenci P. Hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf) 2017;5:138-147.
- 2. Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J, Cordoba J, Ferenci P, Mullen KD, Weissenborn K, Wong P. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology 2014;60:715-735.
- 3. Giménez-Garzó C, Fiorillo A, Ballester-Ferré MP, Gallego JJ, Casanova-Ferrer F, Urios A, Benlloch S, Martí-Aguado D, San-Miguel T, Tosca J, Ríos MP, Montón C, Durbán L, Escudero-García D, Aparicio L, Felipo V, Montoliu C. A new score unveils a high prevalence of mild cognitive impairment in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Med 2021;10:2806.
- 4. Shalimar , Sheikh MF, Mookerjee RP, Agarwal B, Acharya SK, Jalan R. Prognostic role of ammonia in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2019;70:982-994.
- 5. Montagnese S, De Pittà C, De Rui M, Corrias M, Turco M, Merkel C, Amodio P, Costa R, Skene DJ, Gatta A. Sleep-wake abnormalities in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2014;59:705-712.
- 6. Woolf NJ, Butcher LL. Cholinergic systems mediate action from movement to higher consciousness. Behav Brain Res 2011;221:488-498.
- 7. Yang L, Magness ST, Bataller R, Rippe RA, Brenner DA. NF-κB activation in Kupffer cells after partial hepatectomy. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2005;289:G530-G538.
- 8. Reinehr R, Görg B, Becker S, Qvartskhava N, Bidmon HJ, Selbach O, Haas HL, Schliess F, Häussinger D. Hypoosmotic swelling and ammonia increase oxidative stress by NADPH oxidase in cultured astrocytes and vital brain slices. Glia 2007;55:758-771.
- 9. Albrecht J, Norenberg MD. Glutamine: a Trojan horse in ammonia neurotoxicity. Hepatology 2006;44:788-794.
- 10. García-Ayllón MS, Cauli O, Silveyra MX, Rodrigo R, Candela A, Compañ A, Jover R, Pérez-Mateo M, Martínez S, Felipo V, Sáez-Valero J. Brain cholinergic impairment in liver failure. Brain 2008;131:2946-2956.
- 11. Xie G, Wang X, Jiang R, Zhao A, Yan J, Zheng X, Huang F, Liu X, Panee J, Rajani C, Yao C, Yu H, Jia W, Sun B, Liu P, Jia W. Dysregulated bile acid signaling contributes to the neurological impairment in murine models of acute and chronic liver failure. EBioMedicine 2018;37:294-306.
- 12. Raevens S, Geerts A, Paridaens A, Lefere S, Verhelst X, Hoorens A, Van Dorpe J, Maes T, Bracke KR, Casteleyn C, Jonckx B, Horvatits T, Fuhrmann V, Van Vlierberghe H, Van Steenkiste C, Devisscher L, Colle I. Placental growth factor inhibition targets pulmonary angiogenesis and represents a therapy for hepatopulmonary syndrome in mice. Hepatology 2018;68:634-651.
- 13. O’Brien A, China L, Massey KA, Nicolaou A, Winstanley A, Newson J, Hobbs A, Audzevich T, Gilroy DW. Bile duct-ligated mice exhibit multiple phenotypic similarities to acute decompensation patients despite histological differences. Liver Int 2016;36:837-846.
- 14. Cho I, Koo BN, Kam EH, Lee SK, Oh H, Kim SY. Bile duct ligation of C57BL/6 mice as a model of hepatic encephalopathy. Anesth Pain Med 2020;15:19-27.
- 15. Matsubara Y, Kiyohara H, Teratani T, Mikami Y, Kanai T. Organ and brain crosstalk: the liver-brain axis in gastrointestinal, liver, and pancreatic diseases. Neuropharmacology 2022;205:108915.
- 16. Prida E, Álvarez-Delgado S, Pérez-Lois R, Soto-Tielas M, Estany-Gestal A, Fernø J, Seoane LM, Quiñones M, Al-Massadi O. Liver brain interactions: focus on FGF21 a systematic review. Int J Mol Sci 2022;23:13318.
- 17. Swain MG. Fatigue in liver disease: pathophysiology and clinical management. Can J Gastroenterol 2006;20:181-188.
- 18. Bluthé RM, Michaud B, Poli V, Dantzer R. Role of IL-6 in cytokine-induced sickness behavior: a study with IL-6 deficient mice. Physiol Behav 2000;70:367-373.
- 19. Eisenberger NI, Inagaki TK, Mashal NM, Irwin MR. Inflammation and social experience: an inflammatory challenge induces feelings of social disconnection in addition to depressed mood. Brain Behav Immun 2010;24:558-563.
- 20. Henry CJ, Huang Y, Wynne A, Hanke M, Himler J, Bailey MT, Sheridan JF, Godbout JP. Minocycline attenuates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced neuroinflammation, sickness behavior, and anhedonia. J Neuroinflammation 2008;5:15.
- 21. Bilzer M, Roggel F, Gerbes AL. Role of Kupffer cells in host defense and liver disease. Liver Int 2006;26:1175-1186.
- 22. Barak V, Selmi C, Schlesinger M, Blank M, Agmon-Levin N, Kalickman I, Gershwin ME, Shoenfeld Y. Serum inflammatory cytokines, complement components, and soluble interleukin 2 receptor in primary biliary cirrhosis. J Autoimmun 2009;33:178-182.
- 23. Loftis JM, Huckans M, Ruimy S, Hinrichs DJ, Hauser P. Depressive symptoms in patients with chronic hepatitis C are correlated with elevated plasma levels of interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α. Neurosci Lett 2008;430:264-268.
- 24. Aouizerat BE, Dodd M, Lee K, West C, Paul SM, Cooper BA, Wara W, Swift P, Dunn LB, Miaskowski C. Preliminary evidence of a genetic association between tumor necrosis factor alpha and the severity of sleep disturbance and morning fatigue. Biol Res Nurs 2009;11:27-41.
- 25. Clerici M, Arosio B, Mundo E, Cattaneo E, Pozzoli S, Dell’osso B, Vergani C, Trabattoni D, Altamura AC. Cytokine polymorphisms in the pathophysiology of mood disorders. CNS Spectr 2009;14:419-425.
- 26. Ek M, Kurosawa M, Lundeberg T, Ericsson A. Activation of vagal afferents after intravenous injection of interleukin-1β: role of endogenous prostaglandins. J Neurosci 1998;18:9471-9479.
- 27. Goehler LE, Gaykema RP, Hansen MK, Anderson K, Maier SF, Watkins LR. Vagal immune-to-brain communication: a visceral chemosensory pathway. Auton Neurosci 2000;85:49-59.
- 28. Gras G, Kaul M. Molecular mechanisms of neuroinvasion by monocytes-macrophages in HIV-1 infection. Retrovirology 2010;7:30.
- 29. D’Mello C, Le T, Swain MG. Cerebral microglia recruit monocytes into the brain in response to tumor necrosis factorα signaling during peripheral organ inflammation. J Neurosci 2009;29:2089-2102.
- 30. Kjeldsen L, Johnsen AH, Sengeløv H, Borregaard N. Isolation and primary structure of NGAL, a novel protein associated with human neutrophil gelatinase. J Biol Chem 1993;268:10425-10432.
- 31. Kjeldsen L, Bainton DF, Sengeløv H, Borregaard N. Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel matrix protein of specific granules in human neutrophils. Blood 1994;83:799-807.
- 32. Flo TH, Smith KD, Sato S, Rodriguez DJ, Holmes MA, Strong RK, Akira S, Aderem A. Lipocalin 2 mediates an innate immune response to bacterial infection by sequestrating iron. Nature 2004;432:917-921.
- 33. Viau A, El Karoui K, Laouari D, Burtin M, Nguyen C, Mori K, Pillebout E, Berger T, Mak TW, Knebelmann B, Friedlander G, Barasch J, Terzi F. Lipocalin 2 is essential for chronic kidney disease progression in mice and humans. J Clin Invest 2010;120:4065-4076.
- 34. Devireddy LR, Gazin C, Zhu X, Green MR. A cell-surface receptor for lipocalin 24p3 selectively mediates apoptosis and iron uptake. Cell 2005;123:1293-1305.
- 35. Garay-Rojas E, Harper M, Hraba-Renevey S, Kress M. An apparent autocrine mechanism amplifies the dexamethasone- and retinoic acid-induced expression of mouse lipocalin-encoding gene 24p3. Gene 1996;170:173-180.
- 36. Guo H, Jin D, Zhang Y, Wright W, Bazuine M, Brockman DA, Bernlohr DA, Chen X. Lipocalin-2 deficiency impairs thermogenesis and potentiates diet-induced insulin resistance in mice. Diabetes 2010;59:1376-1385.
- 37. Yang J, Bielenberg DR, Rodig SJ, Doiron R, Clifton MC, Kung AL, Strong RK, Zurakowski D, Moses MA. Lipocalin 2 promotes breast cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009;106:3913-3918.
- 38. Lim D, Jeong JH, Song J. Lipocalin 2 regulates iron homeostasis, neuroinflammation, and insulin resistance in the brains of patients with dementia: evidence from the current literature. CNS Neurosci Ther 2021;27:883-894.
- 39. Kling MA, Trojanowski JQ, Wolk DA, Lee VM, Arnold SE. Vascular disease and dementias: paradigm shifts to drive research in new directions. Alzheimers Dement 2013;9:76-92.
- 40. Mesquita SD, Ferreira AC, Falcao AM, Sousa JC, Oliveira TG, Correia-Neves M, Sousa N, Marques F, Palha JA. Lipocalin 2 modulates the cellular response to amyloid beta. Cell Death Differ 2014;21:1588-1599.
- 41. Chia WJ, Dawe GS, Ong WY. Expression and localization of the iron-siderophore binding protein lipocalin 2 in the normal rat brain and after kainate-induced excitotoxicity. Neurochem Int 2011;59:591-599.
- 42. Xiang X, Tang X, Yu Y, Xie S, Liu L, Chen M, Zhang R, Kang X, Zheng Y, Yang G, Gan S, Zhu S. Role of lipocalin-2 in surgery-induced cognitive decline in mice: a signal from neuron to microglia. J Neuroinflammation 2022;19:92.
- 43. Naudé PJ, Nyakas C, Eiden LE, Ait-Ali D, van der Heide R, Engelborghs S, Luiten PG, De Deyn PP, den Boer JA, Eisel UL. Lipocalin 2: novel component of proinflammatory signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J 2012;26:2811-2823.
- 44. Selkoe DJ. American College of Physicians. American Physiological Society. Alzheimer disease: mechanistic understanding predicts novel therapies. Ann Intern Med 2004;140:627-638.
- 45. Asimakopoulou A, Weiskirchen S, Weiskirchen R. Lipocalin 2 (LCN2) expression in hepatic malfunction and therapy. Front Physiol 2016;7:430.
- 46. Chen J, Argemi J, Odena G, Xu MJ, Cai Y, Massey V, Parrish A, Vadigepalli R, Altamirano J, Cabezas J, Gines P, Caballeria J, Snider N, Sancho-Bru P, Akira S, Rusyn I, Gao B, Bataller R. Hepatic lipocalin 2 promotes liver fibrosis and portal hypertension. Sci Rep 2020;10:15558.
- 47. Ariza X, Graupera I, Coll M, Solà E, Barreto R, García E, Moreira R, Elia C, Morales-Ruiz M, Llopis M, Huelin P, Solé C, Fabrellas N, Weiss E, Nevens F, Gerbes A, Trebicka J, Saliba F, Fondevila C, Hernández-Gea V, Fernández J, Bernardi M, Arroyo V, Jiménez W, Deulofeu C, Pavesi M, Angeli P, Jalan R, Moreau R, Sancho-Bru P, Ginès P. CANONIC Investigators, EASL CLIF Consortium. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is a biomarker of acute-on-chronic liver failure and prognosis in cirrhosis. J Hepatol 2016;65:57-65.
- 48. Mohammed RA, Shawky HM, Rashed LA, Elhanbuli HM, Abdelhafez DN, Said ES, Shamardan RM, Mahmoud RH. Combined effect of hydrogen sulfide and mesenchymal stem cells on mitigating liver fibrosis induced by bile duct ligation: Role of anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-apoptotic, and anti-fibrotic biomarkers. Iran J Basic Med Sci 2021;24:1753-1762.
- 49. Borkham-Kamphorst E, Drews F, Weiskirchen R. Induction of lipocalin-2 expression in acute and chronic experimental liver injury moderated by pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin-1β through nuclear factor-κB activation. Liver Int 2011;31:656-665.
- 50. Xu MJ, Feng D, Wu H, Wang H, Chan Y, Kolls J, Borregaard N, Porse B, Berger T, Mak TW, Cowland JB, Kong X, Gao B. Liver is the major source of elevated serum lipocalin-2 levels after bacterial infection or partial hepatectomy: a critical role for IL-6/STAT3. Hepatology 2015;61:692-702.
- 51. Yoshikawa K, Iwasa M, Eguchi A, Kojima S, Yoshizawa N, Tempaku M, Sugimoto R, Yamamoto N, Sugimoto K, Kobayashi Y, Hasegawa H, Takei Y. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin level is a prognostic factor for survival in rat and human chronic liver diseases. Hepatol Commun 2017;1:946-956.
- 52. Xu G, Wang YM, Ying MM, Chen SD, Li ZR, Ma HL, Zheng MH, Wu J, Ding C. Serum lipocalin-2 is a potential biomarker for the clinical diagnosis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin Mol Hepatol 2021;27:329-345.
- 53. Xiong M, Qian Q, Liang X, Wei YD. Serum levels of lipocalin-2 in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurol Sci 2022;43:1755-1759.
- 54. Schrimpf A, Knappe O, Qvartskhava N, Poschmann G, Stühler K, Bidmon HJ, Luedde T, Häussinger D, Görg B. Hyperammonemia-induced changes in the cerebral transcriptome and proteome. Anal Biochem 2022;641:114548.
- 55. Boato F, Hechler D, Rosenberger K, Lüdecke D, Peters EM, Nitsch R, Hendrix S. Interleukin-1 beta and neurotrophin-3 synergistically promote neurite growth in vitro. J Neuroinflammation 2011;8:183.
- 56. Park SY, Kang MJ, Han JS. Interleukin-1 beta promotes neuronal differentiation through the Wnt5a/RhoA/JNK pathway in cortical neural precursor cells. Mol Brain 2018;11:39.
- 57. O’Léime CS, Cryan JF, Nolan YM. Nuclear deterrents: Intrinsic regulators of IL-1β-induced effects on hippocampal neurogenesis. Brain Behav Immun 2017;66:394-412.
- 58. Ma L, Li XW, Zhang SJ, Yang F, Zhu GM, Yuan XB, Jiang W. Interleukin-1 beta guides the migration of cortical neurons. J Neuroinflammation 2014;11:114.
- 59. Lin Q, Shen F, Zhou Q, Huang P, Lin L, Chen M, Chen X, Jiang S, He S, Zeng H, Deng Y. Interleukin-1β disturbs the proliferation and differentiation of neural precursor cells in the hippocampus via activation of notch signaling in postnatal rats exposed to lipopolysaccharide. ACS Chem Neurosci 2019;10:2560-2575.
- 60. Samad TA, Moore KA, Sapirstein A, Billet S, Allchorne A, Poole S, Bonventre JV, Woolf CJ. Interleukin-1β-mediated induction of Cox-2 in the CNS contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. Nature 2001;410:471-475.
- 61. Sommer C, Kress M. Recent findings on how proinflammatory cytokines cause pain: peripheral mechanisms in inflammatory and neuropathic hyperalgesia. Neurosci Lett 2004;361:184-187.
- 62. Neeb L, Hellen P, Boehnke C, Hoffmann J, Schuh-Hofer S, Dirnagl U, Reuter U. IL-1β stimulates COX-2 dependent PGE2 synthesis and CGRP release in rat trigeminal ganglia cells. PLoS One 2011;6:e17360.
- 63. Vardeh D, Wang D, Costigan M, Lazarus M, Saper CB, Woolf CJ, Fitzgerald GA, Samad TA. COX2 in CNS neural cells mediates mechanical inflammatory pain hypersensitivity in mice. J Clin Invest 2009;119:287-294.
- 64. Sugimoto Y, Narumiya S, Ichikawa A. Distribution and function of prostanoid receptors: studies from knockout mice. Prog Lipid Res 2000;39:289-314.
- 65. Breyer RM, Bagdassarian CK, Myers SA, Breyer MD. Prostanoid receptors: subtypes and signaling. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2001;41:661-690.
- 66. Kaltschmidt B, Linker RA, Deng J, Kaltschmidt C. Cyclooxygenase-2 is a neuronal target gene of NF-κB. BMC Mol Biol 2002;3:16.
- 67. Lukiw WJ, Bazan NG. Strong nuclear factor-κB-DNA binding parallels cyclooxygenase-2 gene transcription in aging and in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease superior temporal lobe neocortex. J Neurosci Res 1998;53:583-592.
- 68. Cianciulli A, Calvello R, Porro C, Trotta T, Salvatore R, Panaro MA. PI3k/Akt signalling pathway plays a crucial role in the anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin in LPS-activated microglia. Int Immunopharmacol 2016;36:282-290.
- 69. López-Carballo G, Moreno L, Masiá S, Pérez P, Barettino D. Activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway by retinoic acid is required for neural differentiation of SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem 2002;277:25297-25304.
- 70. Bai D, Ueno L, Vogt PK. Akt-mediated regulation of NFκB and the essentialness of NFκB for the oncogenicity of PI3K and Akt. Int J Cancer 2009;125:2863-2870.
- 71. Sizemore N, Leung S, Stark GR. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in response to interleukin-1 leads to phosphorylation and activation of the NF-κB p65/RelA subunit. Mol Cell Biol 1999;19:4798-4805.
- 72. Aksoy E, Taboubi S, Torres D, Delbauve S, Hachani A, Whitehead MA, Pearce WP, Berenjeno IM, Nock G, Filloux A, Beyaert R, Flamand V, Vanhaesebroeck B. The p110δ isoform of the kinase PI(3)K controls the subcellular compartmentalization of TLR4 signaling and protects from endotoxic shock. Nat Immunol 2012;13:1045-1054.
- 73. Chen G, Liu S, Pan R, Li G, Tang H, Jiang M, Xing Y, Jin F, Lin L, Dong J. Curcumin attenuates gp120-induced microglial inflammation by inhibiting autophagy via the PI3K pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2018;38:1465-1477.
- 74. Ahn JY. Neuroprotection signaling of nuclear Akt in neuronal cells. Exp Neurobiol 2014;23:200-206.
- 75. Pi T, Zhou XW, Cai L, Zhang W, Su CF, Wu WT, Ren XM, Luo HM. PI3K/Akt signaling pathway is involved in the neurotrophic effect of senegenin. Mol Med Rep 2016;13:1257-1262.
- 76. Brunet A, Datta SR, Greenberg ME. Transcription-dependent and -independent control of neuronal survival by the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2001;11:297-305.
- 77. Wang G, Ma N, Meng L, Wei Y, Gui J. Activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway is involved in lipocalin-2-promoted human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation. Mol Cell Biochem 2015;410:207-213.
- 78. Shen F, Hu Z, Goswami J, Gaffen SL. Identification of common transcriptional regulatory elements in interleukin-17 target genes. J Biol Chem 2006;281:24138-24148.
- 79. Lee EK, Kim HJ, Lee KJ, Lee HJ, Lee JS, Kim DG, Hong SW, Yoon Y, Kim JS. Inhibition of the proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by lipocalin 2 through blockade of JNK and PI3K/Akt signaling. Int J Oncol 2011;38:325-333.
- 80. Liang T, Qian ZM, Mu MD, Yung WH, Ke Y. Brain hepcidin suppresses major pathologies in experimental parkinsonism. iScience 2020;23:101284.
- 81. Tsutsumi N, Nishimata S, Shimura M, Kashiwagi Y, Kawashima H. Hepcidin levels and pathological characteristics in children with fatty liver disease. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2021;24:295-305.
- 82. Murphy MP, LeVine H 3rd. Alzheimer’s disease and the amyloid-β peptide. J Alzheimers Dis 2010;19:311-323.
- 83. Meng X, Li T, Wang X, Lv X, Sun Z, Zhang J, Su F, Kang S, Kim S, An SS, Yu X, Zhang C, Wang H. Association between increased levels of amyloid-β oligomers in plasma and episodic memory loss in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 2019;11:89.
- 84. Chaudhary S, Ashok A, McDonald D, Wise AS, Kritikos AE, Rana NA, Harding CV, Singh N. Upregulation of local hepcidin contributes to iron accumulation in Alzheimer’s disease brains. J Alzheimers Dis 2021;82:1487-1497.
- 85. Gratacòs E, Gavaldà N, Alberch J. Bone morphogenetic protein-6 is a neurotrophic factor for calbindin-positive striatal neurons. J Neurosci Res 2002;70:638-644.
- 86. Choi SH, Li Y. Elevated levels of BMP6 impair neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 2011;31:371-372.
- 87. Crews L, Adame A, Patrick C, Delaney A, Pham E, Rockenstein E, Hansen L, Masliah E. Increased BMP6 levels in the brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients and APP transgenic mice are accompanied by impaired neurogenesis. J Neurosci 2010;30:12252-12262.
- 88. Zhao C, Deng W, Gage FH. Mechanisms and functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell 2008;132:645-660.
- 89. Basuli D, Tesfay L, Deng Z, Paul B, Yamamoto Y, Ning G, Xian W, McKeon F, Lynch M, Crum CP, Hegde P, Brewer M, Wang X, Miller LD, Dyment N, Torti FM, Torti SV. Iron addiction: a novel therapeutic target in ovarian cancer. Oncogene 2017;36:4089-4099.
- 90. Refaat B, Abdelghany AH, BaSalamah MA, El-Boshy M, Ahmad J, Idris S. Acute and chronic iron overloading differentially modulates the expression of cellular iron-homeostatic molecules in normal rat kidney. J Histochem Cytochem 2018;66:825-839.
- 91. Lu LN, Qian ZM, Wu KC, Yung WH, Ke Y. Expression of iron transporters and pathological hallmarks of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases in the brain of young, adult, and aged rats. Mol Neurobiol 2017;54:5213-5224.
- 92. Nakamura Y, Nakamichi N, Takarada T, Ogita K, Yoneda Y. Transferrin receptor-1 suppresses neurite outgrowth in neuroblastoma Neuro2A cells. Neurochem Int 2012;60:448-457.
- 93. Matak P, Matak A, Moustafa S, Aryal DK, Benner EJ, Wetsel W, Andrews NC. Disrupted iron homeostasis causes dopaminergic neurodegeneration in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016;113:3428-3435.
- 94. Schneider SA, Hardy J, Bhatia KP. Syndromes of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (NBIA): an update on clinical presentations, histological and genetic underpinnings, and treatment considerations. Mov Disord 2012;27:42-53.
- 95. Zhou JH, Wang XT, Zhou L, Zhou L, Xu FX, Su LD, Wang H, Jia F, Xu FQ, Chen GQ, De Zeeuw CI, Shen Y. Ablation of TFR1 in Purkinje Cells Inhibits mGlu1 Trafficking and Impairs Motor Coordination, But Not Autistic-Like Behaviors. J Neurosci 2017;37:11335-11352.
- 96. Samavati L, Lee I, Mathes I, Lottspeich F, Hüttemann M. Tumor necrosis factor α inhibits oxidative phosphorylation through tyrosine phosphorylation at subunit I of cytochrome c oxidase. J Biol Chem 2008;283:21134-21144.